Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere
Choose the correct option
Question 1
The blanket of air surrounding the earth is known as the:
- Ozone layer
- Nitrogen layer
- Lithosphere
- Atmosphere
Answer
Atmosphere
Question 2
A clean dry sample of air is made up of ............... percent nitrogen:
- 72
- 77
- 78
- 79
Answer
78
Question 3
About 90 percent of air mass lies within about ............... from the earth's surface.
- 20 km
- 22 km
- 25 km
- 30 km
Answer
20 km
Question 4
Name the densest layer of the atmosphere.
- Exosphere
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
Answer
Troposphere
Question 5
Name the layers as we move from space to the surface of the earth.
- Thermosphere - Mesosphere - Stratosphere - Troposphere
- Troposphere - Mesosphere - Stratosphere - Thermosphere
- Troposphere - Stratosphere - Mesosphere - Thermosphere
- Thermosphere - Stratosphere - Mesosphere - Troposphere
Answer
Thermosphere - Mesosphere - Stratosphere - Troposphere
Question 6
Which amongst the following is not a domain of the Biosphere?
- Lithosphere
- Exosphere
- Hydrosphere
- Atmosphere
Answer
Exosphere
Question 7
.............. extends up to a height of about 400 km:
- Mesosphere
- Ionosphere
- Stratosphere
- Troposphere
Answer
Ionosphere
Question 8
The upper limit of the stratosphere is known as:
- Stratopause
- Statapause
- Upper strata
- Upper limital strata
Answer
Stratopause
Question 9
What is the uppermost layer in the structure of the atmosphere?
- Ionosphere
- Exosphere
- Troposphere
- Mesosphere
Answer
Exosphere
Question 10
Water vapour is added to the atmosphere by ................ .
- evaporation
- transpiration
- respiration
- All of the above
Answer
All of the above
Question 11
Which of the following are the functions of the atmosphere?
- Facilitates the cyclic exchange of gases
- Maintain of optimum temperature
- Protects the earth from harmful solar radiation
- All of the above.
Answer
All of the above
Question 12
The decrease in the temperature is known as the:
- Normal temperature rate
- Decreased temperature rate
- Normal lapse rate
- Decreased lapse rate
Answer
Normal lapse rate
Question 13
What contains electrically charged particles called ions which create a sheet like display of light known as Aurora Borealis?
- Ionosphere
- Exosphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
Answer
Ionosphere
Question 14
Which amongst the following is not an impact of Global Warming?
- Precipitation Change
- Radiation Balance
- Rise in Sea Level
- Diseases
Answer
Radiation Balance
Short Answer Questions
Question 1
What is known as atmosphere? State the composition of the atmosphere.
Answer
The blanket of air surrounding the Earth is known as the atmosphere.
he atmosphere is a mixture of many gases and tiny solid particles. Atmosphere contains-
- 78% nitrogen gas
- 21% oxygen gas
- The remaining 1% of air is made up of Carbon dioxide, Water Vapour, Helium, Hydrogen, Argon etc.
Question 2
Name the four layers of the atmosphere. Give one function of the outer most layer.
Answer
The four layers of the atmosphere are-
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
Thermosphere is the outermost layer of the atmosphere where the satellites orbit the earth.
Question 3
What is known as troposphere? List any two characteristics of the troposphere.
Answer
The troposphere is the lowermost and densest layer of the atmosphere. Its height varies from 18 km at the equator to 8 km at the poles.
Two characteristics of the troposphere are:
- Seventy-five per cent of the atmosphere is found in the troposphere and its concentration decreases as we go higher from ground level.
- The troposphere is heated more from below than from above.
Question 4
Mention the chief characteristics of stratosphere.
Answer
The chief characteristics of stratosphere are-
- The air is thin, cold and dry. The temperature is about -55°C.
- The Ozone layer lies within the stratosphere. Ozone is generally found between the altitudes of 20 and 50 km.
- Ozone absorbs the ultraviolet solar radiation coming from above. The insolation received from the Sun is equal to that lost by it. That is why the temperature of the layer is constant. In the higher levels, however, temperature increases with height.
- The lower layer of the stratosphere has a virtual absence of water vapour and has constant temperature conditions, therefore, it is ideal for flying jet aircraft.
- Temperature rises from -60°C at the base of the stratosphere to 0°C at stratopause.
- The upper limit of the stratosphere is known as stratopause.
Question 5
In which layer of atmosphere do all the weather conditions occur? Name the constituent gases of atmosphere which scientists consider responsible for climate change.
Answer
All the weather conditions occur in the troposphere.
The constituent gases of atmosphere which scientists consider responsible for climate change are Carbon dioxide, Methane, Chlorofluorocarbons, Ozone and Water Vapour.
Question 6
What is known as Ozone Layer? What is leading to depletion of Ozone Layer in the atmosphere?
Answer
Ozone layer is a layer in the stratosphere of the atmosphere which keeps temperature constant in the lower levels and absorbs ultraviolet rays of the Sun.
