Solved Sample Paper 5
Section A
Question 1(i)
Pushing a wall yield no work, then where is the energy of our hands transferred?
- To the environment as friction.
- To the wall as friction
- To the environment and wall as heat
- All of the above
Answer
To the environment and wall as heat
Reason — As the wall does not move, the energy supplied by us in pushing it, will be transferred from us to the wall and environment as heat energy.
Question 1(ii)
When a ray of light travel from glass to air, then deviation of ray is
- i - r
- zero
- r - i
- 90°
Answer
r - i
Reason — When a ray of light travels from a denser medium (glass) to a rarer medium (air), then it bends away from the normal, hence, angle of refraction is more than the incident angle. Therefore, deviation of ray is r - i.
Question 1(iii)
Which of the following colours has more lateral displacement?
- Red
- Blue
- Green
- Violet
Answer
Violet
Reason — The lateral displacement of light is inversely proportional to its wavelength. Hence, the shortest wavelength (i.e.,violet) undergo most lateral displacement.
Question 1(iv)
What is ratio of force acting on a body while going upwards and downwards under the influence of earth's gravity?
- 2
- -1
- 1
- -2
Answer
-1
Reason — Acceleration of the body while going down = g
Acceleration of the body while going up = - g
Hence, ratio of acceleration due to gravity upwards and downwards = = -1
Question 1(v)
Which of the following is the electrostatic unit of charge?
- franklin
- q/m2.sec
- becquerel
- calorie
Answer
franklin
Reason — franklin is the electrostatic unit of charge.
Question 1(vi)
A woman pushes a trunk on a railway platform which has a rough surface. She supplies a force of 100 N over a distance of 10 m. Thereafter, she gets progressively tired and her applied force reduces linearly with distance to 50 N. The total distance by which the trunk has been moved is 20 m.
If frictional force between trunk and rough surface is 50 N, then calculate the net work done by the two forces over 20 m.
- 1000 J
- 500 J
- 750 J
- 1500 J
Answer
750 J
Reason — From graph,

Work done by woman (Ww) = area of rectangle ABCD + area of trapezium CEID
= (100 x 10) + [ x (100 + 50) x 10]
= 1000 + 750
= 1750 J
Frictional force opposes motion, so it acts in opposite direction.
Work done by frictional force (Wf) = - area of rectangle AGHI
= - AG x AI
= -50 x 20
= -1000 J
Hence, net work done = 1750 - 1000 = 750 J
Question 1(vii)
Which of the following cannot be a decay product from the parent nuclei?
- An isotope of parent nuclei
- An isobar of parent nuclei
- More stable daughter nuclei
- None of the above
Answer
None of the above
Reason —
one β-decay can form the isobars.
2β deacy and an α decay can form isotopes.
γ decay forms a more stable nuclei.
Question 1(viii)
The refractive indices of kerosene oil, water and turpentine oil are 1.44, 1.33 and 1.87, respectively. In which of these material light travel faster?
- kerosene oil
- Turpentine oil
- Water
- Same in all
Answer
Water
Reason — Speed of light in inversely proportional to its refractive index, hence, speed of light in water is maximum as its refractive index is lowest.
Question 1(ix)
Assertion : The refractive index of a medium decreases with increase in wavelength of incident light.
Reason : The refractive index of a medium decreases with increase in temperature of medium.
- Both Assertion and Reason are true.
- Both Assertion and Reason are false.
- Assertion is false but Reason is true.
- Assertion is true but Reason is false.
Answer
Both Assertion and Reason are true.
Reason — The speed of light is different for different colours because the light travels slower in case of minimum wavelength which leads to increase in refractive index. The refractive index of a medium decreases with increase in temperature of medium. Since, the velocity of light increases with increase in temperature of medium.
Therefore,
μT1 > μT2, as T1 < T2
Question 1(x)
The wave velocity, frequency and wavelength are related as
v = fλ
λ = vf
f =
v =
Answer
V = f λ
Reason — The relation between wave velocity V, frequency f and wavelength λ of a wave is —
V = f λ
Question 1(xi)
Which one of the following is a reliable measure?
- Hotness
- Coldness
- Temperature
- None of these
Answer
Temperature
Reason — Temperature is a reliable measure as it gives us an accurate idea whether a body is hot or cold.
Question 1(xii)
The production of induced current in one coil due to change in magnetic field is called
- electromagnetism
- induction
- mutual induction
- steady current
Answer
induction
Reason — The production of induced current in one coil due to change in magnetic field is called induction or electromagnetic induction.
