Revising Basic Java Concepts
Objective Type Questions
Question 1
Java uses ............... character set.
Answer
Java uses Unicode character set.
Question 2
Smallest individual unit in a program is called ............... .
Answer
Smallest individual unit in a program is called token.
Question 3
Which of the following is not a token ?
- keywords
- identifiers
- statement
- operators
Answer
statement
Reason — Smallest individual unit in a program is called a token and a statement is composed of many tokens like keywords, identifiers, operators, constants etc.
Question 4
Identify the illegal identifier from the following.
- _CHK
- αβγτ
- 20_to_50
- A_to_Z
Answer
20_to_50
Reason — An identifier must not begin with a digit. It may contain underscore.
Question 5
Which of the following does not represent a character literal ?
- 'a'
- '1'
- '\a'
- "a"
Answer
"a"
Reason — Since a is enclosed in double quotes (" "), it becomes a String literal. Character literals are always enclosed within single quotes (' ').
Question 6
Which keyword turns a variable declaration into constant declaration ?
- const
- constant
- final
- fixed
Answer
final
Reason — Keyword final creates a named constant.
Question 7
ch += 2 is equivalent to
- ch = ch + 2
- ch + 2
- ch =+ 2
- none of the above
Answer
ch = ch + 2
Reason — += is a shorthand operator. The operator pair += tells the compiler to assign to ch the value of ch + 2.
Question 8
The Math class is part of which Java library package.
- java.util
- java.io
- java.random
- java.lang
Answer
java.lang
Reason — The Math class is part of java.lang package.
Question 9
Which clause is optional in a switch statement?
- switch
- case
- default
- none of the above
Answer
default
Reason — The default clause is optional and, if it is missing, no action takes place if all matches fail.
Question 10
Absence of which statement causes a fall-through in a switch statement.
- continue
- break
- stop
- fall
Answer
break
Reason — In the absence of break statement, the control flows to the next case below the matching case leading to fall-through.
Question 11
By default, the if-part and else-part of an if statement can contain these many statements in it.
- 2
- 1
- 5
- as many
Answer
1
Reason — By default, the if-part and else-part can contain only one statement. To include more than one statements, the set of statements need to be enclosed in curly braces and included as one compound statement.
Question 12
Which of the following loops is mostly used for fixed number of iterations ?
- for
- do-while
- while
- none of the above
Answer
for
Reason — for loop is usually used when the number of iterations are fixed.
Question 13
Which of the following is not an entry controlled loop ?
- for
- do-while
- while
- none of the above
Answer
do-while
Reason — do-while is an exit controlled loop as it executes atleast once even when the condition is false.
Question 14
Which of the following is an exit controlled loop?
- for
- do-while
- while
- none of the above
Answer
do-while
Reason — do-while is an exit controlled loop as it executes atleast once even when the condition is false. The condition is checked at the time of exit.
Question 15
Which of the following statements terminates the complete execution of a loop ?
- break
- continue
- terminate
- System.exit(0)
Answer
break
Reason — break statement is used to terminate the complete execution of a loop.
Assignment Questions
Question 1
What is meant by token? Name the tokens available in Java.
Answer
The smallest individual unit in a program is called a token.
Keywords, identifiers, literals, operators and punctuators are tokens available in Java.
Question 2
What are keywords ? Can keywords be used as identifiers ?
Answer
Keywords are the words with special meaning associated with them. These are reserved for special purpose and must not be used as normal identifier names. Some keywords of Java are default, return, if, private etc.
No, keywords cannot be used as identifiers.
Question 3
What is an identifier ? What is the identifier forming rule(s) of Java?
Answer
Identifiers are the names given by the programmer to various program units of Java. Identifiers are the names of variables, methods, classes, packages and interfaces etc.
Identifier forming rules of Java state the following:
- Identifiers can have alphabets, digits, _ (underscore) and characters and can be of any length.
- They must not be a keyword or Boolean literal or null literal.
- They must not begin with a digit.
- Java is case sensitive i.e., upper-case letters and lower-case letters are treated differently.
Question 4
What kind of program elements are the following ?