Many chemicals like Chlorine, Bromine and Chlorofluorocarbons are leading to depletion of Ozone Layer in the atmosphere. Chlorofluorocarbon compounds escape into the atmosphere and finally break down in the Stratosphere. They produce Chlorine atoms which destroy the Ozone layer.
Sulphur dioxide given out during volcanic eruptions, solar storms and human activities also lead to depletion of Ozone layer.
Question 7
What would be the effect of Ozone Layer depletion? List the natural causes of Ozone Layer depletion.
Answer
The effects of ozone layer depletion are as follows:
- Increased levels of harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation reaching the Earth's surface.
- Ultraviolet radiation can lead to skin cancer, eye damage, cataracts and weakened immune systems.
- It can cause damage to marine ecosystems.
- Increased UV radiation can harm crops, leading to reduced agricultural productivity and food scarcity.
- It can affect biogeochemical cycles, including those of nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon.
- It can influence climate patterns, altering atmospheric temperatures and precipitation levels.
The natural causes of ozone layer depletion are volcanic eruptions and solar flares.
Question 8
What is known as Global Warming? Name important Greenhouse gases.
Answer
The rise in average mean temperature of the Earth on account of enhanced concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is known as global warming.
Some important Greenhouse gases are Carbon dioxide, Methane, Chlorofluorocarbons, Ozone and Water Vapour.
Structured Questions
Question 1(a)
Define atmosphere. Name the four layers of atmosphere.
Answer
The blanket of air surrounding the Earth is known as the atmosphere.
The four layers of the atmosphere are-
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
Question 1(b)
Mention any two functions of the atmosphere.
Answer
Two functions of the atmosphere are-
- It protects the Earth from the harmful ultraviolet and infrared rays of the Sun.
- It helps in retaining the necessary warmth on the Earth.
Question 1(c)
Give a reason for each of the following:
(i) We find it difficult to breathe when we climb mountains.
(ii) The atmosphere is the most dynamic entity.
(iii) All the weather phenomena takes place in the troposphere.
Answer
(i) We find it difficult to breathe when we climb mountains because the layers of atmosphere become thinner at high altitudes. This means that there is less pressure to push the air into the lungs and a lower percentage of Oxygen in the air. This makes it harder to breath.
(ii) The atmosphere is the most dynamic entity because of its composition. Large masses of air are being moved up and down and across the surface of the Earth.
(iii) The troposphere is characterised by regular decrease in temperature with altitude. This decrease in temperature is known as normal lapse rate. The average decrease is 1°C for every 166 metre altitude gain. This temperature variation is responsible for many turbulences which result in all weather phenomena taking place in the troposphere.
Question 1(d)
Draw a well labelled diagram of the structure of the Earth's atmosphere.
Answer
Below diagram shows the structure of the Earth's atmosphere:

Question 2(a)
Describe the structure of the atmosphere.
Answer
The atmosphere consists of concentric layers of air. On the basis of the characteristics of temperature and air pressure, it can be divided into four thermal layers — Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere and Thermosphere. The Thermosphere is divided into Ionosphere and Exosphere. The four layers are briefly described below:
- Troposphere — It is the lowermost and densest layer. Its height varies from 18 km at the Equator to 8 km at the Poles.
- Stratosphere — This layer lies above the Troposphere. It extends to a height of 50 km from sea level.
- Mesosphere — This layer lies above the Stratosphere. It extends to a height of 80 km from ground level.
- Thermosphere — It lies above Mesosphere and consists of two parts:
- Ionosphere — It extends up to a height of about 400 km.
- Exosphere — It is the uppermost layer of the atmosphere. It lies between 400 to 1500 km above the earth.
Question 2(b)
Explain the factors responsible for depletion of Ozone in atmosphere.
Answer
The factors responsible for depletion of Ozone in atmosphere are-
- Chemicals like Chlorine and Bromine
- Chlorofluorocarbon gases used in refrigerators, aircraft and air conditioners. CFC compounds escape into the atmosphere and finally break down in the stratosphere, producing Chlorine atoms which destroy the Ozone layer.
- Sulphur dioxide given out during volcanic eruptions, speeds up destructive chemical reactions.
- Solar storms consist of coronal mass ejections and solar flares associated with explosions on the surface of the Sun. They also cause Ozone layer depletion.
- Human activities also result in Ozone layer depletion. Due to bitterly cold Antarctic winter, the stratospheric ice clouds promote the production of chemically active Chlorine and Bromine. This leads to Ozone destruction when sunlight returns in the Antarctic spring.
Question 2(c)
State any three factors that lead to Global Warming.
