Input In Java
a package needed to import scanner class
java.util
a method that accepts a character through scanner object
charAt()
a package needed to import Stream Reader Class
java.io
a method to accept an exponential value through scanner object
nextDouble()
a method that accepts an integer token through scanner object
nextInt()
to accept an integral value 'p' through Stream Class
InputStreamReader read = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(read);
int p = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());to accept a fractional value (float) 'm' through Scanner Class
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
float m = in.nextFloat();to accept a character 'd' through Stream Class
InputStreamReader read = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(read);
char d = (char)in.read();to accept a fraction value 'n' in double data type through Stream Class
InputStreamReader read = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(read);
double n = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());to accept a word 'wd' through Stream Class
InputStreamReader read = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(read);
String wd = in.readLine();to create a scanner object
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);nextInt( ) and nextFloat( ) methods
| nextInt( ) | nextFloat( ) |
|---|---|
| Scans the next token of input as an int | Scans the next token of input as a float |
Syntax and logical errors
| Syntax Errors | Logical Errors |
|---|---|
| Syntax Errors occur when we violate the rules of writing the statements of the programming language. | Logical Errors occur due to our mistakes in programming logic. |
| Program fails to compile and execute. | Program compiles and executes but doesn't give the desired output. |
| Syntax Errors are caught by the compiler. | Logic errors need to be found and corrected by the people working on the program. |
What do you mean by scanner class?
Scanner class is used to get user input. It is present in java.util package.
What are the different ways to give inputs in a Java Program?
Java provides the following ways to give input in a program:
- Using Function Argument.
- Using InputStreamReader class.
- Using Scanner class.
- Using Command Line Arguments.
What is the use of the keyword import?
import keyword is used to import built-in and user-defined packages into our Java program.
What is a package? Give an example.
In Java, a package is used to group related classes. Packages are of 2 types:
- Built-In packages — These are provided by Java API
- User-Defined packages — These are created by the programmers to efficiently structure their code.
java.util, java.lang are a couple of examples of built-in packages.
What is the use of the keyword 'import' in Java programming?
import keyword is used to import built-in and user-defined packages into our Java program.
What is a compound statement? Give an example.
Two or more statements can be grouped together by enclosing them between opening and closing curly braces. Such a group of statements is called a compound statement.
if (a < b) {
/*
* All statements within this set of braces
* form the compound statement
*/
System.out.println("a is less than b");
a = 10;
b = 20;
System.out.println("The value of a is " + a);
System.out.println("The value of b is " + b);
}
Write down the syntax to input a character through scanner class with an example.
Syntax:
char <variable name> = <Scanner Object>.next().charAt(0);Example:
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
char ch = in.next().charAt(0);What do you understand by 'Run Time' error? Explain with an example
Errors that occur during the execution of the program primarily due to the state of the program which can only be resolved at runtime are called Run Time errors.
Consider the below example:
import java.util.Scanner;
class RunTimeError
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
int result = 100 / n;
System.out.println("Result = " + result);
}
}This program will work fine for all non-zero values of n entered by the user. When the user enters zero, a run-time error will occur as the program is trying to perform an illegal mathematical operation of division by 0. When we are compiling the program, we cannot say if division by 0 error will occur or not. It entirely depends on the state of the program at run-time.
What are the different types of errors that take place during the execution of a program?
Logical errors and Run-Time errors occur during the execution of the program.
Distinguish between:
(a) Testing and Debugging
| Testing | Debugging |
|---|---|
| In the process of Testing, we check if the program is working as expected and find out the errors if it is not giving the expected output. | In the process of Debugging, we correct the errors that were found during testing. |
(b) Syntax error and Logical error
| Syntax Error | Logical Error |
|---|---|
| Syntax Errors occur when we violate the rules of writing the statements of the programming language. | Logical Errors occur due to our mistakes in programming logic. |
| Program fails to compile and execute. | Program compiles and executes but doesn't give the desired output. |
| Syntax Errors are caught by the compiler. | Logical errors need to be found and corrected by people working on the program. |
The time period of a Simple Pendulum is given by the formula:
T = 2π√(l/g)
Write a program to calculate the time period of a Simple Pendulum by taking length and acceleration due to gravity (g) as inputs.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSimplePendulum
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter length: ");
double l = in.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter g: ");
double g = in.nextDouble();
double t = 2 * (22.0 / 7.0) * Math.sqrt(l/g);
System.out.println("T = " + t);
}
}
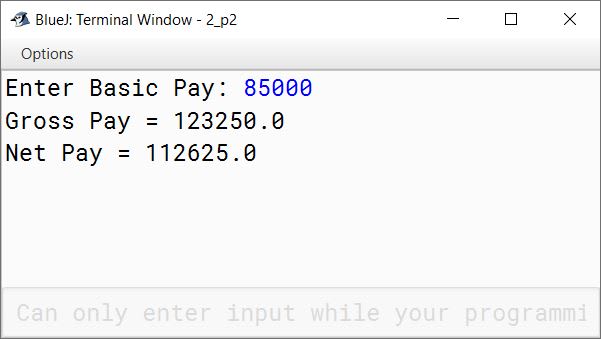
Write a program by using class 'Employee' to accept Basic Pay of an employee. Calculate the allowances/deductions as given below.