13, 'a', 4.38925, "a", main( )
Answer
| 13 | Integer Literal |
| 'a' | Character Literal |
| 4.38925 | Floating point Literal |
| "a" | String Literal |
| main( ) | Method |
Question 5
What kind of constants are the following ?
14, 011, 0X2A, 17, 014, 0XBC1
Answer
| 14 | Decimal Integer Literal |
| 011 | Octal Integer Literal |
| 0X2A | Hexadecimal Integer Literal |
| 17 | Decimal Integer Literal |
| 014 | Octal Integer Literal |
| 0XBC1 | Hexadecimal Integer Literal |
Question 6
What is a character constant in Java ? How are non graphic characters represented in Java ?
Answer
Single character enclosed in single quotation marks (' ') makes a character literal. For example, 'a', '5', , '1' are character literals.
Non-graphic characters are represented in Java using escape sequence. An escape sequence is represented by a backslash (\) followed by one or more characters. For example, '\n', '\t' are escape sequences for new line and tab respectively.
Question 7(a)
Write an equivalent Java expression for the following expressions:
Answer
u * t + (1.0 / 2.0) * f * t * t
Question 7(b)
Write an equivalent Java expression for the following expressions:
Answer
Math.sqrt(Math.pow(a,2) + Math.pow(b,2))
Question 7(c)
Write an equivalent Java expression for the following expressions:
ab + b >= ba + a
Answer
Math.pow(a, b) + b >= Math.pow(b, a) + a
Question 7(d)
Write an equivalent Java expression for the following expressions:
Answer
Math.pow(((3 * x + 5 * y) / (5 * x + 3 * y)) - ((8 * x * y) / (2 * y * x)), 3.0 / 2)
Question 8
What is meant by implicit and explicit type conversion ?
Answer
In an implicit conversion, the result of a mixed mode expression is obtained in the higher most data type of the variables without any intervention by the user. For example:
int a = 10;
float b = 25.5f, c;
c = a + b;
In case of explicit type conversion, the data gets converted to a type as specified by the programmer. For example:
int a = 10;
double b = 25.5;
float c = (float)(a + b);
Question 9
What do you mean by type casting? What is type cast operator in Java?
Answer
The explicit conversion of an operand to a specific type is called Type Casting.
Type Casting in Java is done using the type cast operator. It is a unary operator. It's syntax is:
(<target datatype>) <value>
For example :
int a = 10;
double b = 25.5;
float c = (float)(a + b);
Question 10
What will be the resultant type of the following expression if bh represents a byte variable, i is an int variable, fl is a float variable and db is a double variable ?
bh - i + db / fl - i * fl + db / i
Answer
The resultant data type will be double.
Explanation
bh - i + db / fl - i * fl + db / i
⇒ byte - int + double / float - int * float + double / int
⇒ byte - int + double - float + double
⇒ int + double - float + double
⇒ double - float + double
⇒ double + double
⇒ double
Question 11
What will be the resultant type of the following expression if fl is a float variable and db is a double variable?
(int) (fl + db)
Answer
The resultant data type will be int.
Explanation
Here, the programmer is performing an explicit type conversion to int using the type cast operator. Hence, the resultant data type will be int.
Question 12
Determine the data type of the expression
If p is an int, r is a float, q is a long and s is double.
Answer
The result of the given expression will be double type.
Explanation
Question 13
Determine the data type of the expression
if x is int, y is long, w is float, z is double, p is short and q is long double.
Answer
The result will be of long double data type.
Explanation
Question 14(a)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.abs(-5) - Math.abs(-7)Answer
The output value is -2. The type of expression is int.
Explanation
Math.abs(-5) - Math.abs(-7)
⇒ 5 - 7
⇒ -2
Question 14(b)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.abs(-1e-1) + Math.abs(-2e-2)Answer
The output value is 0.12. The type of expression is double.
Explanation
Math.abs(-1e-1) + Math.abs(-2e-2)
⇒ 0.1 + 0.02
⇒ 0.12
Question 14(c)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.sqrt(0.0064)Answer
The output value is 0.08. The type of expression is double.
