Input in Java
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1
A programmer wrote the following statement:
netPay = grossPay + providentFund;
instead of:
netPay = grossPay - providentFund;
Assuming all the unseen code is correct, what kind of error is it?
- Syntax error
- Runtime error
- Logical error ✓
- None of these
Question 2
Which of the following might make the Java compiler report a syntax error in a particular line of a program?
- The program is typed in the wrong font.
- The line contains a comma (,) instead of a dot (.). ✓
- It is caused by Java runtime.
- Program takes too long to compile.
Question 3
Which of the following statement is true for logical errors?
- The compiler does not detect these errors.
- There is no indication of error when the program is executed.
- The program may produce correct results for some input data and wrong results for other input data.
- All of the above ✓
Question 4
Which keyword do you use to include a class in your program?
- import ✓
- export
- include
- impart
Question 5
Which of the following is not a valid method of the Scanner class?
- next()
- nextInt()
- nextLong()
- nextNumber() ✓
Question 6
Default delimiter used in the Scanner class is ...........
- Comma
- Whitespace ✓
- Colon
- There is no default delimiter.
Question 7
Which package would you import to display the date and time?
- java.util.* ✓
- java.Date.*
- java.io.*
- java.lang.*
Question 8
Which package would you import for the Scanner class?
- java.util.* ✓
- java.awt.*
- java.io.*
- java.lang.*
Question 9
Errors occur in a program when ...........
- Syntax of the programming language is not followed.
- The program does not run properly or does not execute at all.
- The program produces an incorrect result.
- All of the above ✓
Question 10
The Scanner class can be used to read input from ...........
- a keyboard
- a file
- a string
- All of these ✓
Assignment Questions
Question 1
Suppose you want to use the class MyClass of the package MyPackage.UtilityLibrary in a program you are writing. What do you need to do to make the following?
i. class MyClass available to your program
Answer
import MyPackage.UtilityLibrary.MyClass;ii. all the classes of the package available to your program
Answer
import MyPackage.UtilityLibrary.*;Question 2
Explain data input technique in a program using the Scanner class.
Answer
The data entered by the user through the keyboard is provided to our Java program with the help of standard input stream that is specified as System.in in the program. We connect our Scanner class to this stream while creating its object. The input received by Scanner class is broken into tokens using a delimiter pattern. The default delimiter is whitespace. Scanner class provides various next methods to read these tokens from the stream. The different next methods provided by Scanner class are next(), nextShort(), nextInt(), nextLong(), nextFloat(), nextDouble(), nextLine(), next().charAt(0).
Question 3
What are delimiters? Which is the default delimiter used in the Scanner class?
Answer
A delimiter is a sequence of one or more characters that separates two tokens. The default delimiter is a whitespace.
Question 4
What are errors in a program?
Answer
Errors are mistakes in a program that prevents it from its normal working. They are often referred to as bugs. Errors are classified into three categories — Syntax Errors, Runtime Errors and Logical Errors.
Question 5
Explain the following terms, giving an example of each.
i. Syntax error
Answer
Syntax Errors are the errors that occur when we violate the rules of writing the statements of the programming language. These errors are reported by the compiler and they prevent the program from executing. For example, the following statement will give an error as we missed terminating it with a semicolon:
int sumii. Runtime error
Answer
Errors that occur during the execution of the program primarily due to the state of the program which can only be resolved at runtime are called Run Time errors.
Consider the below example:
import java.util.Scanner;
class RunTimeError
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
int result = 100 / n;
System.out.println("Result = " + result);
}
}This program will work fine for all non-zero values of n entered by the user. When the user enters zero, a run-time error will occur as the program is trying to perform an illegal mathematical operation of division by 0. When we are compiling the program, we cannot say if division by 0 error will occur or not. It entirely depends on the state of the program at run-time.
iii. Logical error
Answer
When a program compiles and runs without errors but produces an incorrect result, this type of error is known as logical error. It is caused by a mistake in the program logic which is often due to human error. Logical errors are not caught by the compiler. Consider the below example for finding the perimeter of a rectangle with length 2 and breadth 4:
class RectanglePerimeter
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
int l = 2, b = 4;
double perimeter = 2 * (l * b); //This line has a logical error
System.out.println("Perimeter = " + perimeter);
}
}Output
Perimeter = 16
The program gives an incorrect perimeter value of 16 as the output due to a logical error. The correct perimeter is 12. We have written the formula of calculating perimeter incorrectly in the line double perimeter = 2 * (l * b);. The correct line should be double perimeter = 2 * (l + b);.
