Solved 2019 Question Paper ICSE Class 10 Chemistry
An electrolyte which completely dissociates into ions is:
- Alcohol
- Carbonic acid
- Sucrose
- Sodium hydroxide
Answer
Sodium hydroxide
Reason — Sodium hydroxide is a strong electrolyte hence, it completely dissociates into ions.
The most electronegative element from the following elements is:
- Magnesium
- Chlorine
- Aluminium
- Sulphur
Answer
Chlorine
Reason — Chlorine is the most electronegative element among the given options because electronegativity increases left to right in a period.
The reason for using Aluminium in the alloy duralumin is:
- Aluminium is brittle.
- Aluminium gives strength.
- Aluminium brings lightness.
- Aluminium lowers melting point.
Answer
Aluminium brings lightness.
Reason — As aluminum gives strength and brings lightness, hence, it is used in the alloy duralumin.
The drying agent used to dry HCl gas is:
- Conc. H2SO4
- ZnO
- Al2O3
- CaO
Answer
Conc. H2SO4
Reason — Drying agent used for drying should only remove the moisture and not react with it, hence, conc. sulphuric acid is used as the drying agent.
A hydrocarbon which is a greenhouse gas is:
- Acetylene
- Ethylene
- Ethane
- Methane
Answer
Methane
Reason — Methane is a green house gas.
Fill in the blanks with the choices given in brackets:
(i) Conversion of ethanol to ethene by the action of concentrated sulphuric acid is an example of ............... (dehydration/dehydrogenation/dehydrohalogenation)
(ii) When sodium chloride is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid below 200°C, one of the products formed is ............... (sodium hydrogen sulphate / sodium sulphate / chlorine)
(iii) Ammonia reacts with excess chlorine to form ............... (nitrogen / nitrogen trichloride / ammonium chloride)
(iv) Substitution reactions are characteristic reactions of ............... (alkynes / alkenes / alkanes)
(v) In Period 3, the most metallic element is ............... (sodium / magnesium / aluminium)
Answer
(i) Conversion of ethanol to ethene by the action of concentrated sulphuric acid is an example of dehydration
(ii) When sodium chloride is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid below 200°C, one of the products formed is sodium hydrogen sulphate (sodium hydrogen sulphate / sodium sulphate / chlorine)
(iii) Ammonia reacts with excess chlorine to form nitrogen trichloride
(iv) Substitution reactions are characteristic reactions of alkanes
(v) In Period 3, the most metallic element is sodium.
Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following reactions:
(i) Reduction of copper (II) oxide by hydrogen.
(ii) Action of dilute sulphuric acid on sodium hydroxide.
(iii) Action of dilute sulphuric acid on zinc sulphide.
(iv) Ammonium hydroxide is added to ferrous sulphate solution.
(v) Chlorine gas is reacted with ethene.
Answer
(i) Reduction of copper (II) oxide by hydrogen.
(ii) Action of dilute sulphuric acid on sodium hydroxide.
2NaOH + H2SO4 ⟶ Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(iii) Action of dilute sulphuric acid on zinc sulphide.
ZnS + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2S
(iv) Ammonium hydroxide is added to ferrous sulphate solution.
2NH4OH + FeSO4 ⟶ (NH4)2SO4 + Fe(OH)2
(v) Chlorine gas is reacted with ethene.

State one observation for each of the following:
(i) Concentrated nitric acid is reacted with sulphur.
(ii) Ammonia gas is passed over heated copper (II) oxide.
(iii) Copper sulphate solution is electrolysed using copper electrodes.
(iv) A small piece of zinc is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
(v) Lead nitrate is heated strongly in a test tube.
Answer
(i) Reddish brown nitrogen dioxide gas is evolved.
S + 6HNO3 [conc.] ⟶ H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO2
(ii) Black copper [II] oxide is reduced to brown copper.
2NH3 + 3CuO ⟶ 3Cu + 3H2O + N2 [g]
(iii) A brownish pink deposit of copper metal is seen at the cathode when copper solution is electrolyzed using copper electrodes. The blue colour of Copper Sulphate solution does not fade and Copper anode diminishes in mass.
(iv) Effervescence of H2 gas can be seen.
Zn + 2HCl ⟶ ZnCl2 + H2
(v) White precipitate of PbCl2 is formed which is soluble in hot water.
