Physical Quantities and Measurement
Objective Questions
Question 1
Write true or false for each statement:
(a) The S.I. unit of volume is litre.
(b) A measuring beaker of capacity 200 mL can measure only the volume of 200 mL of a liquid.
(c) cm2 is a smaller unit of area than m2.
(d) Equal volumes of two different substances have equal masses.
(e) The S.I. unit of density is g cm-3.
(f) 1 g cm-3 = 1000 kg m-3.
(g) The density of water is maximum at 4°C.
(h) The speed 5 m s-1 is less than 25 km h-1.
(i) The S.I. unit of speed is m s-1.
Answer
(a) False
Correct Statement — The S.I. unit of volume is cubic metre (m3).
(b) True
(c) True
(d) False
Correct Statement — Equal volumes of two different substances have different masses.
(e) False
Correct Statement — The S.I. unit of density is kg m-3.
(f) True
(g) True
(h) True
(i) True
Question 2
Fill in the blanks:
(a) 1 m3 = ............... cm3
(b) The volume of an irregular solid is determined by the method of ............... .
(c) Volume of a cube = ............... .
(d) The area of an irregular lamina is measured by using a ............... .
(e) Mass = density x ............... .
(f) The S.I. unit of density is ............... .
(g) 1 g cm-3 = ............... kg m-3.
(h) 36 km h-1 = ............... m s -1.
(i) Distance travelled D = ............... x time t.
Answer
(a) 106
(b) displacement of liquid
(c) (one side)3
(d) graph paper
(e) volume
(f) kg m-3
(g) 1000
(h) 10
(i) speed v
Question 3
Match the following:
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| (a) Volume of a liquid | (i) kg m-3 |
| (b) Area of a leaf | (ii) m3 |
| (c) S.I. unit of volume | (iii) graph paper |
| (d) S.I. unit of density | (iv) m s-1 |
| (e) S.I. unit of speed | (v) measuring cylinder |
Answer
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| (a) Volume of a liquid | (v) measuring cylinder |
| (b) Area of a leaf | (iii) graph paper |
| (c) S.I. unit of volume | (ii) m3 |
| (d) S.I. unit of density | (i) kg m-3 |
| (e) S.I. unit of speed | (iv) m s-1 |
Question 4a
Select the correct alternative:
One litre is equal to:
- 1 cm3
- 1 m3
- 10-3 cm3
- 10-3 m3
Answer
10-3 m3
Reason — 1 litre = 10-3 m3
Question 4b
Select the correct alternative:
A metallic piece displaces water of volume 15 mL. The volume of piece is:
- 15 cm3
- 15 m3
- 15 x 103 cm-3
- 15 x 103 cm3
Answer
15 cm3
Reason — Volume of body is equal to volume of liquid displaced = 15 mL.
1 mL = 1 cm3, so 15 mL = 15 cm3.
Question 4c
Select the correct alternative:
A piece of paper of dimensions 1.5 m x 20 cm has area:
- 30 m2
- 300 cm2
- 0.3 m2
- 3000 m3
Answer
0.3 m2
Reason — 20 cm = 0.2 m
Area of paper = 1.5 m x 0.2 m = 0.3 m2
Question 4d
Select the correct alternative:
The correct relation is:
- d = M x V
- M = d x V
- V = d x M
- d = M + V
Answer
M = d x V
Reason — Mass = Volume x density
Question 4e
Select the correct alternative:
The density of alcohol is 0.8 g cm-3. In S.I. unit, it will be:
- 0.8 kg m-3
- 0.0008 kg m-3
- 800 kg m-3
- 8 x 103 kg m-3
Answer
800 kg m-3
Reason — 1 g cm-3 = 1000 kg m-3
So 0.8 g cm-3 = 800 kg m-3
Question 4f
Select the correct alternative:
The density of aluminium is 2.7 g cm-3 and of brass is 8.4 g cm-3. For the same mass, the volume of:
- both will be same
- aluminium will be less than that of brass
- aluminium will be more than that of brass
- nothing can be said
Answer
aluminium will be more than that of brass
Reason — For a given mass of a substance, volume is inversely proportional to density. As density of aluminium is less than that of brass, so volume of aluminium will be more than that of brass.