Question 1(xiii)
EMF of a cell is dependent on
- the shape of electrodes
- the material of electrodes
- the distance between the electrodes
- Both (a) and (b)
Answer
the material of electrodes
Reason — EMF of a cell is dependent on :
- the material of electrode
- the material of electrolyte
It is independent of
- the shape of electrode
- the distance between the electrodes
- amount of electrolyte.
Question 1(xiv)
An object is vibrating at 4000 Hz. The time period of sound produced is
- 0.0025 s
- 0.025 s
- 0.00025 s
- 0.005 s
Answer
0.00025 s
Reason — Given, frequency (f) = 4000 Hz
Time period = = = 0.00025 s
Question 1(xv)
Conduction is the method of transfer of heat in
- liquids
- solids
- gases
- vacuum
Answer
solids
Reason — Transfer of heat from an area of more heat to area of less heat by direct contact or directly through the matter is called conduction.
Question 2(i)
(a) If the moment of force is assigned a negative sign, then will the turning tendency of the force be clockwise or anti-clockwise?
(b) Complete the following nuclear reactions given below
I.
II.
Answer
(a) If the moment of force is assigned a negative sign, then the turning tendency of the force will be in clockwise direction.
(b)
I. When there is an α emission from , then the atomic number decreases by 2 and mass number decreases by 4. Hence, we get .
Now, when undergoes β emission, the atomic number increases by 1 and the mass number is unchanged. Hence, we get .
In the final step when undergoes β emission again the atomic number increases by 1 and the mass number is unchanged. Hence we get .
So the complete nuclear change is as follows —
II. When there is an α emission from , then the atomic number decreases by 2 and mass number decreases by 4. Hence, we get
After the γ emission, there is no change in atomic number and mass number. Hence, we get
In the final step when there are two β emissions, the atomic number increases by 2 and the mass number is unchanged and we get
Hence, the nuclear change is as follows —
Question 2(ii)
If a man is travelling in a car in a straight line path and the car suddenly turns right, then the man experiences a severe push towards the left. Explain.
Answer
Inertia of motion would cause the man to continue moving in a straight line, so he would feel a force pushing him towards the left, opposite to the direction of the car's turn.
Question 2(iii)
(a) Define couple.
(b) State the SI unit of moment of couple.
Answer
(a) Two equal and opposite parallel forces, not acting along the same line, form a couple.
(b) The S.I. unit of moment of couple is Newton x meter or Nm.
Question 2(iv)
(a) What is meant by an ideal machine?
(b) Write a relationship between the mechanical advantage (MA) and velocity ratio (VR) of an ideal machine.
Answer
(a) An ideal machine is that where there is no loss of energy i.e. the work output is equal to the work input. An ideal machine is 100% efficient.
(b) For an ideal machine (free from friction etc.), work output is equal to the work input, so the efficiency is equal to 1 ( or 100% ) and the mechanical advantage is numerically equal to the velocity ratio. So,
For an ideal machine, M.A. = V.R.
Question 2(v)
Define work. State the conditions when the work done by a force acting on a body is zero.
Answer
The definition of work states that when force is applied on a body and the body moves then work is said to be done.
The two conditions for the work done to be zero are,
(i) When there is no displacement of the body on application of force
i.e. S = 0 and
(ii) When displacement is normal to the direction of force
i.e. θ = 90° as cos 90° = 0
Question 2(vi)
The given figure shows a trace of a sound wave which is produced by a particular tuning fork.

(a) Draw a trace of the sound wave which has a higher pitch than that shown in figure.
(b) Draw a trace of the sound wave which is louder than that shown in figure.
Answer
Sound waves with higher pitch and which is louder are shown in the figure:

Question 2(vii)
Why should a fuse with defined rating not be replaced by one with a larger rating?
Answer
The fuse is rated for a certain maximum current and blows off when a current more than the rated value flows through it. If a fuse is replaced by one with larger ratings, the appliances may get damaged as the protecting fuse will not melt and the circuit will not be broken.
Question 3(i)
If the refractive index of air with respect to glass is expressed as answer the following:
(a) Express the similar expression for in terms of i and r.
(b) If angle r = 90°, what is the corresponding angle (i) is called?
(c) Write down the physical significance of angle (i) in part (b).
Answer
(a) The expression for aμg =
(b) When refractive angle r = 90° then, the corresponding angle of incidence i will be equal to critical angle.
(c) The phenomenon of total internal reflection occurs when the angle of incidence exceeds the value of i obtained in part (b).
Question 3(ii)
How does increase in the temperature affect the specific resistance of a metal and semiconductor?