Pb(NO3)2 + 2HCl ⟶ PbCl2 + 2HNO3
(i) Calculate:
The number of moles in 12g of oxygen gas. [O = 16]
The weight of 1022 atoms of carbon.
[C = 12, Avogadro’s No. = 6 x 1023]
(ii) Molecular formula of a compound is C6H18O3. Find its empirical formula.
Answer
(i) Gram molecular mass of oxygen = 32 g = 1 mole
32 g = 1 mole
∴ 12 g = x 12 = 0.375 moles.
6 x 1023 atoms of carbon weigh = 12 g
∴ 1022 atoms of carbon will weigh = x 1022 = 0.2 g.
Hence, number of moles = 0.375 moles and weight of 1022 atoms of carbon = 0.2 g.
(ii) Molecular formula of the compound is C6H18O3
Molecular formula = n x (Empirical Formula)
C6H18O3 can be written as 3(C2H6O)
∴ Molecular formula = 3 x (C2H6O)
∴ Empirical Formula of the compound is C2H6O
(i) Give the IUPAC name of the following organic compounds:
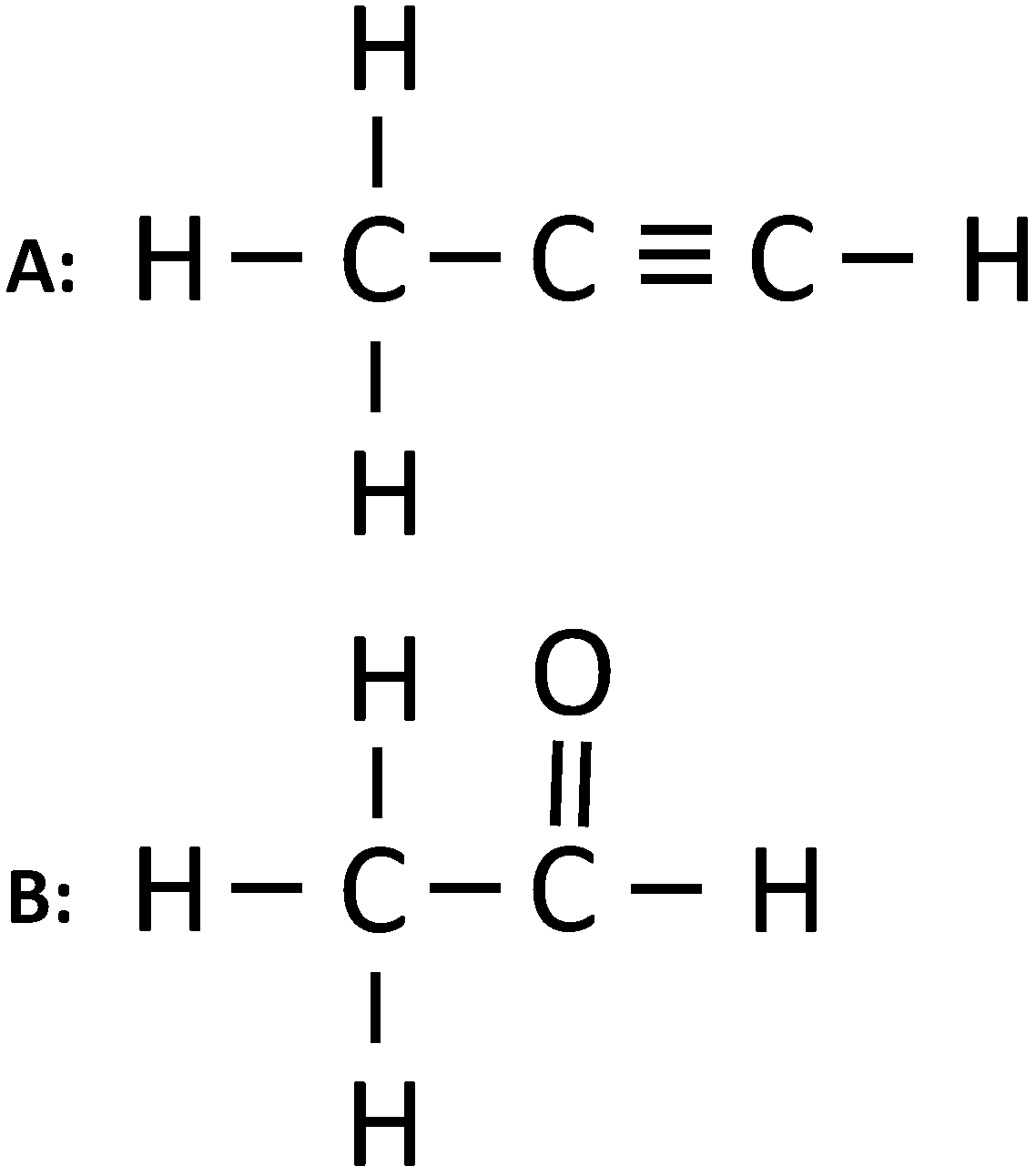
(ii) What is the special feature of the structure of ethyne
(iii) Name the saturated hydrocarbon containing two carbon atoms.