Question 4g
Select the correct alternative:
A block of wood of density 0.8 g cm-3 has a volume of 60 cm3. The mass of block will be:
- 60.8 g
- 75 g
- 48 g
- 0.013 g
Answer
48 g
Reason — Mass = density x volume
= 0.8 x 60
= 48 g
So, mass of block is 48 g.
Question 4h
Select the correct alternative:
The correct relation for speed is:
Speed = distance x time
Speed =
Speed =
Speed =
Answer
Speed =
Reason — Speed of a body =
Question 4i
Select the correct alternative:
A boy travels a distance 150 m in 1 minute. His speed is:
- 150 m s-1
- 2.5 m s-1
- 25 m s-1
- 9 m s-1
Answer
2.5 m s-1
Reason — time = 1 min = 60 sec, distance = 150 m Speed = 2.5 m s-1
Short/Long Answer Questions
Question 1
Define the term volume of an object.
Answer
The space occupied by an object is called its volume.
Question 2
State and define the S.I. unit of volume.
Answer
The S.I. unit of volume is cubic metre (m3). One cubic metre is the volume of a cube with each side 1 metre long.
Question 3
State two smaller units of volume. How are they related to the S.I. unit?
Answer
The two smaller units of volume are cubic centimetre (cm3), cubic decimetre (dm3).
1 m3 = 1 m x 1 m x 1 m
= 100 cm x 100 cm x 100 cm
= 1000000 cm3
= 106 cm3
So, 1 m3 = 106 cm3
1 m3 = 1 m x 1 m x 1 m
= 10 dm x 10 dm x 10 dm
= 1000 dm3
= 103 dm3
So, 1 m3 = 103 dm3
Question 4
How will you determine the volume of a cuboid? Write the formula you will use.
Answer
The volume of a cuboid is determined by finding its three dimensions i.e., length, breadth and height.
The formula for volume of cuboid is length x breadth x height
Question 5
Name two devices which are used to measure the volume of an object. Draw their neat diagrams.
Answer
The two devices which are used to measure the volume of an object are:
- Measuring cylinder

- Measuring beaker

Question 6
How can you determine the volume of an irregular solid (say a piece of brass)? Describe in steps with neat diagrams.
Answer