Answer
Specific resistance increases with increase in temperature for metals but it decreases with the increase in temperature for semiconductors.
Question 3(iii)
The magnetic field produced by a current carrying conductor is shown below. Is there a similar magnetic field produced around a thin beam of moving α-particles and neutrons? Justify your answer.

Answer
In case of movement of a charged particle, the magnetic field is created around the particle. The field is around the path on which the charged particle moves. So, a thin beam of α-particles (which are positively charged) is like a straight conductor carrying current in the direction of motion of α-particles. But, as neutrons carry no charge, so no magnetic field would be created around their path.
Question 3(iv)
What do you understand by the following statements?
(a) The heat capacity of the body is 60 JK-1.
(b) The specific heat capacity of lead is 130 Jkg-1K-1
Answer
(a) Heat energy required to raise the temperature of a body by 1 K is 60 J.
(b) Heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 Kg of lead by 1 K is 130 J.
Question 3(v)
(a) What is the origin of β -particles?
(b) Under what condition β -particles produce X rays?
Answer
(a) β -particles are given out from the nucleus of radioactive atom.
(b) β -particles produce X-rays when they are stopped by the metals having high atomic number and high melting point.
Section B
Question 4(i)
An narrow beam of white light is incident on three glass objects as shown below. Comment on the nature of behaviour of the emergent beam in all three cases.

Answer
(a) The incident beam of light after refraction though glass slab emerges out parallel to the incident beam but laterally shifted. No dispersion takes place in this case.
(b) When the beam of light passes through the first prism, it splits into its seven constituent colours, however, these seven colours on passing through the second inverted prisms recombine. The emergent ray is parallel to the incident beam but slightly shifted outwards.
(c) When the incident beam passes through the prism, it splits into its constituent colours. These split further on emerging out of the prism and dispersion pattern is observed.
Question 4(ii)
A diver in water looks obliquely at an object AB in air.

(i) Does the object appear taller, shorter or of the same size to the diver?
(ii) Show the path of two rays AC & AD starting from the tip of the object as it travels towards the diver in water and hence obtain the image of the object.
Answer
(i) The object appears taller to the diver.
(ii) Below diagram shows the path of two rays AC & AD:

Question 4(iii)
(a) With the help of a suitable diagram, represent the refraction of light rays from
I. rarer to denser medium
II. denser to rarer medium.
(b) Does the depth of a tank of water appear to change or remains the same when viewed normally from the above?
