Animal Tissues
Check your progress
Question 1
............... epithelium lines the blood vessels and forms the epidermis of the skin.
Answer
Squamous epithelium lines the blood vessels and forms the epidermis of the skin.
Question 2
............... epithelium is found in the thyroid gland.
Answer
Cuboidal epithelium is found in the thyroid gland.
Question 3
Voluntary muscles are also called ............... muscles.
Answer
Voluntary muscles are also called striated muscles.
Question 4
............... muscles cells have only one nucleus and have no striations.
Answer
Involuntary muscles cells have only one nucleus and have no striations.
Question 5
............... muscles work continuously and do not get tired.
Answer
Cardiac muscles work continuously and do not get tired.
Tick the most appropriate answer
Question 1
Voluntary muscles are
- cylindrical and branched
- cylindrical and unbranched
- spindle-shaped
- spherical
Answer
cylindrical and unbranched
Reason — Voluntary muscles are cylindrical and unbranched.
Question 2
The short thread-like branches arising from the cell body of a nerve cell are called
- cytons
- axons
- neurons
- dendrons
Answer
dendrons
Reason — The short thread-like branches arising from the cell body of a nerve cell are called dendrons, which further divide to form dendrites.
Question 3
The white fibrous tissue present in tendons joins
- bone to a bone
- muscles to a bone
- muscles to a muscles
- all of these
Answer
muscles to a bone
Reason — The tendons join the muscles to the bones.
Question 4
Cartilage cells lie in fluid-filled spaces called
- plasma
- stroma
- lacunae
- matrix
Answer
matrix
Reason — The cartilage cells are found dispersed in the the ground substance called matrix.
Question 5
These are the most abundant component of the blood.
- Platelets
- RBCs
- WBCs
- Lymph
Answer
RBCs
Reason— RBCs are the most abundant component of the blood.
Fill in the blanks
Question 1
Epithelial tissue consists of cells without any ............... spaces.
Answer
Epithelial tissue consists of cells without any intercellular spaces.
Question 2
............... muscles help in the movement of the limbs.
Answer
Skeletal muscles help in the movement of the limbs.
Question 3
The ............... or nerve fibres constitute the nerves.
Answer
The neurons or nerve fibres constitute the nerves.
Question 4
A ............... connects one bone to another.
Answer
A ligament connects one bone to another.
Question 5
............... tissue cushions and insulates the body.
Answer
Adipose tissue cushions and insulates the body.
Question 6
............... is a fluid connective tissue without red blood cells.
Answer
Lymph is a fluid connective tissue without red blood cells.
Define the following terms
Question 1
Voluntary muscles
Answer
Voluntary muscles — The muscles that are under our control and help in the movement of the bones are called voluntary muscles. For Example - muscles of hands and legs.
Question 2
Cardiac muscles
Answer
Cardiac muscles — The special type of involuntary muscles, present in heart, that work continuously without getting tired are called cardiac muscles.
Question 3
Connective tissue
Answer
Connective tissue — Connective tissues join different parts of the body and provide support to them. They also fill up the space between various organs.
Question 4
Connective tissue proper
Answer
Connective tissue proper — Connective tissue proper connects various parts of the body, like muscles to bones or bones to other bones and gives support by filling up spaces between the organs.
Question 5
Adipose tissue
Answer
Adipose tissue — The type of connective tissue which is primarily located beneath the skin, and is also found around the internal organs, providing cushion and insulation to the body is called adipose tissue.
Question 6
Cartilage
Answer
Cartilage — The highly elastic skeletal tissue that consists of a ground substance called matrix with cells is called Cartilage.
Write true or false. Correct the false statements
Question 1
Voluntary muscles are present in the internal organs of the body.
Answer
False
Corrected statement — Involuntary muscles are present in the internal organs of the body.
Question 2
Cardiac muscles have dark and light bands.
Answer
True
Question 3
The yellow fibrous tissue, a type of connective tissue, is found in ligaments.
Answer
True
Question 4
RBCs and WBCs are formed in the bone marrow.
Answer
True
Question 5
Most plant tissues are dead on maturity.
Answer
True
Differentiate between
Question 1
voluntary muscle and involuntary muscle.
Answer
| Sl. No. | Voluntary Muscle | Involuntary Muscle |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | These muscles are under our control. | These muscles are not under our control. |
| 2. | They help in the movement of the bones of limbs. | They are present in internal organs and help in movement of food, movement of urine from urinary bladder and so on. |
| 3. | The cells are long, cylindrical and unbranched. | The cells are spindle shaped. |
| 4. | They are multinucleate. | They are uninucleate. |
| 5. | They are striated. | The are unstriated. |
Question 2
tendon and ligament
Answer
| Sl. No. | Tendon | Ligaments |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | They are white fibrous tissue. | They are yellow fibrous tissue. |
| 2. | They connect muscles to the bones. | They connect bone to another bone. |
| 3. | They are strong and elastic. | They are strong but less elastic. |
Question 3
adipose tissue and areolar tissue.
Answer
| Sl. No. | Adipose Tissue | Areolar Tissue |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Located beneath the skin and around the internal organs. | Forms a continuous layer under the skin. |
| 2. | Stores energy in form of fat. | Binds the skin with underlying organs. |