Question 6
If a student forgot to put a closing quotation mark on a string, what kind error would occur?
Answer
Syntax error
Question 7
A program has compiled successfully without any errors. Does this mean the program is error free? Explain.
Answer
Successful compilation of the program only ensures that there are no syntax errors. Runtime and logical errors can still be there in the program so we cannot say that the program is error free. Only after comprehensive testing of the program, we can say that the program is error free.
Question 8
A program needed to read an integer, but the user entered a string instead, and an error occurred when the program was executed. What kind of error is this?
Answer
This is a Runtime error.
Question 9
A student was asked to write a program for computing the area of a rectangle and he, mistakenly, wrote the program to compute the perimeter of a rectangle. What kind of error is this?
Answer
This is a Logical error.
Question 10
What is a java package? Give an example.
Answer
A package is a named collection of Java classes that are grouped on the basis of their functionality. For example, java.util.
Question 11
Explain the use of import statement with an example.
Answer
import statement is used to import built-in and user-defined packages and classes into our Java program. For example, we can import all the classes present in the java.util package into our program using the below statement:
import java.util.*;Question 12
Distinguish between the following:
i. next() and nextLine()
Answer
| next() | nextLine() |
|---|---|
| It reads the input only till the next complete token until the delimiter is encountered. | It reads the input till the end of line so it can read a full sentence including spaces. |
| It places the cursor in the same line after reading the input. | It places the cursor in the next line after reading the input. |
ii. next() and next().charAt(0)
Answer
| next() | next().charAt(0) |
|---|---|
| It reads the input only till the next complete token until the delimiter is encountered. | It reads the complete token and then the first character is returned using the charAt(0) method. |
| It returns the read data as a String value. | It returns the read data as a char value. |
iii. next() and hasNext()
Answer
| next() | hasNext() |
|---|---|
| It reads the input till the next complete token until the delimiter is encountered. | It checks if the Scanner has another token in its input. |
| It returns a String value. | It returns a boolean value. |
iv. hasNext() and hasNextLine()
Answer
| hasNext() | hasNextLine() |
|---|---|
| Returns true if the Scanner object has another token in its input. | Returns true if there is another line in the input of the Scanner object. |
Question 13
Consider the following input:
one, two three, four, five
What values will the following code assign to the variables input1 and input2?
String input1 = keyboard.next();
String input2 = keyboard.next();
Answer
input1 ⇒ one,
input2 ⇒ two
Question 14
Write a line of code that:
i. Creates a Scanner object named scanner to be used for taking keyboard input.
Answer
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);ii. Uses the object scanner to read a word from the keyboard and store it in the String variable named stg.
Answer
String stg = scanner.next();Question 15
Write a code that creates a Scanner object and sets its delimiter to the dollar sign.
Answer
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
scanner.useDelimiter("$");Question 16
Write a statement to let the user enter an integer or a double value from the keyboard.
Answer
Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in);
double num = keyboard.nextDouble();Question 17
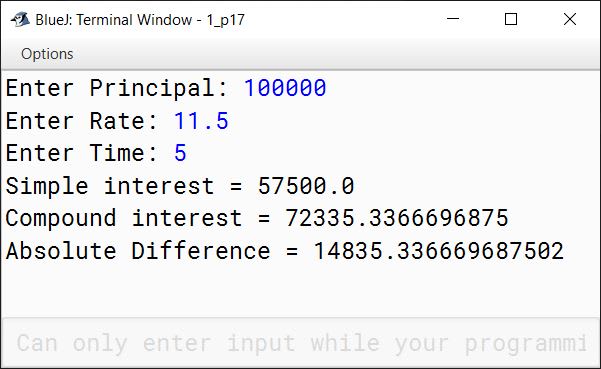
Write a program in Java that takes input using the Scanner class to calculate the Simple Interest and the Compound Interest with the given values:
i. Principle Amount = Rs.1,00,000
ii. Rate = 11.5%
iii. Time = 5 years
Display the following output:
i. Simple interest
ii. Compound interest
iii. Absolute value of the difference between the simple and compound interest.