| Allowance / Deduction | Rate |
|---|---|
| Dearness Allowance (DA) | 30% of Basic Pay |
| House Rent Allowance (HRA) | 15% of Basic Pay |
| Provident Fund (PF) | 12.5% of Basic Pay |
Finally, find and print the Gross and Net pay.
Gross Pay = Basic Pay + Dearness Allowance + House Rent Allowance
Net Pay = Gross Pay - Provident Fund
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Employee
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter Basic Pay: ");
double bp = in.nextDouble();
double da = 0.3 * bp;
double hra = 0.15 * bp;
double pf = 0.125 * bp;
double gp = bp + da + hra;
double np = gp - pf;
System.out.println("Gross Pay = " + gp);
System.out.println("Net Pay = " + np);
}
}
A shopkeeper offers 10% discount on the printed price of a Digital Camera. However, a customer has to pay 6% GST on the remaining amount. Write a program in Java to calculate the amount to be paid by the customer taking printed price as an input.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatCameraPrice
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter printed price of Digital Camera:");
double mrp = in.nextDouble();
double disc = mrp * 10 / 100.0;
double price = mrp - disc;
double gst = price * 6 / 100.0;
price += gst;
System.out.println("Amount to be paid: " + price);
}
}
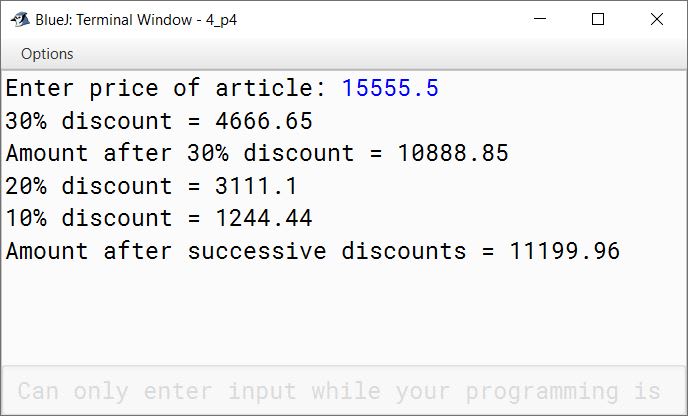
A shopkeeper offers 30% discount on purchasing articles whereas the other shopkeeper offers two successive discounts 20% and 10% for purchasing the same articles. Write a program in Java to compute and display the discounts.
Take the price of an article as the input.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatDiscounts
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter price of article: ");
double price = in.nextDouble();
double d1 = price * 30 / 100.0;
double amt1 = price - d1;
System.out.println("30% discount = " + d1);
System.out.println("Amount after 30% discount = " + amt1);
double d2 = price * 20 / 100.0;
double amt2 = price - d2;
double d3 = amt2 * 10 / 100.0;
amt2 -= d3;
System.out.println("20% discount = " + d2);
System.out.println("10% discount = " + d3);
System.out.println("Amount after successive discounts = " + amt2);
}
}
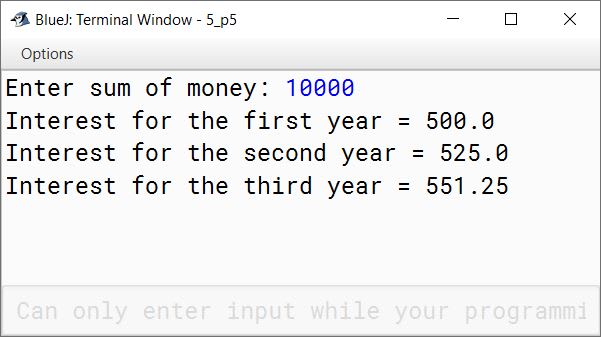
Mr. Agarwal invests certain sum at 5% per annum compound interest for three years. Write a program in Java to calculate:
(a) the interest for the first year
(b) the interest for the second year
(c) the amount after three years.
