Solved 2017 Question Paper ICSE Class 10 Biology
Name the following: [5]
(i) The process by which root hairs absorb water from the soil.
(ii) The organ which produces urea.
(iii) The kind of lens required to correct Myopia.
(iv) The pituitary hormone which stimulates contraction of uterus during child birth.
(v) The international health organization which educates people in accident prevention.
Answer
(i) Osmosis
(ii) Liver
(iii) Concave
(iv) Oxytocin
(v) Red Cross
Choose the correct answer from each of the four options given below: [5]
(i) The prime source of chlorofluorocarbons is:
- Vehicular emissions
- Industrial effluents
- Domestic sewage
- Refrigeration equipments
(ii) Penicillin obtained from a fungus is:
- Antibiotic
- Antiseptic
- Antibody
- Antiserum
(iii) Marine fish when placed in tap water bursts because of:
- Endosmosis
- Exosmosis
- Diffusion
- Plasmolysis
(iv) Surgical method of sterilization in a woman involves cutting and tying of:
- Ureter
- Uterus
- Urethra
- Oviduct
(v) Synthesis phase in the cell cycle is called so, because of the synthesis of more:
- RNA
- RNA and proteins
- DNA
- Glucose
Answer
(i) Refrigeration equipments
(ii) Antibiotic
(iii) Endosmosis
(iv) Oviduct
(v) DNA
The statements given below are incorrect. Rewrite the correct statement by changing the underlined words of the statements. [5]
(i) The Graafian follicle, after ovulation turns into a hormone producing tissue called Corpus callosum.
(ii) Deafness is caused due to the rupturing of the Pinna.
(iii) Gyri and Sulci are the folds of Cerebellum.
(iv) Free movement of solutes in and out of the cell takes place across the cell membrane.
(v) The solvent used to dissolve the chlorophyll pigments while testing a leaf for starch is Soda lime.
Answer
(i) The Graafian follicle, after ovulation turns into a hormone producing tissue called Corpus luteum.
(ii) Deafness is caused due to the rupturing of the eardrum / tympanum.
(iii) Gyri and Sulci are the folds of Cerebrum.
(iv) Free movement of solutes in and out of the cell takes place across the Cell Wall.
(v) The solvent used to dissolve the chlorophyll pigments while testing a leaf for starch is Methylated spirit / alcohol.
Given below are sets of five terms each. Rewrite the terms in correct order in a logical sequence. [5]
Example: Large intestine, Stomach, Mouth, Small intestine, Oesophagus.
Answer: Mouth → Oesophagus → Stomach → Small intestine → Large intestine.
(i) Fibrin, Platelets, Thromboplastin, Fibrinogen, Thrombin.
(ii) Cochlea, Malleus, Pinna, Stapes, Incus.
(iii) Receptor, Spinal cord, Effector, Motor neuron, Sensory neuron.
(iv) Uterus, Parturition, Fertilisation, Gestation, Implantation.
(v) Caterpillar, Snake, Owl, Frog, Green leaves.
Answer
(i) Platelets → Thromboplastin → Thrombin → Fibrinogen → Fibrin.
(ii) Pinna → Malleus → Incus → Stapes → Cochlea.
(iii) Receptor → Sensory neuron → Spinal cord → Motor neuron → Effector.
(iv) Fertilisation → Uterus → Implantation → Gestation → Parturition.
(v) Green leaves → Caterpillar → Frog → Snake → Owl.
Choose the ODD one out of the following terms given and name the CATEGORY to which the others belong: [5]
(i) Aqueous humour, Vitreous humour, Iris, Central canal
(ii) Formalin, Iodine, DDT, Lime
(iii) ACTH, TSH, ADH, FSH
(iv) Phosphate, RNA, Sugar, Nitrogenous base
(v) Bile, Urea, Uric acid, Ammonia
Answer
(i) Odd term: Central Canal
Category: Others are Parts of eye.
(ii) Odd term: Iodine
Category: Others are Disinfectants.
(iii) Odd term: ADH
Category: Others are Hormones of Anterior lobe of Pituitary gland.
(iv) Odd term: RNA
Category: Others are Parts of Nucleotide.
(v) Odd term: Bile
Category: Others are Nitrogenous wastes / Excretory substances.
Given below are groups of terms. In each group the first pair indicates the relationship between the two terms. Rewrite and complete the second pair on a similar basis. [5]
Example: Oxygen : Inspiration : : Carbondioxide : Expiration
(i) Eye : Optic nerve : : Ear : ...............
(ii) Cytoplasm : Cytokinesis : : Nucleus : ...............
(iii) TT : Homozygous : : Tt : ...............
(iv) Foetus : Amnion : : Heart : ...............
(v) Adenine : Thymine : : Cytosine : ...............
Answer
(i) Eye : Optic nerve : : Ear : Auditory nerve
(ii) Cytoplasm : Cytokinesis : : Nucleus : Karyokinesis
(iii) TT : Homozygous : : Tt : Heterozygous
(iv) Foetus : Amnion : : Heart : Pericardium
(v) Adenine : Thymine : : Cytosine : Guanine
Match the items given in Column A with the most appropriate ones in Column B and rewrite the correct matching pairs. [5]
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| Sacculus | dynamic body balance |
| Birth rate | Hyperglycemia |
| DNA and histones | Hypoglycemia |
| Euro norms | Natality |
| Diabetes mellitus | static body balance |
| vehicular standards | |
| nucleosome |
Answer
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| Sacculus | Static body balance |
| Birth rate | Natality |
| DNA and histones | Nucleosome |
| Euronorms | Vehicular standards |
| Diabetes mellitus | Hyperglycemia |
The diagram given below represents the location and structure of an endocrine gland. Study the same and answer the questions that follow: [5]