(iv) Give the structural formula of acetic acid.
Answer
(i) The IUPAC names are:
A: Propyne
B: Ethanal
(ii) The special feature of the structure of ethyne is that the two carbon atoms are linked by triple covalent bond formed by sharing three pairs of electrons between the two carbon atoms. The availability of electrons on the triple bond makes ethyne more reactive and hence it undergoes characteristics addition reactions only.
(iii) Ethane [C2H6]
(iv) Structural formula of acetic acid is shown below:

Give the appropriate term defined by the statements given below:
(i) The formula that represents the simplest ratio of the various elements present in one molecule of the compound.
(ii) The substance that releases hydronium ion as the only positive ion when dissolved in water.
(iii) The tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself when combined in a covalent compound.
(iv) The process by which certain ores, specially carbonates, are converted to oxides in the absence of air.
(v) The covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally between the combining atoms.
Answer
(i) Empirical formula
(ii) Acid
(iii) Electronegativity
(iv) Calcination
(v) Non-polar covalent bond
Arrange the following according to the instructions given in brackets:
(i) K, Pb, Ca, Zn. (In the increasing order of the reactivity)
(ii) Mg2+, Cu2+, Na1+, H1+ (In the order of preferential discharge at the cathode)
(iii) Li, K, Na, H (In the decreasing order of their ionization potential)
(iv) F, B, N, O (In the increasing order of electron affinity)
(v) Ethane, methane, ethene, ethyne. (In the increasing order of the molecular weight) [H = 1, C = 12]
Answer
(i) Pb < Zn < Ca < K
(ii) Cu2+, H1+, Mg2+, Na1+
Lower the position of the ion, greater the tendency to be liberated at the cathode (or respective electrode).
(iii) H > Li > Na > K
Ionization Potential decreases as we move down the group.
(iv) B < N < O < F
Electron Affinity increases from left to right across a period.
(v) Methane < Ethyne < Ethene < Ethane
Ethane [C2H6] : M.W. = 2[12] + 6[1] = 30
Methane [CH4] : M.W. = 12 + 4[1] = 16
Ethene [C2H4] : M.W. = 2[12] + 4[1] = 28
Ethyne [C2H2] : M.W. = 2[12] + 2[1] = 26
Hence, increasing order of molecular weight : Methane < Ethyne < Ethene < Ethane
Draw the electron dot structure of:
(i) Nitrogen molecule [N = 7]
(ii) Sodium chloride [Na = 11, Cl = 17]
(iii) Ammonium ion [N = 7, H = 1]
Answer
(i) Electron dot structure of Nitrogen molecule is shown below:

(ii) Electron dot structure of Sodium chloride is shown below:

(iii) Electron dot structure of Ammonium ion is shown below:

The pH values of three solutions A, B and C are given in the table. Answer the following questions:
| Solution | pH value |
|---|---|
| A | 12 |
| B | 2 |
| C | 7 |
(i) Which solution will have no effect on litmus solution?
(ii) Which solution will liberate CO2 when reacted with sodium carbonate?
(iii) Which solution will turn red litmus solution blue?
Answer
(i) Solution C : pH value 7
(ii) Solution B : pH value 2
(iii) Solution A : pH value 12
Study the extract of the Periodic Table given below and answer the questions that follow.
Give the alphabet corresponding to the element in question. DO NOT repeat an element.
| A | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | D | E | ||||||
| B | G | F | ||||||
(i) Which element forms electrovalent compound with G?