Answer
Three factors that lead to Global Warming are-
- Destruction of Ozone layer
- Greenhouse effect in the atmosphere
- Deforestation
Question 2(d)
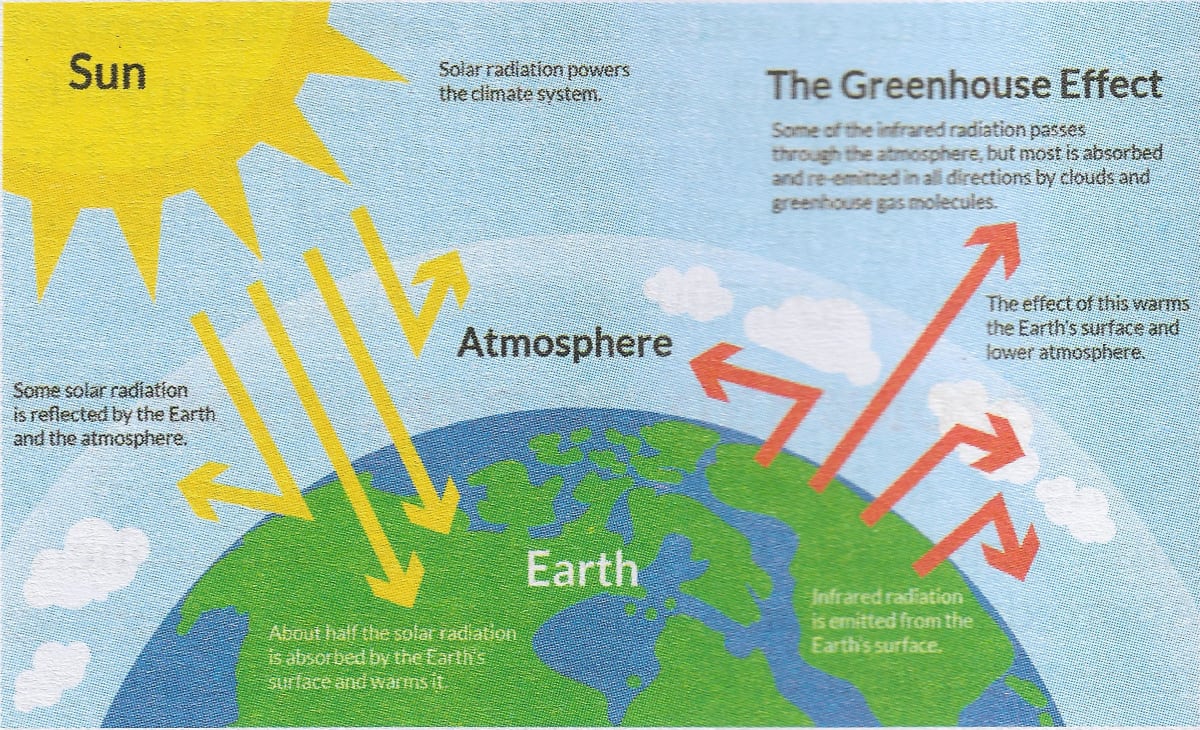
Draw a well labelled diagram to explain the Greenhouse Effect.
Answer
Below diagram shows the Greenhouse Effect:
Thinking Skills
Question 1
Do you think any one layer of the atmosphere is more significant than the other layers? If yes, which one and why? If not, reasons to support your answer.
Answer
No single layer of the atmosphere can be considered more significant than the others. Each layer plays a unique and important role in the functioning of the Earth's atmosphere.
All the layers of the atmosphere are interconnected and work together to create a balanced and supportive environment for life on Earth. The layers include the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere, each with distinct characteristics and functions.
The troposphere, closest to the Earth's surface, is crucial for weather patterns and the sustenance of life. The stratosphere contains the ozone layer, which protects against harmful ultraviolet radiation. The mesosphere helps protect the Earth from meteoroids. The thermosphere is responsible for the absorption of solar radiation. The exosphere extends into space and allows gases to gradually dissipate.
Therefore, all layers of the atmosphere are essential for maintaining a stable climate, protecting life from harmful radiation, facilitating weather patterns, and supporting the overall functioning of the Earth's ecosystem.
Question 2
How is atmosphere responsible for Global Warming? What changes human beings can make in their lifestyle to preserve the atmosphere and check Global Warming?
Answer
The atmosphere plays a significant role in global warming due to the greenhouse effect. Certain gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), trap heat from the sun, leading to an increase in the Earth's temperature.
To preserve the atmosphere and mitigate global warming, humans can make the following lifestyle changes:
- Reduce Carbon Footprint — Minimize the use of fossil fuels by opting for sustainable transportation. Choosing energy-efficient appliances and renewable energy sources like solar or wind power will also help.
- Conserve Energy — Practice energy-saving habits such as turning off lights and appliances when not in use, using natural lighting, and optimizing heating and cooling systems.
- Promote Sustainable Agriculture — Support local and organic farming practices that minimize the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, reduce food waste, and prioritize sustainable food choices.
- Conserve Water — Use water efficiently by fixing leaks, employing water-saving devices, and practicing responsible water consumption habits.
- Adopt Waste Management Practices — Reduce, reuse, and recycle materials to minimize waste generation. Properly dispose of hazardous materials and support recycling initiatives.
Question 3
Mention one significant effect of climate change that affects you.
Answer
One significant effect of climate change that affects me is the increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. This includes events such as hurricanes, cyclones, floods, heatwaves, and droughts. These extreme weather events can cause significant damage to infrastructure, disrupt livelihoods, lead to loss of life, and result in economic hardships for affected communities.