Answer
(a)
I. The below ray diagram shows the refraction of light from rarer (air) to denser (glass) medium:
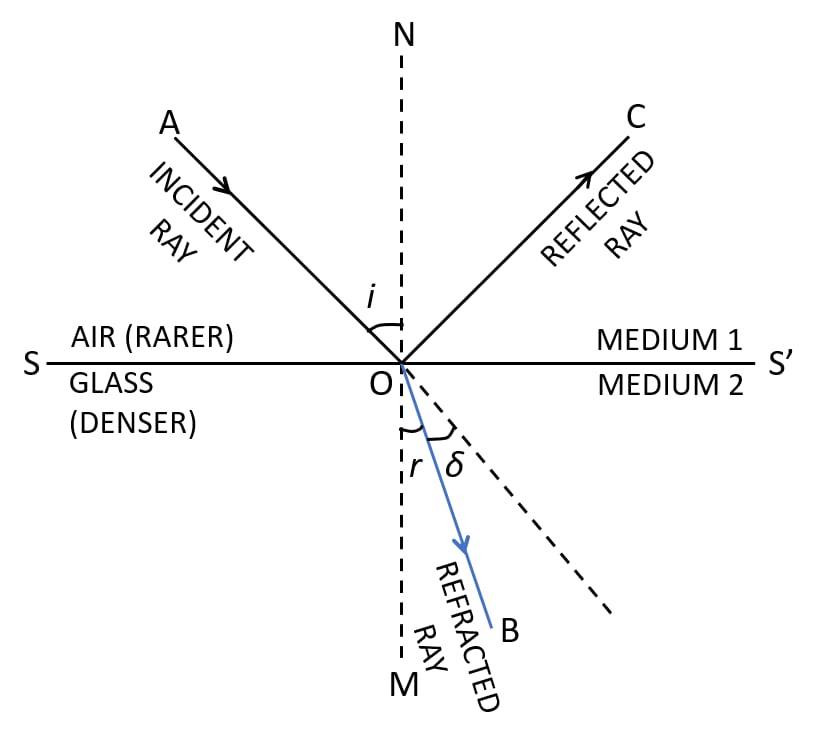
II. The below ray diagram shows the refraction of light from denser (glass) to rarer (air) medium:
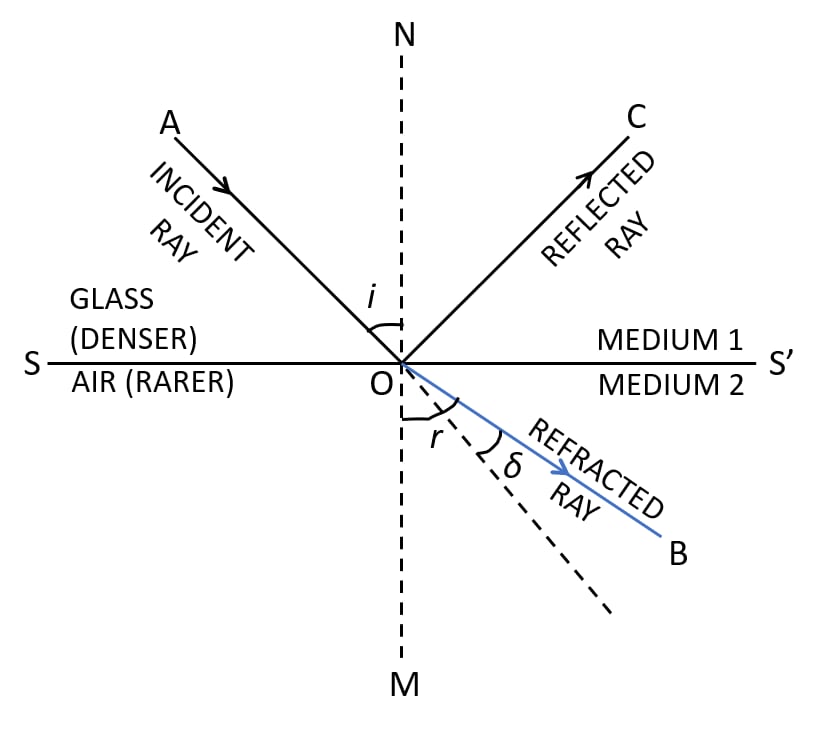
(b) When a tank is viewed normally from above, the apparent depth of the tank will remain the same as the incident light striking normally on the surface will pass undeviated. Hence, no phenomenon of refraction is observed and depth of pond appears same.
Question 5(i)
You are provided with a printed piece of paper. Using this paper, how will you differentiate between a convex lens and concave lens?
(b) What are the uses of convex lens?
Answer
(a) On keeping the lens near a printed page, if letters appear magnified, the lens is convex and if the letters appear diminished, the lens is concave.
(b) Uses of convex lens are:
- Convex lens are used in microscopes and magnifying glasses.
- The objective lens of a telescope, camera, slide projector, etc., is a convex lens which forms the real and inverted image of the object.
Question 5(ii)
(a) How many surfaces bound a prism?
(b) Give the relationship between wavelength of light and amount by which it deviates when it is passed through a prism.
(c) What will be the colour of the emergent light ray when a ray of white light is incident on a thin walled hollow glass prism?
Answer
(a) A prism is a transparent medium bounded by five plane surfaces i.e., 2 triangular faces and three rectangular lateral surfaces.
(b) Wavelength (λ) ∝
(c) The emergent light will be white because the outer surface of the prism behave like a hollow glass plate.
Question 5(iii)
(a) Define convex lens and give its nature of refraction.
(b) A 6 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of convex lens of focal length 25 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 40 cm.
By calculation determine
the position and
the size of the image formed.
Answer
(a) A lens which is thicker at the centre and thinner at its ends is called convex lens. It converges the light rays passing through and is called a converging lens.
(b) Given,
f = 25 cm
u = -40 cm
v = ?
As we know, the lens formula is —
Substituting the values in the formula, we get,
∴ Image distance is 66.67 cm
u = -40 cm
v = 66.67 cm
height of object (ho) = 6 cm
height of image (hi) = ?
From formula:
Substituting the values in the formula, we get,
Hence, height of image = -10 cm
Question 6(i)
A pulley system with V.R. = 4 is used to lift a load of 175 kgf through a vertical height of 15 m. The effort required is 50 kgf in the downward direction. (g = 10 N kg-1).
Calculate:
(i) Distance moved by the effort.
(ii) Work done by the effort.
(iii) M.A. of the pulley system.
(iv) Efficiency of the pulley system.
