Solved 2023 Question Paper CBSE Class 10 Science
Section A (Objective Type Questions 1 Mark Each)
Question 1
In the experimental setup given below, it is observed that on passing the gas produced in the reaction in the solution 'X' the solution 'X' first turn milky and then colourless.

The option that justifies the above stated observation is that 'X' is aqueous calcium hydroxide and
it turns milky due to carbon dioxide gas liberated in the reaction and after sometime it becomes colourless due to formation of calcium carbonate.
it turns milky due to formation of calcium carbonate and on passing excess of carbon dioxide it becomes colourless due to formation of calcium hydrogen carbonate which is soluble in water.
it turns milky due to passing of carbon dioxide through it. It turns colourless as on further passing carbon dioxide, sodium hydrogen carbonate is formed which is soluble in water.
the carbon dioxide liberated during the reaction turns lime water milky due to formation of calcium hydrogen carbonate and after some time it turns colourless due to formation of calcium carbonate which is soluble in water.
Answer
it turns milky due to formation of calcium carbonate and on passing excess of carbon dioxide it becomes colourless due to formation of calcium hydrogen carbonate which is soluble in water.
Reason — The reaction between sodium carbonate and HCl gas produces carbon dioxide gas.
Na2CO3 + 2HCl (dil.) ⟶ 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
Solution X is aq. calcium hydroxide which reacts with carbon dioxide gas and forms calcium carbonate, which turns the solution milky.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 ⟶ CaCO3 + H2O
However, on passing excess carbon dioxide, the calcium hydrogen carbonate is formed, which is soluble in water and hence, the solution X becomes colourless.
CaCO3 + H2O + CO2 ⟶ Ca(HCO3)2
Question 2
The emission of brown fumes in the given experimental set-up is due to

- thermal decomposition of lead nitrate which produces brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide.
- thermal decomposition of lead nitrate which produces brown fumes of lead oxide.
- oxidation of lead nitrate forming lead oxide and nitrogen dioxide.
- oxidation of lead nitrate forming lead oxide and oxygen.
Answer
thermal decomposition of lead nitrate which produces brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide.
Reason — Thermal decomposition of lead nitrate takes place which produces brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide.
2Pb(NO3)2 ⟶ 2PbO + 4NO2 + O2
Question 3
MnO2 + xHCl ⟶ MnCl2 + yH2O + zCl2
In order to balance the above chemical equation, the values of x, y and z respectively are
- 6, 2, 2
- 4, 1, 2
- 4, 2, 1
- 2, 2, 1
Answer
4, 2, 1
Reason — The balanced equation is as follows:
MnO2 + 4HCl ⟶ MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
Question 4
The table below has information regarding pH and the nature (acidic/basic) of four different solutions. Which one of the options in the table is correct ?
| Option | Solution | Colour of pH paper | Approximate pH value | Nature of solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Lemon juice | Orange | 3 | Basic |
| (b) | Milk of magnesia | Blue | 10 | Basic |
| (c) | Gastric juice | Red | 6 | Acidic |
| (d) | Pure water | Yellow | 7 | Neutral |
Answer
| Milk of magnesia | Blue | 10 | Basic |
Reason — For lemon juice pH is 3 but colour of pH paper is orange and nature is given as basic which is incorrect. For Gastric juice, pH value of 6 is incorrect. For pure water, colour of pH paper is incorrect. It should be green not yellow.
Question 5
A metal 'X' is used in thermite process. When X is burnt in air it gives an amphoteric oxide 'Y'. 'X' and 'Y' are respectively :
- Fe and Fe2O3
- Al and Al2O3
- Fe and Fe3O4
- Al and Al3O4
Answer
Al and Al2O3
Reason — Aluminium is used in thermite process. When aluminium is heated in oxygen it forms aluminium oxide which is amphoteric in nature .
4Al + 3O2 ⟶ 2Al2O3
Question 6
Select washing soda from the following :
- NaHCO3
- Na2CO3.5H2O
- Na2CO3.10H2O
- NaOH
Answer
Na2CO3.10H2O
Reason — The formula of washing soda is : Na2CO3.10H2O
Question 7
Consider the structures of the three cyclic carbon compounds A, B and C given below and select the correct option from the following:

- A and C are isomers of hexane and B is benzene.
- A is an isomer of hexane, B is benzene and C is an isomer of hexene.
- A is a saturated cyclic hydrocarbon and B and C are unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons.
- A is cyclohexane and B and C are the isomers of benzene.
Answer
A is a saturated cyclic hydrocarbon and B and C are unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons.
Reason — A is having all the single bonds hence it is a saturated hydrocarbon whereas B and C have double bonds so they are unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons.
Question 8
An organism which breaks down the food material outside the body and then absorbs it is
- a plant parasite, Cascuta
- an animal parasite, Tapeworm
- a bacteria, Rhizobium
- a fungi, Rhizopus
Answer
a fungi, Rhizopus
Reason — Fungi show extra-cellular digestion. The cell wall of fungi secretes enzymes that digest the food outside the body of fungi. The digested food is then absorbed by the fungi.
Question 9
Consider the following statements about small intestine and select the one which is NOT correct :
- The length of the small intestine in animals differs as it depends on the type of food they eat.
- The small intestine is the site of complete digestion of food.
- The small intestine receives secretions from liver and pancreas.
- The villi of the small intestine absorbs water from the unabsorbed food before it gets removed from the body via the anus.
Answer
The villi of the small intestine absorb water from the unabsorbed food before it gets removed from the body via the anus.
Reason — The villi of the small intestine absorbs digested food. Excess water is absorbed in large intestine.
Question 10
The statement that correctly describes the characteristic(s) of a gene is :
- In individuals of a given species, a specific gene is located on a particular chromosome.
- A gene is not the information source for making proteins in the cell.
- Each chromosome has only one gene located all along its length.
- All the inherited traits in human beings are not controlled by genes.
Answer
In individuals of a given species, a specific gene is located on a particular chromosome.
Reason— In individuals of a given species, each gene has a fixed locus on a specific chromosome.
Question 11
Select from the following the correct statement about tropic movement in plants:
- It is due to stimulus of touch and temperature.
- It does not depend upon the direction of stimulus received.
- It is observed only in roots and not in stems.
- It is a growth related movement.
Answer
It is a growth related movement.
Reason — Tropic movement in plants is related to growth. It occurs in stem as well as roots. It is affected by touch, gravitation and light.
Question 12
Select the INCORRECT match (between the plant and its vegetative part) from the following :
- Bryophyllum, leaf
- Potato, stem
- Money-plant, stem
- Rose, root
Answer
Rose, root
Reason— Rose is propagated by stem.
Question 13
If four identical resistors, of resistance 8 ohm, are first connected in series so as to give an effective resistance Rs, and then connected in parallel so as to give an effective resistance Rp then the ratio is
- 32
- 2
- 0.5
- 16
Answer
16
Reason — Four identical resistors of resistance 8 Ω are connected in series :
So, Rs = 8+8+8+8 = 32 Ω
When connected in parallel:
= + + +
= = =
So, Rp = 2 Ω
= = 16
Question 14
In domestic electric circuits the wiring with 15 A current rating is for the electric devices which have
- higher power ratings such as geyser.
- lower power ratings such as fan.
- metallic bodies and low power ratings.
- non-metallic bodies and low power ratings.
Answer
higher power ratings such as geyser.
Reason — As P = i2R
Hence, in domestic electric circuits the wiring with 15 A current rating is for the electric devices which have higher power ratings such as geyser.
Question 15
In the following diagram, the position of the needle is shown on the scale of a voltmeter. The least count of the voltmeter and the reading shown by it respectively are :

- 0.15 V and 1.6 V
- 0.05 V and 1.6 V
- 0.15 V and 1.8 V
- 0.05 V and 1.8 V
Answer
0.15 V and 1.8 V
Reason — Least count of any scale is the value measured by a single division on it.
10 div = 1.5 V
So, 1 div = = 0.15 V
Hence, least count = 0.15 V
Reading shown = least count x no. of div. = 0.15 x 12 = 1.8 V
Hence, Reading shown = 1.8 V
Question 16
The resultant magnetic field at point 'P' situated midway between two parallel wires (placed horizontally) each carrying a steady current I is