The volume of an irregular solid can be measured by using a measuring cylinder by the method of displacement of liquid.
- Place a measuring cylinder on a flat horizontal surface.
- Fill it partially with water.
- Note the reading of water level very carefully. Let it be V1.
- Now tie the piece of brass with a thread and dip it completely into water.
- The level of water rises. Note the reading of new water level V2. The difference in the two levels of water gives the volume of the piece of brass.
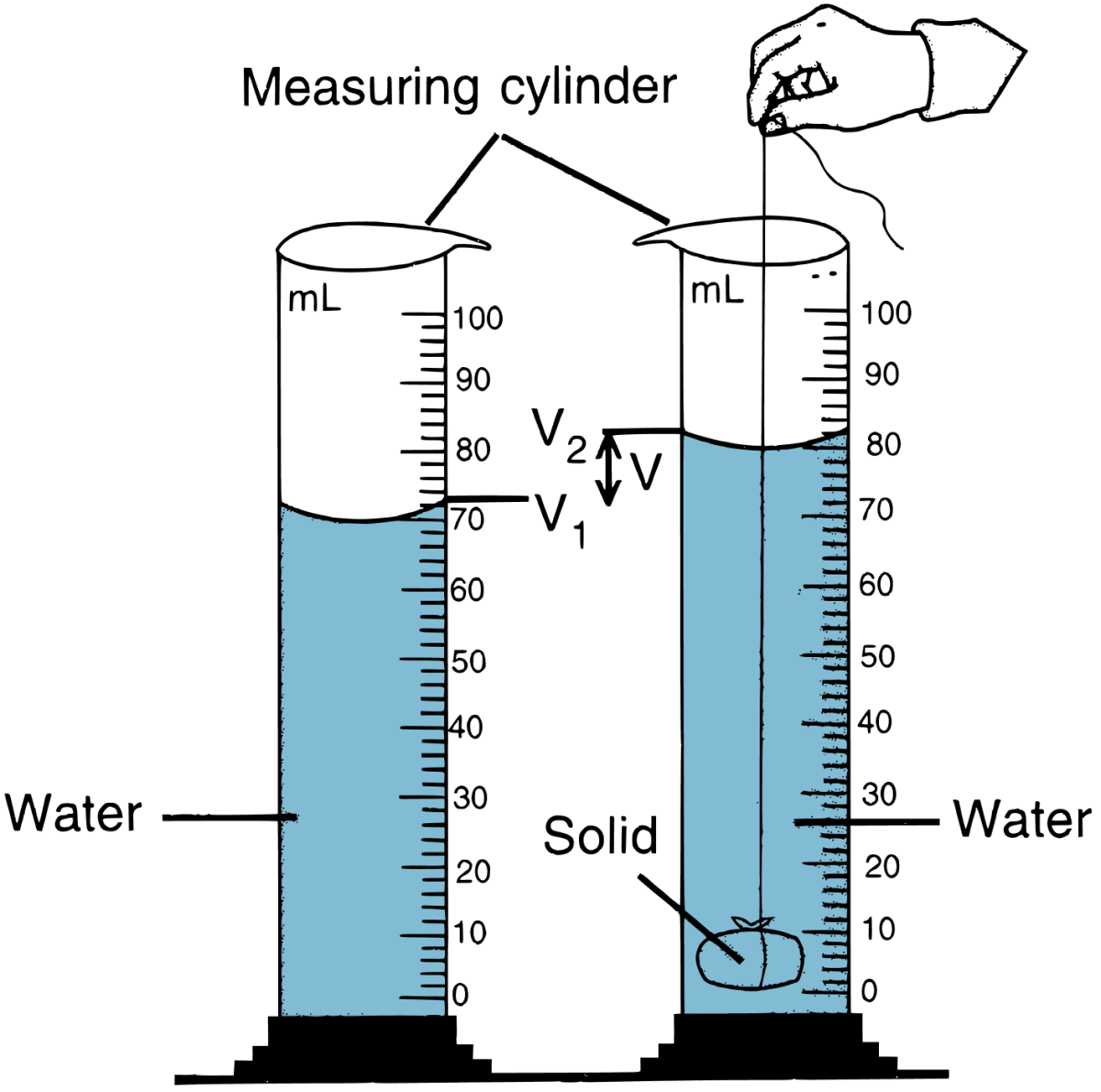
Question 7
You are required to take out 200 mL of milk from a bucket full of milk. How will you do it?
Answer
A measuring beaker of 200 mL is used to measure 200 mL of milk from a bucket full of milk.
- Take a measuring beaker of 200 mL, wash and dry it.
- Immerse the beaker inside the bucket full of milk.
- Fill the beaker completely with the milk.
- Take out the beaker from bucket gently so that no milk splashes out.
- Pour the milk from measuring beaker into another empty vessel.
Question 8
Describe the method in steps to find the area of an irregular lamina using a graph paper.
Answer
To find the area of an irregular lamina using a graph paper.
- Place the lamina over a graph paper.
- Draw its boundary line on the graph paper with a pencil.
- Remove the lamina.
- Count and note the number of complete squares, half squares and more than half squares within the boundary line. Ignore the squares which are less than half.
The sum of the areas of the number of complete squares and the number of incomplete squares gives the approximate area of the irregular object.
Question 9
Define the term density of a substance.
Answer
The density of a substance is defined as the mass of a unit volume of that substance.
Question 10
State the S.I. and C.G.S. units of density. How are they related?
Answer
The S.I. unit of density is kg m-3 and its C.G.S. unit is g cm-3.
1 g cm-3 = 1000 kg m-3.
Question 11
The density of brass is 8.4 g cm-3. What do you mean by the statement?