(i) Name the endocrine gland shown in the diagram.
(ii) Name the secretion of the gland which regulates basal metabolism.
(iii) Name the mineral element required for the synthesis of the above mentioned hormone.
(iv) Name the disease caused due to under secretion of the above mentioned hormone in children.
(v) Name the disease caused due to hypersecretion of the above mentioned hormone.
Answer
(i) The gland shown in the diagram is Thyroid gland.
(ii) Thyroxine regulates the basal metabolism.
(iii) The mineral element required for the synthesis of the above mentioned hormone is Iodine.
(iv) The disease caused due to under secretion of the above mentioned hormone in children is Cretinism.
(v) The disease caused due to hypersecretion of the above mentioned hormone is Exophthalmic goitre.
Study the diagram given below which represents a stage during the mitotic cell division and answer the questions that follow: [5]

(i) Identify the stage giving suitable reasons.
(ii) Name the parts numbered 1 and 2.
(iii) What is the technical term for the division of nucleus?
(iv) Mention the stage that comes before the stage shown in the diagram. Draw a neat labelled diagram of the stage mentioned.
(v) Which is the cell division that results in half the number of chromosomes in daughter cells?
Answer
(i) The stage shown in the diagram is telophase. During telophase, the mitotic spindle disappears, the chromosomes uncoil and two sets of daughter chromosomes reach opposite poles and the nuclear envelope reforms.
(ii) Part numbered 1 and 2 are:
- 1 → Daughter chromosome
- 2 → Nuclear membrane.
(iii) The technical term for the division of nucleus is Karyokinesis.
(iv) The stage that comes before this stage is Anaphase. It's labelled diagram is shown below:

(v) Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in half the number of chromosomes in daughter cells.
Differentiate between the following pairs on the basis of what is mentioned in brackets: [5]
(i) Active Transport and Diffusion [significance in plants]
(ii) Demography and Population density [Definition]
(iii) Antibiotic and Antibody [Source]
(iv) Renal cortex and Renal medulla [Parts of the nephrons present]
(v) NADP and ATP [Expand the abbreviation]
Answer
(i) Difference between Active Transport and Diffusion [significance in plants]
| Active Transport | Diffusion |
|---|---|
| Certain nutrients such as ios of nitrates, sulphates, potassium, zinc, manganese, etc. are taken up by the roots from the soil through Active transport using the energy supplied by the cell in the form of ATP. | Carbon dioxide needed for the process of photosynthesis enters the leaf through the stomata by the process of Diffusion. |
(ii) Difference between Demography and Population density [Definition]
| Demography | Population density |
|---|---|
| Statistical study of human population with reference to size, density and distribution. | Number of individuals per square km at any given time. |
(iii) Difference between Antibiotic and Antibody [Source]
| Antibiotic | Antibody |
|---|---|
| They are the medicines extracted from some bacteria and fungi. Antibiotics destroy or inhibit the growth of pathogens. | They are produced by lymphocytes in response to the entry of pathogens in the bloodstream. |
(iv) Difference between Renal cortex and Renal medulla [Parts of the nephrons present]
| Renal cortex | Renal medulla |
|---|---|
| Bowman's capsule, Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT), Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) are present in Renal cortex | Loop of Henle and Collecting Ducts are present in Renal medulla |
(v) Difference between NADP and ATP [Expand the abbreviation]
| NADP | ATP |
|---|---|
| Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate | Adenosine Tri Phosphate. |
The diagram given below represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow: [5]

(i) What is the state of the cell shown in the diagram?
(ii) Name the structure that acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
(iii) Label the parts numbered 1 to 4 in the diagram.
(iv) How can the above cell be brought back to its original condition? Mention the scientific term for the recovery of the cell.
(v) State any two features of the above plant cell which is not present in animal cells.
Answer
(i) The cell is in plasmolysed or flaccid state.
(ii) Plasma membrane
(iii) Parts numbered 1 to 4 are:
- 1 → Cell wall
- 2 → Strong sugar solution
- 3 → Cell membrane
- 4 → Nucleus
(iv) If the cell is placed in the hypotonic solution (water), the cell will be brought to it's original condition. The scientific term for the recovery of the cell is deplasmolysis.
(v) Cell wall, large prominent vacuole.
Given below is a representation of a kind of pollution. Study the same and answer the questions that follow: [5]

(i) Name the kind of pollution.
(ii) List any three common sources of this pollution.
(iii) Mention three harmful effects of this pollution on human health.
(iv) Explain the term 'Pollutant'.
(v) Name two soil pollutants.
Answer
(i) Noise pollution
(ii) Three common sources of noise pollution are :
- Vehicular Traffic
- Industrial machines & workshops
- Loudspeakers
(iii) Harmful effects of noise pollution on human health are :
- Interrupts concentration of thought and disturbs peace of mind.
- Disturbs sleep and leads to nervous irritability.
- Lowers efficiency of work.
(iv) Any such constituent the addition of which to air, water or land deteriorates the natural quality of the environment is termed as a Pollutant.
(v) Two soil pollutants are:
- Industrial wastes
- Biomedical wastes
The diagrams given below represent the relationship between a mouse and a physiological process that occurs in green plants. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: [5]
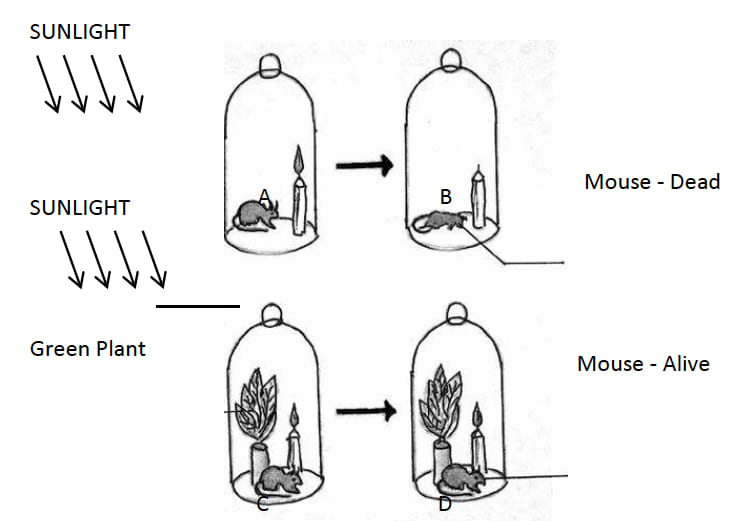
(i) Name the physiological process occurring in the green plant that has kept the mouse alive.
(ii) Explain the physiological process mentioned above.
(iii) Why did the mouse die in bell jar B?
(iv) What is the significance of the process as stated in (i) for life on earth.
(v) Represent the above mentioned physiological process in the form of a chemical equation.
Answer
(i) Photosynthesis occurring in the green plant that has kept the mouse alive.
(ii) Photosynthesis is the process by which living plant cells, containing chlorophyll produce food substances (glucose and starch), from carbon dioxide and water, by using light energy. Plants release Oxygen as a by-product during Photosynthesis.
(iii) Mouse died in bell jar B because the source of oxygen i.e., the green plant was missing and the oxygen present in the bell jar was utilized in burning of candle.
(iv) The significance of Photosynthesis for life on earth is:
- Provides food for all organisms
- Provides oxygen for respiration.
(v) Balanced chemical equation representing the process of photosynthesis is given below:
Mention the exact location of the following: [5]
(i) Prostate gland
(ii) Myelin sheath
(iii) Islets of Langerhans
(iv) Semi-circular canals
(v) Eustachian tube
Answer
(i) Surrounds urethra close to its origin from urinary bladder.
(ii) Surrounds the axon of neuron.
(iii) In Pancreas.
(iv) Inner ear / Part of the membranous labyrinth.
(v) Between middle ear and pharynx.
The diagram shown below is the longitudinal section of a testis of man. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow: [5]