- in the same direction as the current in the wires.
- in the vertically upward direction.
- zero
- in the vertically downward direction.
Answer
zero
Reason — The magnetic fields produced at the midpoint P, by the currents flowing in the same direction in the two parallel wires will be equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
Hence, the resultant magnetic field at P will be zero.
Question 17
Assertion (A) : The colour of aqueous solution of copper sulphate turns colourless when a piece of lead is added to it.
Reason (R) : Lead is more reactive than copper, and hence displaces copper from its salt solution.
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- (A) is true, but (R) is false.
- (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Reason — When a piece of lead is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate, a displacement reaction takes place as lead is more reactive than copper hence lead displaces copper from the copper sulphate solution. The chemical equation for the reaction is:
Pb + CuSO4 ⟶ PbSO4 + Cu
This results in a colorless solution [PbSO4].
Question 18
Assertion (A) : Genes inherited from the parents decide the sex of a child.
Reason (R) : X chromosome in a male child is inherited from his father.
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- (A) is true, but (R) is false.
- (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer
(A) is true, but (R) 1s false.
Reason — Sex of a child is decided by the chromosome (X or Y) of father that is inherited by the embryo. Genes on chromosome Y are responsible for male child.
Question 19
Assertion (A) : Blood clotting prevents excessive loss of blood.
Reason (R) : Blood clotting is due to blood plasma and white blood cells present in the blood.
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- (A) is true, but (R) is false.
- (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
Reason — Blood clotting is due to blood platelets, fibrinogen and Prothrombin.
Question 20
Assertion (A) : The strength of the magnetic field produced at the centre of a current carrying circular coil increases on increasing the number of turns in it.
Reason (R) : The current in each circular turn has the same direction and the magnetic field due to each turn then just adds up.
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- (A) is true, but (R) is false.
- (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Reason — Magnetic field strength is directly proportional to the number of turns of the circular coil. Hence, strength of the magnetic field increases on increasing the number of turns in it because current in each circular turn has the same direction and the magnetic field due to each turn then just adds up.
Section B (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Marks Each)
Question 21(a)
(i) A compound 'X' which is prepared from gypsum has the property of hardening when mixed with proper quantity of water.
Identify 'X' and write its chemical formula.
(ii) State the difference in chemical composition between baking soda and baking powder.
Answer
(i) Plaster of paris — CaSO4.H2O
(ii) Difference in chemical composition between baking soda and baking powder:
| Baking soda | Baking powder |
|---|---|
| It has only one ingredient – sodium hydrogen carbonate [NaHCO3]. | For making baking powder, baking soda is mixed with mild edible acids such as (tartaric acid). |
Question 21(b)
Write balanced chemical equation for the reaction that occurs when :
(i) blue coloured copper sulphate crystals are heated and
(ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated during cooking.
Answer
(i) When blue coloured copper sulphate crystals are heated :
CuSO4.5H2O CuSO4 + 5H2O
(ii) When sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated during cooking
2NaHCO3 Na2CO3 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (↑)
Question 22
(a) Write the role of insulin in regulating blood sugar levels in human body. Mention the disease caused due to it.
(b) How is the timing and the amount of release of insulin in the blood regulated ?
Answer
(a) The role of insulin in regulating blood sugar levels in human body are:
- It promotes glucose utilisation by the body cells, thereby reducing the blood sugar level.
- It stimulates deposition of extra glucose of the blood as glycogen in liver and muscles.
(b) The timing and amount of release of insulin is regulated by the feedback mechanism. Insulin is released by beta-cells of pancreas when there is increase of sugar level in blood. The amount of insulin is also decided by the amount of sugar in the blood. When the level of sugar in the blood decreases the negative feedback will allow the pancreas to stop the secretion of insulin.
Question 23(a)
Name the type of blood (oxygenated / deoxygenated) transported by each of the following mentioning the path (i.e. from one organ (which place) to another (which place)).
(i) Vena cava
(ii) Pulmonary artery
Answer
(i) Vena cava: It transports deoxygenated blood from whole body to the heart.
(ii) Pulmonary artery: It transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to lungs.
Question 23(b)
With the help of a schematic flow chart, show the breakdown of glucose in a cell to provide energy —
(i) in the presence of oxygen
(ii) in lack of oxygen
Answer
Below schematic flow chart shows the breakdown of glucose in a cell in the presence and absence of oxygen:

Question 24
Name the part of the human excretory system where nephrons are found. Write the structure and function of nephrons.
Answer
The part of the human excretory system where nephrons are found are Kidneys.
Structure of Nephron — Nephron is the basic filtration unit in the kidney. It consists of a tubule which is connected with a collecting duct at one end and a cup shaped structure at the other end, called Bowman's capsule. Every Bowman's capsule contains a cluster of capillaries called glomerulus within the cup-shaped structure.
Function of Nephron — The blood enters into glomerulus through afferent arteriole of renal artery and leaves it through efferent arteriole. This causes filtration of the blood. Then the filtrate passes into the tubular part of the nephron. Here, useful substances such as glucose, amino acids, salts and some water are re-absorbed into the blood by the capillaries surrounding the nephron tubule. The filtrate which remains after the re-absorption is called the urine, which is collected from nephron by the collecting duct to carry it to the urinary bladder and then to the urethra.
Question 25(a)
A narrow beam XY of white light is passing through a glass prism ABC as shown in the diagram :

Trace it on your answer sheet and show the path of the emergent beam as observed on the screen PQ.
Name the phenomenon observed and state its cause.
Answer
The path of the emergent beam is shown in the diagram below:

The phenomenon of the splitting up of the white light into its constituent colours is called dispersion of light.
The cause of dispersion of white light is the change in speed of light with wavelength.
When white light enters the first surface of a prism, light of different colours due to their different speeds in glass, get deviated through different angles towards the base of the prism. On the second surface of prism, only refraction takes place (from glass to air) and different colours are deviated through different angles. As a result, colours get further separated on refraction at the second surface.
Question 25(b)
It is observed that the power of an eye to see nearby objects as well as far off objects diminishes with age.
(i) Give reason for the above statement.
(ii) Name the defect that is likely to arise in the eyes in such a condition.
(iii) Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the type of corrective lens used for restoring the vision of such an eye.
Answer
(i) The power of an eye to see nearby objects as well as far off objects diminishes with age because the power of accommodation of the eye usually decreases with ageing due to weakening of ciliary muscles and decrease in flexibility of eye lens.
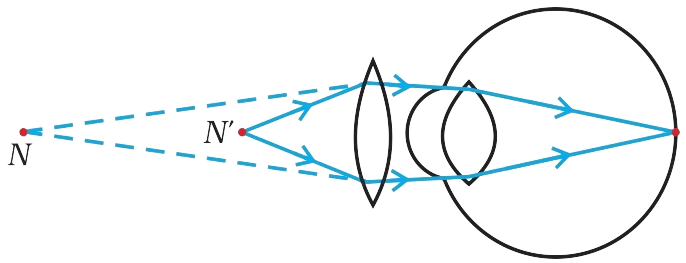
(ii) The defect that is likely to arise in the eyes in such a condition is Presbyopia. For most people, the near point gradually recedes away. They find it difficult to see nearby objects comfortably and distinctly without corrective eye-glasses.
(iii) Presbyopia can be corrected by using a convex lens as shown in the diagram below:
Question 26
How do harmful chemicals get accumulated progressively at each trophic level in a food chain ?
Answer
Several pesticides and other chemicals are used to protect our crops from diseases and pests. These chemicals are either washed down into the soil or into the water bodies. From the soil, these are absorbed by the plants along with water and minerals, and from the water bodies these are taken up by aquatic plants and animals. This is one of the ways in which they enter the food chain. As these chemicals are not degradable, these get accumulated progressively at each trophic level.
Section C (Short Answer Questions 3 Marks Each)
Question 27
(a) Identify the reducing agent in the following reactions :
(i) 4NH3 + 5O2 ⟶ 4NO + 6H2O
(ii) H2O + F2 ⟶ HF + HOF
(iii) Fe2O3 + 3CO ⟶ 2Fe + 3CO2
(iv) 2H2 + O2 ⟶ 2H2O
(b) Define a redox reaction in terms of gain or loss of oxygen.
Answer
(a) The reducing agents are:
(i) Ammonia (NH3)
(ii) Water (H2O)
(iii) Carbon monoxide (CO)
(iv) Hydrogen (H2)
(b) A redox reaction is one in which one reactant gains oxygen and becomes oxidized while the other reactant loses oxygen and is reduced.
For example :
CuO + H2 ⟶ Cu + H2O
Hydrogen is oxidized to water and CuO is reduced to Cu
Question 28
(a) Suggest one remedial measure each to counteract the change in pH in human beings in following cases :
(i) Production of too much acid in stomach during indigestion
(ii) Stung by a honey bee / nettle leaves
(b) Fresh milk has a pH of 6. When it changes into curd will its pH increase or decrease ? Why ?
Answer
(a) (i) Production of too much acid in stomach during indigestion leads to pain and irritation. Antacid is given in such case to neutralize the acid of the stomach. The antacids neutralise the excess acid. Magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia) is a mild base, often used for this purpose.
(ii) In case of a honeybee sting formic acid is released into the skin which causes pain and irritation. To reduce the pain caused due to the sting, bases like baking soda are used which neutralize acid and relieve the pain. Stinging hair of nettle leaves inject methanoic acid causing burning pain. It is also treated with rubbing mild base.
(b) When the milk is turned into curd then its pH value decreases. This is due to the production of lactic acid in curd which is acidic in nature.
Question 29(a)
(i) State the role of ATP in cellular respiration.
(ii) What ensures sufficient exchange of gases in plants?
(iii) State the conditions on which the direction of diffusion of gases in plant depend upon.
Answer
(i) ATP is consumed in glycolysis to convert glucose to pyruvate. It is also produced in electron transport chain.
(ii) Maximum amount of gaseous exchange occur in plants through stomata and lenticels present on leaf and stem surface respectively and the large inter-cellular spaces ensure that all cells are in contact with air.
(iii) The direction of diffusion depends upon the environmental conditions and the requirements of the plant. At night, when there is no photosynthesis occurring, CO2 elimination is the major exchange activity going on. During the day, CO2 generated during respiration is used up for photosynthesis, hence there is no CO2 release. Instead, oxygen release is the major event at this time.
Question 29(b)
(i) What is the internal energy reserve in plants and animals ?
(ii) How desert plants perform photosynthesis if their stomata remain closed during the day ?
Answer
(i) Internal Energy reserve in plants is starch and in animals it is glycogen.
(ii) Desert plants take up carbon dioxide at night and prepare an intermediate which is acted upon by the energy absorbed by the chlorophyll during the day.
Question 30
(a) Complete the following ray diagram to show the formation of image :