(ii) The ion of which element will migrate towards the cathode during electrolysis?
(iii) Which non-metallic element has the valency of 2?
(iv) Which is an inert gas?
Answer
(i) B forms an electrovalent compound with G.
(ii) A has positive ions which migrate towards cathode.
(iii) E is non-metallic and has a valency of 2 as it belongs to group 16.
(iv) F is an inert gas as it belongs to the zero group.
Name the particles present in:
(i) Strong electrolyte
(ii) Non- electrolyte
(iii) Weak electrolyte
Answer
(i) Ions only
(ii) Molecules only
(iii) Ions and Molecules
Distinguish between the following pairs of compounds using the reagent given in the bracket.
(i) Manganese dioxide and copper (II) oxide. (using concentrated HCl)
(ii) Ferrous sulphate solution and ferric sulphate solution. (using sodium hydroxide solution)
(iii) Dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute sulphuric acid. (using lead nitrate solution)
Answer
(i) When each of the compound is heated with conc. hydrochloric acid, greenish yellow (chlorine) gas is evolved in case of manganese dioxide and filtrate is brownish in colour whereas, no chlorine gas is evolved in case of copper (II) oxide and filtrate is bluish in colour.
MnO2 + 4HCl ⟶ MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
CuO + 2HCl ⟶ CuCl2 + H2O
(ii) When sodium hydroxide is added to the two solns., ferrous sulphate solution gives a dirty green ppt. of Fe(OH)2 whereas, ferric sulphate solution forms a reddish brown ppt. of Fe(OH)3. Hence, the two compounds can be distinguished.
(iii) Sulphuric acid forms a white precipitate with lead nitrate solution. This precipitate does not dissolve on warming the reaction mixture.
H2SO4 (dil.) + Pb(NO3)2 ⟶ 2HNO3 + PbSO4 ↓ [white ppt. formed which does not dissolve on warming the mixture].
Hydrochloric acid forms a white precipitate with lead nitrate solution. This precipitate dissolves on warming the reaction mixture so as to form clear solution.
2HCl (dil.) + Pb(NO3)2 ⟶ 2HNO3 + PbCl2 ↓ [white ppt. formed which dissolves on warming the mixture].
Hence, dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute sulphuric acid can be distinguished using lead nitrate solution.
Choose the method of preparation of the following salts, from the methods given in the list:
[List:
A. Neutralization
B. Precipitation
C. Direct combination
D. Substitution]
(i) Lead chloride
(ii) Iron (II) sulphate
(iii) Sodium nitrate
(iv) Iron (III) chloride
Answer
(i) Lead chloride — B: Precipitation
(ii) Iron [II] Sulphate — D: Substitution
(iii) Sodium nitrate — A: Neutralization
(iv) Iron [III] chloride — C: Direct combination
Complete the following equations:
(i) S + Conc. HNO3 ⟶
(ii) C + conc. H2SO4 ⟶
(iii) Cu + dil. HNO3 ⟶
Answer
(i) S + 6HNO3 [conc.] ⟶ H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO2
(ii) C + 2H2SO4 (conc.) ⟶ CO2 + 2SO2 + 2H2O
(iii) 3Cu + 8HNO3 [dil.] ⟶ 3Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO (g) + 4H2O
Write a balanced chemical equation for the preparation of:
(i) Ethene from bromoethane
(ii) Ethyne using calcium carbide
(iii) Methane from sodium acetate.
Answer
(i) Ethene from bromoethane
(ii) Ethyne from calcium carbide
(iii)
Name the following organic compounds:
(i) The compound with 3 carbon atoms whose functional group is a carboxyl.
(ii) The first homologue whose general formula is CnH2n
(iii) The compound that reacts with acetic acid to form ethyl ethanoate.
(iv) The compound formed by complete chlorination of ethyne.
Answer
(i) Propanoic acid [C3H7CHO]
(ii) Ethene [C2H4]
(iii) Ethyl alcohol
(iv) 1,1,2,2 tetrachloroethane

Give the chemical formula of:
(i) Bauxite
(ii) Cryolite
(iii) Sodium aluminate
Answer
(i) Al2O3.2H2O — Bauxite
(ii) Na3AlF6 — Cryolite
(iii) NaAlO2 — Sodium aluminate
Answer the following questions based on the extraction of aluminium from alumina by Hall-Heroult's Process.:
(i) What is the function of cryolite used along with alumina as the electrolyte?