Explanation
Math.sqrt() method returns the square root of its argument. As square root of 0.0064 is 0.08 hence that is the output. The return type of Math.sqrt() is double so the type of expression is double.
Question 14(d)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.sqrt(Math.pow(2.7, 2))Answer
The output value is 2.7. The type of expression is double.
Explanation
Math.pow(2.7, 2) will calculate square of 2.7 as we are raising it to the power 2. After this, calculating square root with Math.sqrt() will return the same number 2.7. The return type of Math.sqrt() is double so the type of expression is double.
Question 14(e)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.round(3.499)Answer
The output value is 3. The type of expression is long.
Explanation
Math.round() rounds off its argument to the nearest mathematical integer. If argument is float, return type is int, if argument is double, return type is long. In this case, 3.499 will be treated as double because suffix 'f' is not there. Hence, it will return a value of long data type.
Question 14(f)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.max(1.5e-2, 0.095)Answer
The output value is 0.095. The type of expression is double.
Explanation
Math.max(a, b) returns the maximum of a and b. As 0.095 is greater than 1.5e-2, hence, 0.095 is the output. Since the argument is double so the data type of return value is also double.
Question 14(g)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.ceil(4.002)Answer
The output value is 5.0. The type of expression is double.
Explanation
Math.ceil(x) returns the smallest double value that is greater than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. Hence, output is 5.0 and data type of result is double.
Question 14(h)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.min(-5, 1.0)Answer
The output value is -5.0. The type of expression is double.
Explanation
Math.min(a, b) returns the minimum of a and b. As one of the arguments is of double type hence, data type of return value is also double.
Question 14(i)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.floor(7.99)Answer
The output value is 7.0. The type of expression is double.
Explanation
Math.floor( ) returns the largest double value that is less than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. Hence, output is 7.0 and data type of result is double.
Question 14(j)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.ceil(-2.73)Answer
The output value is -2.0. The type of expression is double.
Explanation
Math.ceil( ) returns the smallest double value that is greater than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. -2.0 is the smallest mathematical integer greater than -2.73. Hence, output is -2.0 and data type of result is double.
Question 14(k)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.pow(16, 0.25)Answer
The output value is 2.0. The type of expression is double.
Explanation
Math.pow(x, y) returns x raised to the power of y as a double value. Math.pow(16, 0.25) is equivalent to . Hence, output is 2.0 and data type of result is double.
Question 14(l)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.pow(4, -2)Answer
The output value is 0.0625. The type of expression is double.
Explanation
Math.pow(x, y) returns x raised to the power of y as a double value. Math.pow(4, -2) is equivalent to 4-2 i.e., = 0.0625. Hence, output is 0.0625 and data type of result is double.
Question 14(m)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.round(1.49 + 0.1)Answer
The output value is 2. The type of expression is long.
Explanation
Math.round() rounds off its argument to the nearest mathematical integer. If argument is float, return type is int, if argument is double, return type is long. In this case, 1.49 + 0.1 = 1.59 so it will be rounded of to 2, the nearest mathematical integer. 1.59 will be treated as double because suffix 'f' is not there. Hence, it will return a value of long data type.
Question 14(n)
State the value and type of each expression.
Math.round(1.49) + 0.1Answer
The output value is 1.1. The type of expression is long.
Explanation
Math.round() rounds off its argument to the nearest mathematical integer.
Math.round(1.49) + 0.1
⇒ 1 + 0.1
⇒ 1.1
If argument is float, return type is int, if argument is double, return type is long. In this case, 1.49 will be treated as double because suffix 'f' is not there. Hence, it will return a value of long data type.
Question 15(a)
Write the following as Java expressions.
Answer
Math.sqrt(Math.pow(a,2) - Math.pow(b,2))
Question 15(b)
Write the following as Java expressions.
π(x6 - y6)
Answer
Math.PI * (Math.pow(x,6) - Math.pow(y,6))
Question 15(c)
Write the following as Java expressions.
Answer
4.0 / 3.0 * Math.PI * Math.pow(r,3)
Question 15(d)
Write the following as Java expressions.
| z4 - 1 |
Answer
Math.abs(Math.pow(z,4) - 1)
Question 16
A student incorrectly attempted to produce a random value in the range 1.6 using the expression.