(b) Mention the nature, position and size of the image formed in this case.
(c) State the sign of the image distance in this case using the Cartesian sign convention.
Answer
(a) The completed ray diagram showing the formation of image is given below:

(b) The image formed is virtual, erect, diminished and located behind the mirror between P and F.
(c) positive
Question 31
Give reasons for the following :
(a) Danger signals installed at airports and at the top of tall buildings are of red colour.
(b) The sky appears dark to the passengers flying at very high altitudes.
(c) The path of a beam of light passing through a colloidal solution is visible.
Answer
(a) Red colour has the longest wavelength and it deviates the least, hence, danger signals installed at airports and at the top of tall buildings are of red colour so that they can be easily seen from a distance.
(b) Scattering of light takes place because of the particles present in the atmosphere. At high altitude, the atmospheric medium is rarer so the scattering of light taking place is very low. Hence, the sky appears dark to passengers flying at high altitudes.
(c) The path of a beam of light passing through a colloidal solution is visible due to scattering of light by colloidal particles and this is known as Tyndall effect.
Question 32(a)
(i) State the rule used to find the force acting on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field.
(ii) Given below are three diagrams showing entry of an electron in a magnetic field. Identify the case in which the force will be
(1) maximum
(2) minimum respectively.
Give reason for your answer.