| 3. | Cushions and insulates the body and provides protective padding around the organs. | Fills up the space between various organs and act as a packing material around them. |
Question 4
bone and cartilage
Answer
| Sl. No. | Bone | Cartilage |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | It consists of the ground substance or matrix that is filled with cells called osteocytes and various inorganic compounds. | It consists of ground substance called matrix that contains cartilage cells. |
| 2. | It is hard tissue. | It is highly elastic and less harder than bone. |
| 3. | It supports the body and help in the movement of body parts. | It protects the bones from the shock and reduces friction between bones |
Question 5
red blood cells and white blood cells
Answer
| Sl. No. | Red Blood Cells | White Blood Cells |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Red Blood Cells are red in colour due to presence of haemoglobin. | White Blood Cells are colourless. |
| 2. | Red Blood Cells are produced in bone marrow. | White Blood Cells are produced in bone marrow as well as lymph nodes. |
| 3. | Red Blood Cells carry oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from various parts of the body to the lungs. | White Blood Cells fight against infections. |
| 4. | Red Blood Cells are disc shape and without nucleus. | White Blood Cells are irregular and have large nucleus. |
| 5. | Red Blood Cells are small. | White Blood Cells are larger. |
Find the odd one out. Give reasons for your answers
Question 1
lymph, white fibrous tissue, yellow fibrous tissue, areolar tissue
Answer
lymph
Reason — Lymph is a fluid connective tissue while others are connective tissue proper.
Question 2
tendon, squamous epithelium, ligament, bone
Answer
Squamous epithelium
Reason — Squamous epithelium is epithelial tissue while others are connective tissue.
Question 3
thrombocytes, erythrocytes, epithelium, leucocytes
Answer
epithelium
Reason — Thrombocytes, erythrocytes and leucocytes are components of blood whereas epithelium is epithelial tissue.
Answer the following in short
Question 1
Write any two functions of epithelial tissues.
Answer
Two functions of epithelial tissues:
- They provide protection and prevent the entry of germs.
- They are specialized to secrete enzymes as in salivary gland.
Question 2
Explain the structure and function of a neuron.
Answer
Neuron has a central part called the cell body or cyton. Many thread-like branches extend from the cyton. These thread-like branches extending from all sides of the cell body are called dendrons. Dendrons further divide to form dendrites. One of these extensions is longer than the rest and is called the axon. Functions of neuron:
- Neuron help in the control and coordination of the body.
- The information or message is transmitted by a neuron in the form of impulses and in one direction only.
- Many neurons or nerve fibres bound together constitute a nerve.
Question 3
What is the difference between a white fibrous tissue and a yellow fibrous tissue?
Answer
| Sl. No. | White Fibrous Tissue | Yellow Fibrous Tissue |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | White Fibrous Tissue are found in the tendons. | Yellow Fibrous Tissue are found in the ligaments |
| 2. | White Fibrous Tissue connect muscles to the bones. | Yellow Fibrous Tissue connect bone to another bone. |
| 3. | White Fibrous Tissue have considerable strength and high elasticity. | Yellow Fibrous Tissue are strong but less elastic. |
Answer the following in detail
Question 1
Name the various types of animal tissues and state their functions.
Answer
The animal tissues are of following types:
- Epithelial Tissue— They are further classified as follows:
- Squamous epithelium — It protects the body and the organs from injury and entry of germs.
- Columnar epithelium — They are present in the linings of the stomach, intestines and pharynx. They are specialized to absorb nutrients.
- Cuboidal epithelium — They are found in thyroid gland, kidney tubules, salivary gland, pancreas and liver. They are specialized to secrete enzymes and hormones and remove waste (as in kidneys).
- Muscular tissue— They are of following types:
- Voluntary muscles — These muscles help in the movement of the bones.
- Involuntary muscles — These muscles are not under our control or will. They help in movement of food, movement of urine from urinary bladder and so on.
- Cardiac muscles — Cardiac muscles cause the rhythmic movement of the heart resulting in circulation of blood in the body.
- Nervous tissues— Nervous tissues help in the control and coordination of the body. The information or message is transmitted by a neuron in the form of impulses and in one direction only.
- Connective tissue— They are further classified into following types:
- Connective tissue proper — This tissue connects various parts of the body. It connects muscles to bones, bones to other bones and gives support by filling up spaces between the organs.
- Skeletal tissue — It is solid connective tissue which provide support to the body. It constitutes of bone and cartilage.
- Fluid connective tissue — It is the liquid connective tissue consisting of blood and lymph. It has functions like transportation of oxygen and nutrients and fighting infection.
Question 2
Explain the structure and functions of various types of epithelial tissue.
Answer
On the basis of shape of the cells, epithelial tissues are classified into three types :
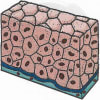
- Squamous epithelium — The cells of squamous epithelium are flat, hexagonal or irregular in shape. These cells line the inner walls of the blood vessels, lungs, heart and oesophagus. They also form the epidermis of the skin, where they provide protection and prevent the entry of germs.
Below diagram shows the structure of Squamous epithelium:

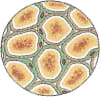
- Columnar epithelium — The length of the cells of Columnar epithelium appears much more than their width. The cells are placed side by sides like columns. The nucleus is present towards the base of the cell. They are present in the linings of the stomach, intestines and pharynx. They are specialized to absorb nutrients.
Below diagram shows the structure of Columnar epithelium:

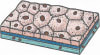
- Cuboidal epithelium — The cells of Cuboidal epithelium have almost equal height and width. The nucleus is centrally located. They are found in thyroid gland, kidney tubules, salivary gland, pancreas and liver. They are specialized to secrete enzymes and hormones and remove waste (as in kidneys).
Below diagram shows the structure of Cuboidal epithelium:

Question 3
Describe the types of muscular tissue with examples.
Answer
Based on the structure and functions performed muscular tissues are of three types — Voluntary muscles, Involuntary muscles and Cardiac muscles.
- Voluntary muscles — These muscles are under our control or will. For example, we can control the muscles in our arms and legs when we run, walk or jump. These muscles are also called skeletal muscles as they are attached to the bones. These muscles help in the movement of the bones. The cells of these muscles are long and cylindrical with many nuclei and dark and light bands called striations. Hence, they are also called striated muscles.
- Involuntary muscles — They are present in the internal organs of our body like stomach, intestine, bladder etc. They are not under our control. The cells of these muscles are spindle-shaped and have only one nucleus. They do not have any bands or striations, hence these are also called unstriated muscles.
- Cardiac muscles — The heart is made up of special type of involuntary muscles called cardiac muscles. Cardiac muscles works continuously without getting tired. Structurally, these muscles resemble voluntary muscles . However, cardiac muscles are similar to involuntary muscles in their function.
Question 4
Describe connective tissue. How is it different from other tissues?
Answer
The connective tissue consists of cells with spaces between them. These spaces are filled with a matrix or ground substance. The living cells produce the non-living matrix, which could be a liquid (in blood), semi-solid (connective tissue proper) or solid (bone). The connective tissues join different parts of the body and provide support to them. They also fill up the space between various organs. They are further classified into following types:
- Connective tissue proper — This tissue connects various parts of the body. It connects muscles to bones, bones to other bones and gives support by filling up spaces between the organs.
- Skeletal tissue — It is solid connective tissue which provide support to the body. It constitutes of bone and cartilage.
- Fluid connective tissue — It is the liquid connective tissue consisting of blood and lymph. It has functions like transportation of oxygen and nutrients and fighting infection.
The connective tissue is different from other tissues because it has cells that are separated from each other. The space between the cells is composed of different intercellular substances that form the matrix or ground substance.
Table showing animal tissues
Question 1
Given below is a table showing animal tissues. Identify them, give their location and write one important function of each.
Answer
Identify diagrams and label parts
Question 1
Identify the following diagrams and label the parts marked.



Answer
The labelled diagrams are shown below:



Correctly label nerve cell
Question 1
Some of the parts of the nerve cell are marked incorrectly. Write the correct names in the space provided.

Answer
The correctly labelled nerve cell is shown below:

Identify blood cells
Question 1
Identify the types of cells present in the blood.



Answer

Red Blood Cells

White Blood Cells

Blood Platelets
Think and answer
Question 1
On the basis of the clues given, identify the following tissues in humans:
- The length of the cells of this tissue appears much more than their breadth. These cells are found in the lining of the stomach and intestines.
- It is a special type of involuntary muscle. These muscles work continuously and do not get tired.
- This tissue is primarily located beneath the skin, but also found around internal organs. Its main function is to store energy and provide protective padding around organs.
Answer
- Columnar epithelium tissue
- Cardiac Muscles
- Adipose tissue