6*(int)Math.random( ) + 1
Correct the error in expression above to get the desired result.
Answer
The correct expression to get the desired result is given below:
(int)(6 * Math.random( )) + 1
Explanation
The formula to get an integer number between 1 and n is:
int r = (int) (n * Math.random()) + 1
Question 17
What is the significance of a break statement in a switch statement ?
Answer
The break statement when used inside a switch, ends that case and proceeds to the first statement that follows switch statement. In case, the break statement is missing, the control flows to the next case below the matching case and continues to execute all the cases, till the end of switch statement. This is called fall through.
Question 18
What are iteration statements ? Name the iteration statements provided by Java.
Answer
The iterative constructs or iteration statements allow a set of instructions to be performed repeatedly until a certain condition is fulfilled. The iteration statements are also called loops or looping statements.
Java provides three iteration statements:
- for
- while
- do-while
Question 19
What is meant by an entry-controlled loop? Which Java loops are entry-controlled?
Answer
The loop which tests the condition before entering the loop is called entry-controlled loop. It does not execute if the condition is false.
for and while are entry controlled loops in Java.
Question 20
What is meant by an exit-controlled loop ? Which Java loops are exit-controlled ?
Answer
If a loop tests the condition at the time of exit from the loop, it is called exit-controlled loop. This loop executes at least once even if the condition is false.
do-while loop is an exit controlled loop in Java.
Question 21
What is the difference between a while and do-while loop ?
Answer
| while loop | do-while loop |
|---|---|
| while is an entry-controlled loop. | do-while is an exit-controlled loop. |
| while loop checks the test condition at the beginning of the loop. | do-while loop checks the test condition at the end of the loop. |
| while loop executes only if the test condition is true. | do-while loop executes at least once, even if the test condition is false. |
| while loop is helpful in situations where number of iterations is not known. | do-while loop is suitable when we need to display a menu to the user. |
| Syntax: while(test condition) { ... } | Syntax: do { ... }while(condition); |
Question 22
How many times is the loop body executed in a do loop, even if the test-condition is false ?
Answer
do-while loop is an exit controlled loop. Thus, its body is executed atleast once even if the test-condition is false.
Question 23
What is nested loop ?
Answer
A loop may contain another loop in its body. This form of a loop is called nested loop. In a nested loop, the inner loop must terminate before the outer loop.
For example:
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
System.out.print(j + ' ');
}
System.out.println();
}
Question 24
Write a program to print pattern like :
1
2 1
3 2 1
4 3 2 1
5 4 3 2 1
Answer
public class KboatPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 4; j >= i; j--)
System.out.print(" ");
for (int k = i; k >= 1; k--)
System.out.print(k);
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output

Question 25
Write a program to print a pattern as :
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4
1 2 3
1 2
1
Answer
public class KboatPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
for (int i = 5; i >= 1; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output

Question 26
Write a program to print a pattern as :
1
1 0
1 0 1
1 0 1 0
1 0 1 0 1
Answer
//
public class KboatPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 1, b = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
if (j % 2 == 0)
System.out.print(b + " ");
else
System.out.print(a + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output

Question 27
Write a program to print a pattern as :
* * * * *
* * * *
* * *
* *
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
* * * * *
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
for (int i = 5; i >= 1; i--) {
for (int j = i; j < 5; j++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++) {
System.out.print('*');
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = 4; i >= 1; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int k = i; k <= 5; k++) {
System.out.print('*');
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output

Question 28
Classify the following as primitive or non-primitive datatypes :
- char
- arrays
- int
- classes
Answer
- Primitive data type
- Non-primitive data type
- Primitive data type
- Non-primitive data type
Question 29
System.out.print("BEST");
System.out.println("OF LUCK");
Choose the correct option for the output of the above statements
(i) BEST OF LUCK
(ii) BEST
OF LUCK
Answer
Option 1 — BEST OF LUCK is the correct option.
Explanation
System.out.print does not print a newline at the end of its output so the println statement begins printing on the same line. So the output is BEST OF LUCK printed on a single line.