Answer
(i) Fleming's left hand rule is used to find the direction of force acting on a current carrying conductor, placed in a magnetic field.
According to this rule : Stretch the thumb, fore finger and middle finger of your left hand such that they are mutually perpendicular. If the forefinger points in the direction of magnetic field and the middle finger in the direction of current, then the thumb will point in the direction of motion or force acting on conductor.
(ii) (1) Force on electron is maximum in case (i) because here direction of motion of electron is at right angles to the magnetic field.
(2) Force on electron is minimum in case (iii) because here direction of motion of electron is along the direction of the magnetic field.
Question 32(b)
(i) Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines of
(1) a current carrying solenoid
(2) a bar magnet
(ii) List two distinguishing features between the two fields.
Answer
(i)
(1) The pattern of magnetic field lines of a current carrying solenoid is shown below:

(2) The pattern of magnetic field lines of a bar magnet is shown below:

(ii) Distinguishing features between :
| Magnetic field lines of a current carrying solenoid | Magnetic field lines of a bar magnet |
|---|---|
| If we cut a solenoid into two halves, the magnetic field strength of the halves gets decreased. | When we cut a bar magnet into two halves, the magnetic properties do not change and both act as a magnet. |
| The poles of a solenoid can be altered and hence the direction of magnetic field lines. | In case of a bar magnet, it is fixed. |
Question 33(a)
(i) Why does a kitchen garden called an artificial ecosystem while a forest is considered to be a natural ecosystem ?
(ii) While designing an artificial ecosystem at home, write any two things to be kept in mind to convert it into a self-sustaining system. Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer
(i) Kitchen garden is known as artificial ecosystem because the biotic and abiotic factors are modified by humans and not decided by the nature as in natural ecosystems like forest. In forests, humans do not modify biotic or abiotic factors.
(ii) Two things to be kept in mind to convert an artificial ecosystem into a self-sustaining system are:
- Balance between producers and consumers — We should select inter-dependable producers and consumer to make the ecosystem self sustainable. They should form food web so that their population is controlled.
- Waste management — The involvement of decomposers is very important for sustainable ecosystem.
Natural ecosystems are self sustaining due to a perfect relation of interdependence. For converting an artificial ecosystem into a self-sustaining system we should try to minimize human interference and include organisms that make it sustainable.
Question 33(b)
(i) Construct a food chain of four trophic levels comprising the following :
Hawk, snake, plants, rat.
(ii) 20,000 J of energy was transferred by the producers to the organism of second trophic level. Calculate the amount of energy that will be transferred by organisms of the third trophic level to the organisms of the fourth trophic level.
Answer
(i) Plants → Rat → Snake → Hawk
(ii) According to the 10% rule of energy transfer, 10% of energy is transferred to next trophic level. Amount of energy available to second trophic level = 20,000 J Therefore, amount of energy transferred to third trophic level = 10% of 20,000 J = 2000 J. And, amount of energy transferred to fourth trophic level = 10% of 2000 J = 200 J
Section D (Long Answer Questions 5 Marks Each)
Question 34(a)
A saturated organic compound 'A' belongs to the homologous series of alcohols.
On heating 'A' with concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K, it forms an unsaturated compound 'B' with molecular mass 28 u.
The compound 'B' on addition of one mole of hydrogen in the presence of Nickel, changes to a saturated hydrocarbon 'C'.
(i) Identify A, B and C.
(ii) Write the chemical equations showing the conversion of A into B.
(iii) What happens when compound C undergoes combustion ?
(iv) State one industrial application of hydrogenation reaction.
(v) Name the products formed when compound A reacts with sodium.
Answer
(i) Compounds A, B and C are:
A → Ethanol
B → Ethene
C → Ethane
C2H5OH CH2=CH2
CH2=CH2 + H2 CH3-CH3
(ii) C2H5OH CH2=CH2
(iii) When ethane undergoes combustion, carbon dioxide is produced along with water and heat.
2C2H6 + 7O2 ⟶ 4CO2 + 6H2O + Heat
(iv) In industry, hydrogenation reaction is used for preparing vegetable ghee from vegetable oils
(v) Sodium ethoxide and Hydrogen
2Na + 2C2H5OH ⟶ 2C2H5ONa + H2
Question 34(b)
(i) With the help of a diagram, show the formation of micelles, when soap is applied on oily dirt.
(ii) Take two test tubes X and Y with 10 mL of hard water in each.
In test tube 'X', add few drops of soap solution and in test tube 'Y' add a few drops of detergent solution. Shake both the test tubes for the same period.
(1) In which test tube the formation of foam will be more ? Why ?
(2) In which test tube is a curdy solid formed ? Why ?
Answer
(i) Diagram showing the formation of micelles when soap is applied on oily dirt is given below:

(ii) The test tube containing detergents (i.e. Y) will form more foam because detergents are generally ammonium or sulphonate salts of long carboxylic acids. The charged ends of these compounds do not form insoluble precipitates with the calcium and magnesium ions in hard water. Hence, detergents remain effective even in hard water.
(iii) The test tube containing soap (i.e. X) will show a curdy white precipitate because soap molecules react with calcium and magnesium salts of hard water and form the floating off-white layer over water called as scum.
Question 35
(a) Name the parts of a bisexual flower that are not directly involved in reproduction.
(b) Differentiate between self pollination and cross pollination. List any two significance of pollination.
(c) What is the fate of ovules and ovary after fertilization in a flower?
Answer
(a) Calyx and corolla are the parts of a bisexual flower that are not directly involved in reproduction. Calyx has a protective function while corolla attracts pollinators.
(b)
| Self pollination | Cross pollination |
|---|---|
| Self pollination occurs within a flower or between two flowers of the same plant. | Cross pollination occurs between two flowers of different plants of the same species. |
| No external agent of pollination is required. | External agents such as wind, water, insects, birds and animals are required. |
Significance of pollination — Two significance of pollination are:
- It helps in the production of fruits and seeds.
- It helps in the transfer of characters and traits from both the parents to the offspring.
(c) Ovules mature to form seed and ovary grows to form fruit.
Question 36
(a) An electric iron consumes energy at a rate of 880 W when heating is at the maximum rate and 330 W when the heating is at the minimum. If the source voltage is 220 V, calculate the current and resistance in each case.
(b) What is heating effect of electric current ?
(c) Find an expression for the amount of heat produced when a current passes through a resistor for some time.
Answer
(a) Given,
Power (P) = 880 W [when heating is at the maximum rate ]
Power (P) = 330 W [when heating is at the minimum rate ]
Voltage (V) = 220 V
Case I : When heating is at the maximum rate
We know,
P = VI
Substituting we get,
880 = 220 x I
I = = 4 A
From V = IR
Substituting we get,
220 = 4 x R
R = = 55 Ω
Hence, when heating is at the maximum rate, I = 4 A and R = 55 Ω
Case II : When heating is at the minimum rate
Substituting we get current (I)
330 = 220 x I
I = = = 1.5 A
Substituting we get resistance (R),
220 = 1.5 x R
R = = 1.46 Ω
Hence, when heating is at the minimum rate, I = 1.5 A and R = 1.46 Ω
(b) When the electric circuit is purely resistive, that is, a configuration of resistors only connected to a battery; the source energy continually gets dissipated entirely in the form of heat. This is called heating effect of electric current.
(c) H = I2Rt where
This is known as Joule's law of heating.
Section E (Source/Case Based Questions 4 Marks Each)
Question 37
Almost all metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxides. Metal oxides are generally basic in nature. But some metal oxides show both basic as well as acidic behaviour. Different metals show different reactivities towards oxygen. Some react vigorously while some do not react at all.
(a) What happens when copper is heated in air ? (Give the equation of the reaction involved).
(b) Why are some metal oxides categorized as amphoteric ? Give one example.
(c) Complete the following equations :
(i) Na2O(s) + H2O(l) ⟶
(ii) Al2O3 + 2NaOH ⟶
OR
(c) On burning Sulphur in oxygen a colourless gas is produced.
(i) Write chemical equation for the reaction.
(ii) Name the gas formed.
(iii) State the nature of the gas.
(iv) What will be the action of this on a dry litmus paper ?
Answer
(a) When copper is heated in air, it reacts with the oxygen present in air to form black copper oxide.
2Cu(s) + O2(g) 2CuO(s)
(b) Amphoteric metal oxides behave both as acidic as well as basic oxides.
Example : Aluminium oxide [Al2O3]
It reacts with hydrochloric acid to form water and aluminium chloride
Al2O3 + 6HCl ⟶ 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
It reacts with sodium hydroxide solution and produces water and sodium aluminate (NaAlO2).
Al2O3 + 2NaOH ⟶ 2NaAlO2 + H2O
(c)
(i) Na2O(s) + H2O(l) ⟶ 2NaOH
(ii) Al2O3 + 2NaOH ⟶ 2NaAlO2 + H2O
OR
(i) S + O2 ⟶ SO2
(ii) Sulphur dioxide gas is produced.
(iii) Sulphur dioxide is a non-metal oxide and acidic in nature.
(iv) As the litmus paper is dry there will be no change in colour of litmus.
Question 38
In order to trace the inheritance of traits Mendel crossed pea plants having one contrasting character or a pair of contrasting characters. When he crossed pea plants having round and yellow seeds with pea plants having wrinkled and green seeds, he observed that no plants with wrinkled and green seeds were obtained in the F1 generation. When the F1 generation pea plants were cross-bred by self-pollination, the F2 generation had seeds with different combinations of shape and colour also.
(a) Write any two pairs of contrasting characteristics of pea plant used by Mendel other than those mentioned above.
(b) Differentiate between dominant and recessive traits.
(c) State the ratio of the combinations observed in the seeds of F2 generation (in the above case). What do you interpret from this result ?
OR
(c) Given below is a cross between a pure violet flowered pea plant (V) and a pure white flowered pea plant (v). Diagrammatically explain what type of progeny is obtained in F1 generation and F2 generation :
Pure violet flowered plant (VV) x Pure white flowered plant (vv)
Answer
(a) Two pairs of other contrasting characteristics of pea plant used by Mendel are:
- Purple flower and white flower
- Tall plant and short plant
(b) Differences between dominant and recessive traits:
| Dominant traits | Recessive traits |
|---|---|
| They mask the effect of recessive traits. | They are masked by dominant trait in heterozygous condition. |
| They express themselves in homozygous condition as well as heterozygous condition. | The always express themselves in homozygous condition. |
| The allele for dominant traits are expressed in capital letters. | The allele for recessive traits are expressed in small letters. |
| For example: tall plant in pea. | For example: short plant in pea. |
(c) All plants in F1 generation (in the above case) will have round and yellow seeds. In F2 generation, the phenotypic ratio will be 9:3:3:1.
It is clear from the result that the allele showed independent assortment during gamete formation and combined to give four different phenotypes in ratio 9:3:3:1.
OR
(c) Diagram explaining the type of progeny in F1 generation and F2 generation is shown below:

Violet flower colour is dominant trait and white flower colour is recessive trait in pea. When pure violet flowered plant (VV) is crossed with pure white flowered plant (vv), the F1 generation will have all violet flowered plants (Vv). In F2 generation, the ratio of plants with purple flower and white flower will be 3:1. The genotypic ratio will be 1:2:1.
Question 39
Hold a concave mirror in your hand and direct its reflecting surface towards the sun. Direct the light reflected by the mirror on to a white card-board held close to the mirror. Move the card-board back and forth gradually until you find a bright, sharp spot of light on the board. This spot of light is the image of the sun on the sheet of paper; which is also termed as 'Principal Focus' of the concave mirror.

(a) List two applications of concave mirror.
(b) If the distance between the mirror and the principal focus is 15 cm, find the radius of curvature of the mirror.
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the type of image formed when an object is placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
OR
(c) An object 10 cm in size is placed at 100 cm in front of a concave mirror. If its image is formed at the same point where the object is located, find :
(i) focal length of the mirror, and
(ii) magnification of the image formed with sign as per Cartesian sign convention.
Answer
(a) Two applications of concave mirror are :
- As a reflector — They are used in torches and vehicle headlights to get a powerful parallel beam of light.
- As a shaving mirror — When a concave mirror is held near the face (such that the face is between pole and focus of the mirror), it gives an upright and magnified image. Hence even tiny hair can be seen.
(b) As we know, R = 2f where, R is the radius of curvature and f is the focal length.
Given focal length (f) = 15 cm
So, substituting we get,
R = 2 x 15 = 30 cm
(c) Ray diagram showing the type of image formed when an object is placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror is given below:

OR
(c) Given,
Object distance (u) = -100 cm
Image distance (v) = -100 cm
Focal length (f) = ?
[f in case of a concave mirror is negative.]
Using formula,
= +
We get,
= +
= =
So, f = -50 cm
Hence, focal length = -50 cm.
(ii) Size of object (ho) = 10 cm
magnification = ?
From formula,
m = -
Substituting we get,
m = - = -1
Hence, magnification of the object = -1 i.e., inverted image is formed of same size as object.