(ii) Why is powdered coke sprinkled on top of the electrolyte?
(iii) Name the electrode, from which aluminium is collected.
Answer
(i) Addition of cryolite —
- lowers the fusion point of the mixture i.e., mixture fuses around 950°C instead of 2050°C.
- enhances the mobility of the fused mixture by acting as a solvent for the electrolytic mixture.
- enhances the conductivity of the mixture since, pure alumina is almost a non-conductor of electricity.
(ii) The layer of powdered coke is sprinkled over the electrolytic mixture as :
- it prevents burning of carbon electrodes in air at the emergence point from the bath.
- it minimizes or prevents heat loss by radiation.
(iii) Cathode
Match the alloys given in column I to the uses given in column II:
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| (i) Duralumin | A: Electrical fuse |
| (ii) Solder | B: Surgical instruments |
| (iii) Brass | C: Aircraft body |
| (iv) Stainless steel | D: Decorative articles |
Answer
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| (i) Duralumin | C: Aircraft body |
| (ii) Solder | A: Electrical fuse |
| (iii) Brass | D: Decorative articles |
| (iv) Stainless steel | B: Surgical instruments |
Identify the substances underlined :
(i) The catalyst used to oxidise ammonia.
(ii) The organic compound which when solidified, forms an ice like mass.
(iii) The dilute acid which is an oxidizing agent.
Answer
(i) Platinum
(ii) Glacial acetic acid
(iii) Nitric acid
Copper sulphate solution reacts with sodium hydroxide solution to form a precipitate of copper hydroxide according to the equation:
2NaOH + CuSO4 ⟶ Na2SO4 + Cu(OH)2↓
(i) What mass of copper hydroxide is precipitated by using 200 g of sodium hydroxide.
[H = 1, O = 16, Na = 23, S = 32, Cu = 64]
(ii) What is the colour of the precipitate formed.
Answer
(i)
80 g of sodium hydroxide precipitates 98 g of copper hydroxide.
∴ 200 g of sodium hydroxide will precipitate x 200 = 245 g of copper hydroxide.
Hence, 245 g. of copper hydroxide is precipitated.
(ii) Pale blue precipitate is formed.
Find the empirical formula and the molecular formula of an organic compound from the data given below:
C = 75.92%, H = 6.32% and N = 17.76%
The vapour density of the compound is 39.5.
[C = 12, H = 1, N = 14]
Answer
| Element | % composition | At. wt. | Relative no. of atoms | Simplest ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 75.92 | 12 | = 6.32 | = 5 |
| Hydrogen | 6.32 | 1 | = 6.32 | = 5 |
| Nitrogen | 17.76 | 14 | = 1.26 | = 1 |
Simplest ratio of whole numbers = C : H : N = 5 : 5 : 1
Hence, empirical formula is C5H5N
Empirical formula weight = 5(12) + 5(1) + 14 = 79
V.D. = 39.5
Molecular weight = 2 x V.D. = 2 x 39.5 = 79
∴ Molecular formula = n[E.F.] = 1[C5H5N] = C5H5N
Name the gas evolved in each of the following cases:
(i) Alumina undergoes electrolytic reduction.
(ii) Ethene undergoes hydrogenation reaction.
(iii) Ammonia reacts with heated copper oxide.
Answer
(i) Oxygen gas
(ii) Ethane gas
(iii) Nitrogen gas
Study the flow chart given and give balanced equations to represent the reactions A, B and C:
Answer
A : Mg3N2 + 6H2O ⟶ 3Mg(OH)2 + 2NH3 [g]
B : NH3 + HCl ⟶ NH4Cl
C: NH4Cl + NaOH ⟶ NaCl + H2O + NH3 [g]
Copy and complete the following table which refers to the industrial method for preparation of ammonia and sulphuric acid.
| Name of the compound | Name of the process | Catalytic equation [with the catalyst] |
|---|---|---|
| Ammonia | (i) | (ii) |
| Sulphuric acid | (iii) | (iv) |
Answer
(i) Haber's process
(ii)
(iii) Contact Process
(iv)