Question 30(a)
Write a Java expression for the following :
Answer
Math.sqrt(3 * x + Math.pow(x,2)) / (a + b))
Question 30(b)
What is the value of y after evaluating the expression given below ?
y += ++y + y-- + --y ; when int y = 8
Answer
The value of y will be 33.
Explanation
y += ++y + y-- + --y
⇒ y = y + ++y + y-- + --y y = 8
⇒ y = 8 + 9 + y-- + --y y = 9
⇒ y = 8 + 9 + 9 + --y y = 8
⇒ y = 8 + 9 + 9 + 7 y = 7
⇒ y = 33
Question 30(c)
Give the output of the following :
- Math.floor(-4.7)
- Math.ceil(3.4) + Math.pow(2,3)
Answer
(1) Math.floor(-4.7)
Output
-5.0
Explanation
Math.floor method returns the largest double value that is less than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. As -5.0 is the largest mathematical integer less than -4.7 so it is the output. Note that -4.7 is a negative number so the largest integer less than -4.7 is -5.0 and not -4.0.
(2) Math.ceil(3.4) + Math.pow(2,3)
Output
12.0
Explanation
Math.ceil(x) function returns the smallest whole number greater than or equal to x. Math.ceil(3.4) gives 4.0 and Math.pow(2,3) gives 8.0. So the output is 4.0 + 8.0 = 12.0.
Question 31
What are the values stored in variables r1 and r2 ?
- double r1 = Math.abs(Math.min(-2.83, -5.83));
- double r2 = Math.sqrt(Math.floor(16.3));
Answer
- r1 has 5.83
- r2 has 4.0
Explanation
- Math.min(-2.83, -5.83) returns -5.83 as -5.83 is less than -2.83. (Note that these are negative numbers). Math.abs(-5.83) returns 5.83.
- Math.floor(16.3) returns 16.0. Math.sqrt(16.0) gives square root of 16.0 which is 4.0.
Question 32(a)
Name the operators listed below :
- <
- ++
- &&
- ? :
Answer
- Less than operator. (It is a relational operator)
- Increment operator. (It is an arithmetic operator)
- Logical AND operator. (It is a logical operator)
- Ternary operator. (It is a conditional operator)
Question 32(b)
State the number of bytes occupied by char and int data types.
Answer
char occupies 2 bytes and int occupies 4 bytes.
Question 32(c)
Write one difference between / and % operator.
Answer
/ operator computes the quotient whereas % operator computes the remainder.
Question 33
Predict the output :
class Test {
public static void main (String args[]) {
double x, y, z ;
x = 3;
y = 4;
z = Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y);
System.out.println("z = " + z);
}
}Answer
Output
z = 5.0
Explanation
z = Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y)
⇒ Math.sqrt(3.0 * 3.0 + 4.0 * 4.0)
⇒ Math.sqrt(9.0 + 16.0)
⇒ Math.sqrt(25.0)
⇒ 5.0
Question 34
Predict the output :
class Power {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int e = 5, result, i;
result = 1 ;
i = e ;
while(e > 0) {
result *= 2 ;
e--;
}
int n = result /2, p = i - 1;
System.out.println("2 to the power of " + i + " is " + result);
System.out.println("2 to the power of " + p + " is " + n);
}
}Answer
Output
2 to the power of 5 is 32
2 to the power of 4 is 16
Explanation
The execution of while loop is shown in the table below:
| e | (e > 0) | result | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | True | 2 | result = 1 x 2, e becomes 4 |
| 4 | True | 4 | result = 2 x 2, e becomes 3 |
| 3 | True | 8 | result = 4 x 2, e becomes 2 |
| 2 | True | 16 | result = 8 x 2, e becomes 1 |
| 1 | True | 32 | result = 16 x 2, e becomes 0 |
| 0 | False | Loop terminates |
n = result / 2, p = i - 1;
⇒ n = 32 / 2, p = 5 - 1
⇒ n = 16, p = 4
Question 35
Predict the output :
class FindFac {
public static void main (String args[]) {
for(int i = 2; i <= 100; i++) {
System.out.print("Factors of" + i + ": ");
for(int j = 2; j < i; j++)
if((i % j) == 0)
System.out.print(j + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}Answer
The output of the program is a list of the factors of each integer between 2 and 100, printed to the console.