Take sum as an input from the user.
Sample Input: Principal = ₹5000, Rate =10%, Time = 3 yrs
Sample Output: Interest for the first year: ₹500
Interest for the second year: ₹550
Interest for the third year: ₹605
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatCompoundInterest
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter sum of money: ");
double p = in.nextDouble();
double interest = p * 5 * 1 / 100.0;
System.out.println("Interest for the first year = " + interest);
p += interest;
interest = p * 5 * 1 / 100.0;
System.out.println("Interest for the second year = " + interest);
p += interest;
interest = p * 5 * 1 / 100.0;
System.out.println("Interest for the third year = " + interest);
}
}
A businessman wishes to accumulate 3000 shares of a company. However, he already has some shares of that company valuing ₹10 (nominal value) which yield 10% dividend per annum and receive ₹2000 as dividend at the end of the year. Write a program in Java to calculate the number of shares he has and how many more shares to be purchased to make his target.
Hint: No. of share = (Annual dividend * 100) / (Nominal value * div%)
public class KboatShares
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
int sharesHeld = (2000 * 100)/(10 * 10);
System.out.println("No. of shares held currently = "
+ sharesHeld);
int sharesRequired = 3000 - sharesHeld;
System.out.println("No. of shares to purchase = "
+ sharesRequired);
}
}
Write a program to input the time in seconds. Display the time after converting them into hours, minutes and seconds.
Sample Input: Time in seconds 5420
Sample Output: 1 Hour 30 Minutes 20 Seconds
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatTimeConvert
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter time in seconds: ");
long secs = in.nextLong();
long hrs = secs / 3600;
secs %= 3600;
long mins = secs / 60;
secs %= 60;
System.out.println(hrs + " Hours " + mins
+ " Minutes " + secs + " Seconds");
}
}
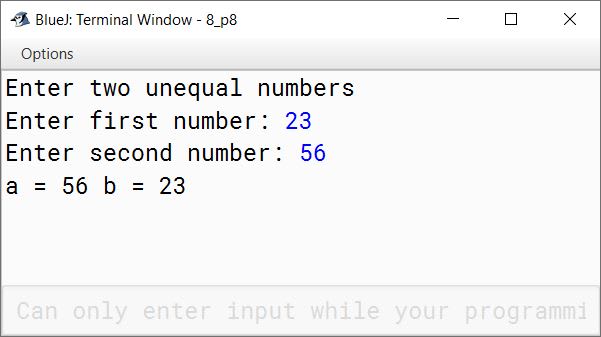
Write a program to input two unequal numbers. Display the numbers after swapping their values in the variables without using a third variable.
Sample Input: a = 23, b = 56
Sample Output: a = 56, b = 23
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatNumberSwap
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter two unequal numbers");
System.out.print("Enter first number: ");
int a = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter second number: ");
int b = in.nextInt();
a = a + b;
b = a - b;
a = a - b;
System.out.println("a = " + a + " b = " + b);
}
}
A certain amount is invested at the rate 10% per annum for 3 years. Find the difference between Compound Interest (CI) and Simple Interest (SI). Write a program to take amount as an input.
Hint: SI = (P * R * T) / 100
A = P * (1 + (R/100))T
CI = A - P
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatInterestDifference
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter Amount: ");
double p = in.nextDouble();
double si = p * 10 * 3 / 100;
double ciAmt = p * Math.pow(1 + (10/100.0), 3);
double ci = ciAmt - p;
System.out.print("Difference between CI & SI: " + (ci - si));
}
}
A shopkeeper sells two calculators for the same price. He earns 20% profit on one and suffers a loss of 20% on the other. Write a program to find his total cost price of the calculators by taking selling price as input.
Hint: CP = (SP / (1 + (profit / 100))) (when profit)
CP = (SP / (1 - (loss / 100))) (when loss)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatShopkeeper
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the selling price: ");
double sp = in.nextDouble();
double cp1 = (sp / (1 + (20 / 100.0)));
double cp2 = (sp / (1 - (20 / 100.0)));
double totalCP = cp1 + cp2;
System.out.println("Total Cost Price = " + totalCP);
}
}