Answer
The statement means one cubic centimeter volume of brass has mass of 8.4 g.
Question 12
Arrange the following substances in order of their increasing density:
- iron
- cork
- brass
- water
- mercury
Answer
Cork < Water < Iron < Brass < Mercury.
Question 13
How does the density of water change when:
(a) it is heated from 0°C to 4°C,
(b) it is heated from 4°C to 10°C ?
Answer
(a) Water when heated from 0°C to 4°C, it contracts so density of water increases and becomes maximum at 4°C.
(b) When water is heated from 4°C to 10°C it expands, so density decreases.
Question 14
Write the density of water at 4°C.
Answer
The density of water at 4°C is 1 g cm-3 or 1000 kg m-3.
Question 15
Explain the meaning of the term speed.
Answer
Speed of the body is distance travelled by the body in unit time. It tells us about the motion of the body i.e. how fast or slow it is moving.
Question 16
Write the S.I. unit of speed.
Answer
The S.I. unit of speed is metre per second (m s-1).
Question 17
A car travels with a speed 12 m s-1, while a scooter travels with a speed 36 km h-1. Which of the two travels faster?
Answer
Speed of car = 12 m s-1
Speed of scooter = 36 km h-1
1 km h-1 = m s-1
36 km h-1 = 36 x = 10 m s-1
So speed of scooter = 10 m s-1
So car travels faster than scooter; since speed of car is more than that of scooter.
Numericals
Question 1
The length, breadth and height of a water tank are 5 m, 2.5 m and 1.25 m respectively. Calculate the capacity of the water tank in:
a. m3
b. litre
Answer
Length = 5 m; breadth = 2.5 m; height = 1.25 m
a. Volume of water tank = length x breadth x height = 5 m x 2.5 m x 1.25 m = 15.625 m3
So, capacity of water tank in m3 = 15.625 m3.
b. 1 m3 = 1000 L
15.625 m3 = 15.625 x 1000 = 15625 L
So, capacity of water tank in litres = 15,625 L.
Question 2
A solid silver piece is immersed in water contained in a measuring cylinder. The level of water rises from 50 mL to 62 mL. Find the volume of silver piece.
Answer
Initial level of water V1 = 50 mL
Final level of water V2 = 62 mL
Volume of silver piece = V2 - V1
= 62 - 50
= 12 mL = 12 cm3
So, volume of silver piece = 12 cm3.
Question 3
Find the volume of a liquid present in a dish of dimensions 10 cm x 10 cm x 5 cm.
Answer
Volume of dish = 10 cm x 10 cm x 5 cm = 500 cm3.
Volume of liquid is equal to volume of dish = 500 cm3.
1 cm3 = 1 mL
500 cm3 = 500 mL
So, volume of a liquid present in the dish = 500 mL.
Question 4
A rectangular field is of length 60 m and breadth 35 m. Find the area of the field.
Answer
Length = 60 m
Breadth = 35 m
Area of the field = Length x Breadth = 60 m x 35 m = 2100 m2.
So, area of the field = 2100 m2.
Question 5
Find the approximate area of an irregular lamina of which boundary line is drawn on the graph paper shown in figure below.