Output
Factors of2:
Factors of3:
Factors of4: 2
Factors of5:
Factors of6: 2 3
Factors of7:
Factors of8: 2 4
Factors of9: 3
Factors of10: 2 5
...
...
Factors of95: 5 19
Factors of96: 2 3 4 6 8 12 16 24 32 48
Factors of97:
Factors of98: 2 7 14 49
Factors of99: 3 9 11 33
Factors of100: 2 4 5 10 20 25 50
Explanation
This Java program finds the factors of integers between 2 and 100.
The program uses two nested for loops to generate the integers to be factored and to find their factors. The outer for loop generates the numbers from 2 to 100 whose factors are to be found.
The inner for loop starts with j = 2 and continues until j < i, incrementing j by 1 each time through the loop. This loop checks whether j is a factor of i by checking whether the remainder of i divided by j is equal to zero. If j is a factor of i, it is printed to the console on the same line as the message "Factors of [i]: ".
After the inner loop has completed, a newline character is printed to the console using System.out.println(). This causes the next message ("Factors of [i+1]: ") to be printed on a new line.
Let us consider the execution of nested 'for' loop for a single value of i (say, i = 6). The given table follows the execution:
| i | i <= 100 | j | j < i | (i % j) == 0 | Output | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | True | 2 | True | True | Factors of 6: 2 | 6 % 2 = 0 |
| 3 | True | True | Factors of 6: 2 3 | 6 % 3 = 0 | ||
| 4 | True | False | 6 % 4 ≠ 0 | |||
| 5 | True | False | 6 % 5 ≠ 0 | |||
| 6 | False | j becomes equal to i, inner loop terminates and i becomes 7 |
Question 36
Give the output of the following program segment and also mention how many times the loop is executed.
int i;
for (i = 5 ; i > 10; i++)
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(i * 4);Answer
Output
20
Explanation
Initially i = 5.
The test condition i > 10 is false and so the control comes to the next statement following 'for' loop — System.out.println(i * 4); and prints 20 (5 * 4) on the screen.
Question 37
Find the error
for(count = 0, count < 5, count = count + 1)
System.out.println("This is count:" + count);
System.out.println("Done!"); Answer
The errors are as follows:
- The variable count is not declared. It needs to be declared before it can be used.
- The syntax of 'for' loop requires semicolons ( ; ) as separators, and not comma ( , ). The correct code is as follows:
for(int count = 0; count < 5; count = count + 1)
System.out.println("This is count:" + count);
System.out.println("Done!");
Question 38
Find the error :
x = 3;
y = 4;
z = math.power(x*x, y/2); Answer
The errors are as follows:
- The variables — x, y, z, are not declared. They need to be declared before they can be used.
- The letter 'm' in
mathshould be in uppercase as Java is a case-sensitive language. Also, the correct name of the function ispow. Hence, it must be written asMath.pow().
The correct code snippet is as follows:
int x = 3;
int y = 4;
double z = Math.pow(x*x, y/2);Question 39
Find the error:
class Test {
public static void main (String args[]) {
int x = 10;
if(x == 10) {
int y = 20;
System.out.println("x and y: "+ x +" "+ y);
x = y * 2;
}
y = 100;
System.out.println("x is"+ x);
}
}Answer
The variable y is declared inside 'if' block. Its scope is limited to if block and it cannot be used outside the block.