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatInterest
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter Principal: ");
double p = in.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter Rate: ");
double r = in.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter Time: ");
int t = in.nextInt();
double si = p * r * t / 100.0;
double cAmt = (p * Math.pow(1 + (r / 100), t));
double ci = cAmt - p;
double diff = Math.abs(si - ci);
System.out.println("Simple interest = " + si);
System.out.println("Compound interest = " + ci);
System.out.println("Absolute Difference = " + diff);
in.close();
}
}Output
Question 18
Write a program to compute the Time Period (T) of a Simple Pendulum as per the following formula:
T = 2π√(L/g)
Input the value of L (Length of Pendulum) and g (gravity) using the Scanner class.
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSimplePendulum
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter Length: ");
double l = in.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter Gravity: ");
double g = in.nextDouble();
double t = 2 * 3.14159 * Math.sqrt(l / g);
System.out.println("Time Period = " + t);
in.close();
}
}Output

Question 19
Write a program that takes the distance of the commute in kilometres, the car fuel consumption rate in kilometre per gallon, and the price of a gallon of petrol as input. The program should then display the cost of the commute.
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatCommuteCost
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter distance of commute in kms: ");
double kms = in.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter fuel consumption rate: ");
double rate = in.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter price of petrol: ");
double price = in.nextDouble();
double cost = kms / rate * price;
System.out.println("Cost of commute = " + cost);
in.close();
}
}Output

Question 20
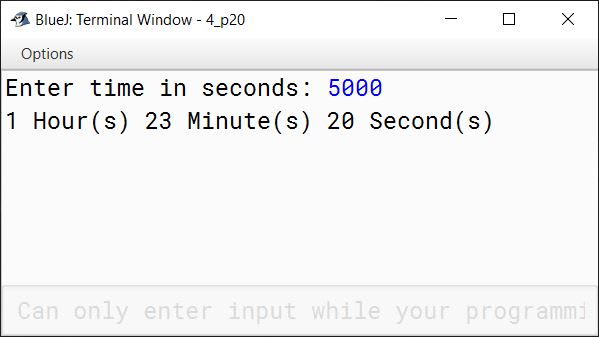
Write a program in Java that accepts the seconds as input and converts them into the corresponding number of hours, minutes and seconds. A sample output is shown below:
Enter Total Seconds:
5000
1 Hour(s) 23 Minute(s) 20 Second(s)
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatTimeConvert
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter time in seconds: ");
long secs = in.nextLong();
long hrs = secs / 3600;
secs %= 3600;
long mins = secs / 60;
secs %= 60;
System.out.println(hrs + " Hour(s) " + mins
+ " Minute(s) " + secs + " Second(s)");
in.close();
}
}Output
Question 21
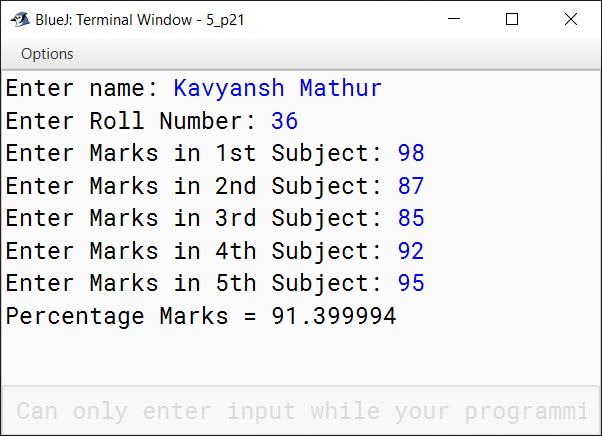
Write a program in Java, using the Scanner methods, to read and display the following details:
Name - as a String data type
Roll Number - as an integer data type
Marks in 5 subjects - as a float data type
Compute and display the percentage of marks.
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatMarks
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter name: ");
String name = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter Roll Number: ");
int rollNo = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter Marks in 1st Subject: ");
float m1 = in.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Enter Marks in 2nd Subject: ");
float m2 = in.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Enter Marks in 3rd Subject: ");
float m3 = in.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Enter Marks in 4th Subject: ");
float m4 = in.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Enter Marks in 5th Subject: ");
float m5 = in.nextFloat();
float t = m1 + m2 + m3 + m4 + m5;
float p = t / 500 * 100;
System.out.println("Percentage Marks = " + p);
in.close();
}
}Output
Question 22
Write a Java program that reads a line of text separated by any number of whitespaces and outputs the line with correct spacing, that is, the output has no space before the first word and exactly one space between each pair of adjacent words.
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatCorrectSpacing
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a sentence: ");
while(in.hasNext()) {
String w = in.next();
System.out.print(w + " ");
}
in.close();
}
}Output