(i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 3 in the diagram.
(ii) In which part of the testis are the sperms produced?
(iii) State the functions of the parts labelled 1 and 3 in the diagram.
(iv) Name the cells that secrete Testosterone.
(v) Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a sperm.
Answer
(i) The parts numbered 1 to 3 are:
- 1 → Scrotum / Scrotal sac
- 2 → Sperm duct / Vas deferens
- 3 → Epididymis
(ii) Seminiferous tubules is the place where the sperms are produced.
(iii) The functions of the parts labelled 1 and 3 are:
- Scrotum (Part 1) — It is a thin-walled sac of skin that protects and surrounds the testes. It also maintains the temperature of testes at 2 to 3°C less than body temperature for the maturation of sperms.
- Epididymis (Part 3) — The epididymis stores the sperms for some days for maturation and transport it to vas deferens.
(iv) Interstitial cells or Leydig cells
(v) Labelled diagram of a sperm is shown below:

Give biological reasons for the following statements: [5]
(i) Some women have facial hair like beard and moustache.
(ii) Cutting of trees should be discouraged.
(iii) In some xerophytes leaves are modified into spines.
(iv) There is frequent urination in winter than in summer.
(v) The left ventricle of the heart has a thicker wall than the right ventricle.
Answer
(i) Due to Adrenal Virilism there is an overgrowth of Adrenal Cortex in some women. This causes the development of certain male characteristics like facial hair (beard and moustache) and deep male voice.
(ii) Cutting of trees results in an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere resulting in global warming. Hence cutting of trees should be discouraged.
(iii) In some xerophytes leaves are modified into spines. This modification helps plant prevent water loss by transpiration by minimizing the surface area. It also defends plants against herbivores animals.
(iv) During summer, the temperature is high. Hence, considerable part of water is lost from the body by means of perspiration. As a result, less water is flushed out from the body by the means of urination. During winter, there is less perspiration due to low temperature. Hence, maximum water is flushed out through urine. Thus, there is frequent urination in winter than in summer.
(v) The left ventricle pumps blood to the farthest points in the body such as the feet, the toes and the brain against the gravity while the right ventricle pumps the blood only up to the lungs. Therefore, the left ventricle has thicker walls than the right ventricle.
The diagram given below represents a section of the human heart. Answer the questions that follow: [5]