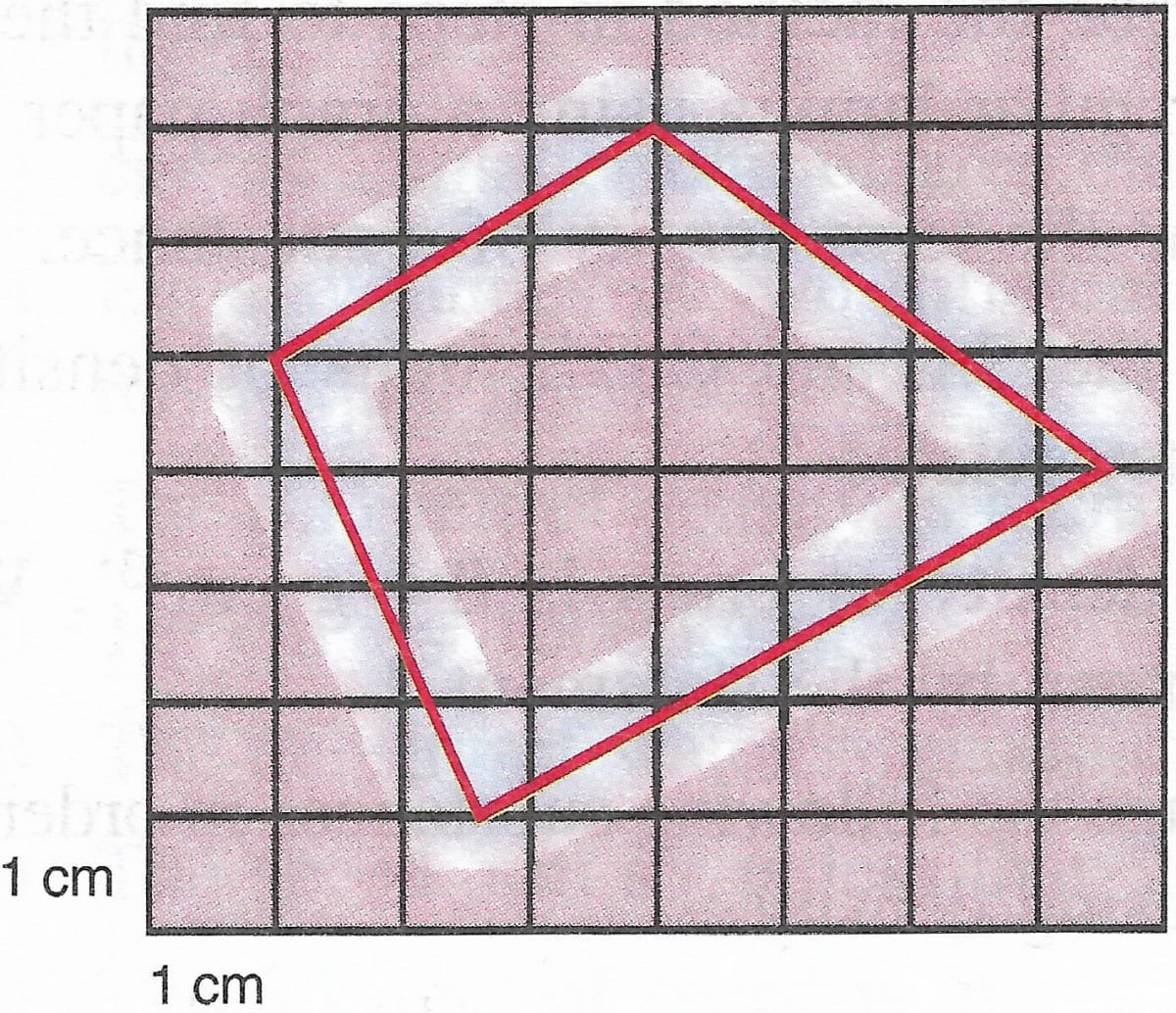
Answer
Number of complete squares = 11
Number of more than half squares = 8
Number of half squares = 2
Total number of squares = 11 + 8 + 2 = 21
Area of the square = 1 cm x 1 cm = 1 cm2
Area of 21 squares = 21 x 1 = 21 cm2
So, approximate area of lamina = 21 cm2.
Question 6
A piece of brass of volume 30 cm3 has a mass of 252 g. Find the density of brass in:
(i) g cm-3
(ii) kg m-3
Answer
Mass = 252 g
Volume = 30 cm-3
Density = ?
(i)
So, Density = 8.4 g cm-3.
(ii) 1 g cm-3 = 1000 kg m-3
8.4 g cm-3 = 8.4 x 1000 = 8400 kg m-3
So, Density = 8400 kg m-3.
Question 7
The mass of an iron ball is 312 g. The density of iron is 7.8 g cm-3. Find the volume of the ball.
Answer
Mass = 312 g
Density = 7.8 g cm-3
Volume = ?