The correct code snippet is as follows:
class Test {
public static void main (String args[]) {
int x = 10;
int y;
if(x == 10) {
y = 20;
System.out.println("x and y: "+ x +" "+ y);
x = y * 2;
}
y = 100;
System.out.println("x is"+ x);
}
}Question 40
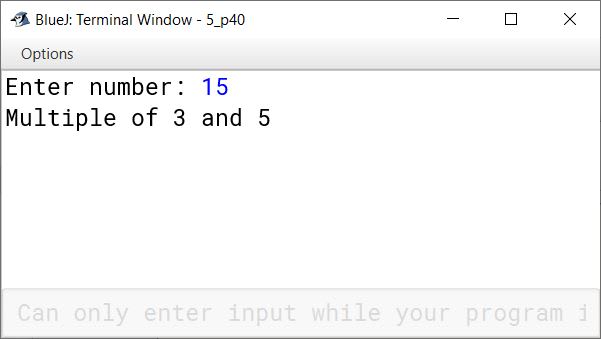
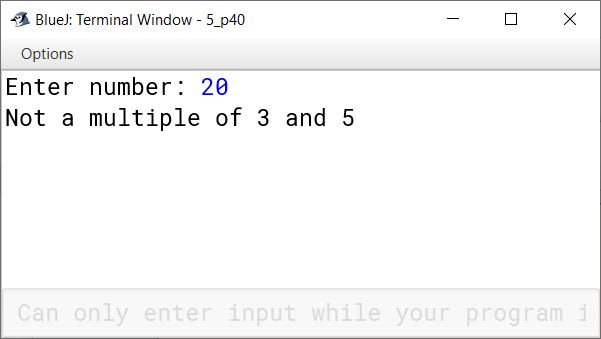
Write a program that inputs a number and tests if the given number is a multiple of both 3 and 5.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatMultipleCheck
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter number: ");
int num = in.nextInt();
if (num % 3 == 0 && num % 5 == 0)
System.out.println("Multiple of 3 and 5");
else
System.out.println("Not a multiple of 3 and 5");
}
}Output
Question 41
Write a program that inputs a character and prints if the typed character is in uppercase or lowercase.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatCheckCase
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter an alphabet: ");
char ch = in.next().charAt(0);
if(Character.isUpperCase(ch))
System.out.println("Upper Case letter");
else if(Character.isLowerCase(ch))
System.out.println("Lower Case Letter");
else
System.out.println("Character not an alphabet");
}
}Output


Question 42
Write a program that inputs a character and prints if the user has typed a digit or an alphabet or a special character.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatCheckLetterDigitSpChar
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a character: ");
char ch = in.next().charAt(0);
if(Character.isLetter(ch))
System.out.println("Letter");
else if(Character.isDigit(ch))
System.out.println("Digit");
else if(!Character.isWhitespace(ch))
System.out.println("Special character");
}
}Output



Question 43
Write a program that inputs an alphabet and checks if the given alphabet is a vowel or not.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatVowelCheck
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a character: ");
char ch = in.next().charAt(0);
ch = Character.toUpperCase(ch);
if(ch == 'A' ||
ch == 'E' ||
ch == 'I' ||
ch == 'O' ||
ch == 'U')
System.out.println("Vowel");
else
System.out.println("Not a vowel");
}
}Output


Question 44
Write a program that takes a number and check if the given number is a 3 digit number or not. (Use if to determine)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Kboat3DigitNumber
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter number: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
if (n >= 100 && n <= 999)
System.out.println("Three Digit Number");
else
System.out.println("Not a three digit number");
}
}Output


Question 45
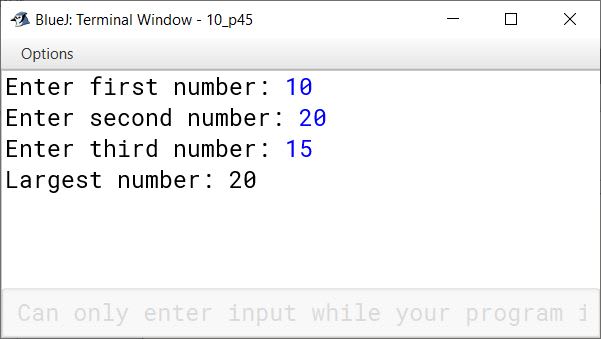
Write a program to input three numbers and print the largest of the three numbers.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatLargestNumber
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter first number: ");
int a = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter second number: ");
int b = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter third number: ");
int c = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Largest number: ");
if (a > b && a > c)
System.out.println(a);
else if (b > a && b > c)
System.out.println(b);
else
System.out.println(c);
}
}Output
Question 46
Write a program that takes a number and check if the given number is a 3 digit number or not. (Use a loop to determine)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatDigitCount
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
int count = 0;
while (n != 0) {
count++;
n = n / 10;
}
if (count == 3)
System.out.println("Three digit number");
else
System.out.println("Not a three digit number");
}
}Output


Question 47
Write a program that prints the squares of 10 even numbers in the range 10 .. 100.