(i) Which parts of heart are in the diastolic phase? Give a reason to support your answer.
(ii) Label the parts numbered 1 and 2 in the diagram. What type of blood flows through them?
(iii) What causes the heart sounds 'LUBB' and 'DUP'?
(iv) Name the blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscles.
(v) Draw neat labelled diagrams of a cross section of an artery and a vein.
Answer
(i) In the diagram, ventricles are in the diastolic phase. The reason is that the arrows are shown from atria to the ventricles. It indicates that tricuspid and bicuspid valves are open and the blood is flowing from the atria to the ventricles. During this, the pressure in the ventricles falls and hence they are in the diastolic phase.
(ii) The parts numbered 1 and 2 are:
- 1 → Pulmonary artery, Deoxygenated blood.
- 2 →Pulmonary veins, Oxygenated blood.
(iii) The first sound "LUBB" is produced when the atrio-ventricular (tricuspid and bicuspid) valves get closed sharply at the start of ventricular systole. The second sound "DUP" is produced when at the beginning of ventricular diastole, the semilunar valves at the roots of aorta and pulmonary artery get closed.
(iv) Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscles.
(v) Below diagrams show the cross section of an artery and a vein:

Give appropriate biological / technical terms for the following: [5]
(i) The type of immunity that exists in our body due to our genetic makeup.
(ii) The suppressed allele of a gene.
(iii) The accessory gland in human males whose secretion activates the sperms.
(iv) An apparatus that measures the rate of water uptake in a cut shoot due to transpiration.
(v) The kind of twins formed from two fertilised eggs.
(vi) A pair of corresponding chromosomes of the same size and shape, one from each parent.
(vii) The mild chemical substance which when applied on the body kills germs.
(viii) The type of waste generated in hospitals and pathological laboratories.
(ix) The antiseptic substance in tears.
(x) Cellular components of blood containing haemoglobin.
Answer
(i) Innate / Inborn / Natural immunity
(ii) Recessive
(iii) Seminal vesicles
(iv) Potometer
(v) Fraternal twins
(vi) Homologous chromosomes
(vii) Antiseptic
(viii) Biomedical waste
(ix) Lysozyme
(x) RBCs / Erythrocytes
In a homozygous pea plant, axial flowers (A) are dominant over terminal flowers (a). [5]
(i) What is the phenotype and genotype of the F1 generation if a plant bearing pure axial flowers is crossed with a plant bearing pure terminal flowers?
(ii) Draw a Punnett square board to show the gametes and offsprings when both the parent plants are heterozygous for axial flowers.
(iii) What is the phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratio of the above cross shown in (ii).
(iv) State Mendel's Law of Dominance.
(v) Name two genetic disorders commonly seen in human males.
Answer
(i) Phenotype – All bear axial flowers
Genotype – All are heterozygous dominant for axial flowers.
(ii) Below is the Punnett square board showing the gametes and offsprings when both the parent plants are heterozygous for axial flowers:
| A | a | |
| A | AA | Aa |
| a | Aa | aa |
(iii) Phenotypic ratio — 3 : 1
Genotypic ratio — 1 : 2 : 1
(iv) Mendel's Law of Dominance — Out of a pair of contrasting characters present together, only one is able to express itself while the other remains suppressed. The one that expresses is the dominant character and the one that is unexpressed is the recessive. The recessive character can express only when the pair consists of both recessives (homozygous recessive).
(v) Two genetic disorders commonly seen in human males are:
- Colour blindness
- Haemophilia
The diagram given below is an external view of the human brain. Study the same and answer the questions that follow: [5]

(i) Name the parts labelled A, B and C in the diagram.
(ii) State the main functions of the parts labelled A and B.
(iii) What are the structural and functional units of the brain? How are the parts of these units arranged in A and C?
(iv) Mention the collective term for the membranes covering the brain.
(v) What is the function of Cerebrospinal fluid?
Answer
(i) The parts labelled A, B and C are:
- A → Cerebrum
- B → Cerebellum
- C → Spinal Cord
(ii) The functions are mentioned below:
- Cerebrum (Part A) — It is the seat of intelligence, consciousness and will power. It controls all voluntary activities.
- Cerebellum (Part B) — It coordinates muscular activities and maintains balance of the body.
(iii) Neurons / nerve cells are the structural and functional units of the brain.
In part A (Cerebrum), Outer grey matter has cytons and inner white matter has axons.
In part C (Spinal Cord), Outer white matter has axons and inner grey matter has cytons.
(iv) Meninges
(v) Cerebrospinal fluid(CSF) acts like a cushion to protect the brain / spinal cord from injuries and shocks.