So, volume of the ball is 40 cm3.
Question 8
A cork has a volume 25 cm3. The density of cork is 0.25 g cm-3. Find the mass of the cork.
Answer
Volume = 25 cm3
Density = 0.25 g cm-3
Mass = ?
So, mass of the cork is 6.25 g.
Question 9
The mass of 5 litre of water is 5 kg. Find the density of water in g cm-3.
Answer
Mass = 5 kg
Volume = 5 litre
Density = ?
Density = 1 kg litre-1
1 kg = 1000 g; 1 litre = 1000 cm3
1 kg litre-1 = = 1 g cm-3
So, density of water = 1 g cm-3.
Question 10
A cubical tank of side 1 m is filled with 800 kg of a liquid. Find:
(i) the volume of tank
(ii) the density of liquid in kg m-3.
Answer
Side = 1 m; mass = 800 kg
(i) Volume of cubical tank = (side)3 = (1 m)3 = 1 m3
So, volume of tank = 1 m3.
(ii)
So, density of liquid = 800 kg m-3.
Question 11
A block of iron has dimensions 2 m x 0.5 m x 0.25 m. The density of iron is 7.8 g cm-3. Find the mass of the block.
Answer
Density of iron = 7.8 g cm-3
1 g cm-3 = 1000 kg m-3
7.8 g cm-3 = 7.8 x 1000 = 7800 kg m-3
Volume of iron = 2 m x 0.5 m x 0.25 m = 0.25 m3
Mass = ?
So, mass of iron = 1950 kg.
Question 12
The mass of a lead piece is 115 g. When it is immersed into a measuring cylinder, the water level rises from 20 mL mark to 30 mL mark. Find:
(i) the volume of the lead piece,
(ii) the density of the lead in kg m-3.
Answer
(i) Mass = 115 g;
Initial volume V1 = 20 mL;
Final volume V2 = 30 mL;
Volume of lead piece = V2 - V1 = 30 - 20 = 10 mL
1 mL = 1 cm3
10 mL = 10 cm3
So, volume of the lead piece = 10 cm3.
(ii) Density = ?
1 g cm-3 = 1000 kg m-3
11.5 g cm-3 = 1000 x 11.5 = 11500 kg m-3
So, density of lead = 11500 kg m-3.
Question 13
The density of copper is 8.9 g cm-3. What will be its density in kg m-3?
Answer
1 g cm-3 = 1000 kg m-3
8.9 g cm-3 = 8.9 x 1000 = 8900 kg m-3
So, density of copper = 8900 kg m-3.
Question 14
A car travels a distance of 15 km in 20 minute. Find the speed of the car in:
(i) km h-1
(ii) m s-1
Answer
(i) distance = 15 km; time = 20 min
60 min = 1 hr
20 min = = h
So, speed of car = 45 km h-1.
(ii) distance = 15 km
1 km = 1000 m
15 km = 15 x 1000 = 15000 m
time = 20 min
1 min = 60 sec
20 min = 20 x 60 = 1200 sec
So, speed of car = 12.5 m s-1.
Question 15
How long a train will take to travel a distance of 200 km with a speed of 60 km h-1?
Answer
distance = 200 km; speed = 60 km h-1
time = ?
So, time taken by train will be 3 hrs 20 minutes.
Question 16
A boy travels with a speed of 10 m s-1 for 30 minute. How much distance does he travel?
Answer
Speed = 10 m s-1
time = 30 minutes
1 min = 60 sec
30 min = 60 x 30 = 1800 sec
distance = ?
So, distance travelled = 18000 m or 18 km.
Question 17
Express 36 km h-1 in m s-1.
Answer
1 km h-1 = m s-1
36 km h-1 = 36 x = 10 m s-1
So, 36 km h-1 = 10 m s-1.
Question 18
Express 15 m s-1 in km h-1.
Answer
1 m s-1 = 3.6 km h-1
15 m s-1 = 3.6 x 15 = 54 km h-1
So, 15 m s-1 = 54 km h-1.