public class KboatSquares
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Squares of even number:");
System.out.println("Number\tSquare");
for(int i = 10; i < 30; i += 2) {
int sq = i * i;
System.out.println(i + "\t" + sq);
}
}
}Output

Question 48
Write a program that inputs a number and checks if the given number is a palindrome. A number that is equal to its reversed number is a palindrome number.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatPalindromeNumber
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number: ");
int num = in.nextInt();
int copyNum = num;
int revNum = 0;
while(copyNum != 0) {
int digit = copyNum % 10;
copyNum /= 10;
revNum = revNum * 10 + digit;
}
if (revNum == num)
System.out.println("A Palindrome number");
else
System.out.println("Not a Palindrome number");
}
}Output


Question 49
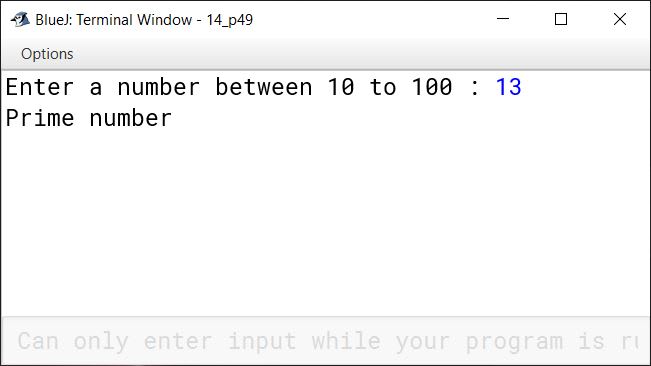
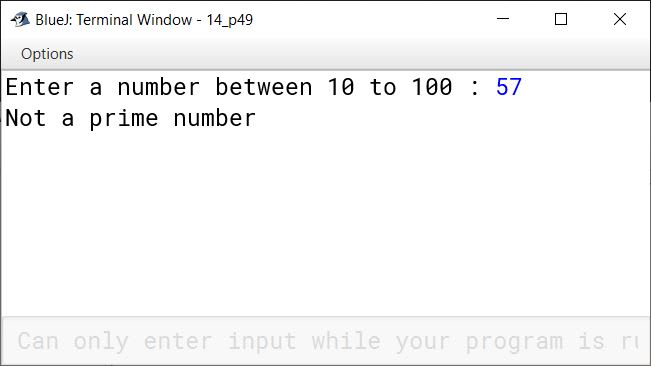
Write a program to input a number in the range 10 to 100 and check if it is a prime number.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatPrime
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.print("Enter a number between 10 to 100 : ");
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = in.nextInt();
int c = 0;
if(num < 10 || num > 100)
System.out.println("Number out of range");
else {
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
if (num % i == 0)
c++;
}
if (c == 2)
System.out.println("Prime number");
else
System.out.println("Not a prime number");
}
}
}Output
Question 50
Write a program to print following series of numbers: 2, 5, 8, 11, 14....
public class KboatSeries
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i += 3) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
}Output

Question 51
Write a program to print Fibonacci series : 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8....
public class KboatFibonacci
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 0;
int b = 1;
System.out.print(a + " " + b);
/*
* i is starting from 3 below
* instead of 1 because we have
* already printed 2 terms of
* the series. The for loop will
* print the series from third
* term onwards.
*/
for (int i = 3; i <= 20; i++) {
int term = a + b;
System.out.print(" " + term);
a = b;
b = term;
}
}
}Output

Question 52
Write a program to print factorial of a given number.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatFactorial
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
long f = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
f *= i;
}
System.out.println("Factorial of " + n
+ " = " + f);
}
}Output

Question 53
Write a program to print Floyd's triangle as shown below:
1
2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatFloydsTriangle
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(a++ + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output