Answer
Given,
V.R. = 4
L = 175 kgf
dL = 15 m
E = 50 kgf
(i) V.R. =
Substituting the values we get,
(ii) Work done by the effort = E x dE
= 50 x 10 x 60
= 3 x 104
(iii) M.A. =
Substituting the values we get,
(iv) Efficiency η =
Substituting the values we get,
Question 6(ii)
(a) How a beam balance comes to static equilibrium?
(b) How a plane moves at a constant height? On which fact it is based?
Answer
(a) In beam balance when the beam is balanced in a horizontal position, it is in static equilibrium. The clockwise and anticlockwise moments balance each other hence the beam has no rotational motion and it is in static equilibrium.
(b) A plane moves at a constant height when upward lift on it balances its weight acting downwards. It is due to dynamic equilibrium of forces.
Question 6(iii)
(a) Calculate the work done when
I. a 20 kg weight is lifted 2 m vertically
II. a bike is moved on a rough road through 35 m against a frictional resistance of 20 N. (g = 9.8 ms-2 )
(b) What is the work done by a force when the force is:
I. normal to the displacement produced.
II. in the same direction as the displacement produced?
Answer
(a) I. Given:
Mass (m) = 20 kg
Distance (d) = Height = 2 m
Force of gravity on mass of 1 kg = 9.8 ms-2
Work done (W) = ?
Force (F) = mg = 20 x 9.8 = 196 N
Work done = Force x distance = 196 x 2 = 392 J
II. Given,
Resisting force = 20 N
Distance = 35 m
Work done = 35 x 20 = 700 J
(b) We know that, W = Fs cos θ
I. when force is normal to the displacement, θ = 90° hence,
W = Fs cos 90° = 0 [∵ cos 90° = 0]
II. when force is in the same direction as the displacement, θ = 0° hence,
W = Fs cos 0° = Fs [∵ cos 0° = 1]
Question 7(i)
A person standing in front of a cliff fires a gun and hears its echo after 3s. If the speed of sound in air is 336 ms-1
(a) Calculate the distance of the person from the cliff.
(b) After moving a certain distance from the cliff, he fires the gun again and this time the echo is heard 1.5 s later than the first. Calculate distance moved by the person.
Answer
(a) Let the distance of the cliff from the initial position of the person be x m.
Time after which echo is heard = 3 sec
So, the distance travelled by sound in 3 sec = 2x m
Speed of sound in air = 336 m/s
Distance = speed x time
Substituting the values we get,
∴ The initial distance of the person from the cliff is 504 m.
(b) As time taken to hear the echo is increased by 1.5 sec, hence, the person has moved away from the cliff.
Let the distance moved by the person from his initial position be y m.
Time after which echo is heard = 1.5 + 3 = 4.5 sec
New distance = 504 + y
So, the distance travelled by sound in 4.5 sec = 2(504 + y) m
Speed of sound in air = 336 m/s
Distance = speed x time
Substituting the values we get,
∴ Distance moved by the person = 252 m
Question 7(ii)
(a) After emission of an α-particle and two β-particles from an element 92P238, we get another element bRa. What is the relation between P and R ?
(b) Name the radiation which is used in carbon dating.
Answer
(a)
As P and R have same atomic number and different mass number hence they are called isotopes.
(c) β radiation is used in carbon dating.
Question 7(iii)
(a) Name the phenomenon involved in tuning a radio set to a particular station
(b) Define the phenomenon named by you in part (a) above.
(c) What do you understand by loudness of sound?
(d) In which unit is the loudness of sound measured?
Answer
(a) Resonance.
(b) Resonance is a special case of forced vibration. When the frequency of the externally applied periodic force on a body is equal to it's natural frequency, the body begins to vibrate with an increased amplitude. This phenomenon is known as resonance.
(c) Loudness is the characteristic by virtue of which a loud sound can be distinguished from a faint one, both having the same pitch and quality.
(d) The unit of loudness is phon. The level of sound is expressed in decibel (dB).
Question 8(i)
Hema uses two appliances in her home. One appliance is rated at 100 W and operates at 220 V, while the other appliance is rated at 60 W and also operates at 220 V. These appliances are connected to the electrical main supply in both series and parallel configurations, as shown in the figure 1 and 2.

(a) Calculate the total power consumption when the two appliances are connected in series.
(b) Calculate the total power consumption when the two appliances are corrected in parallel.
(c) Which configuration results in higher total power consumption, series or parallel?
Answer
(a) Given,
P1 = 100 W
P2 = 60 W
V = 220 V
We know, R1 =
=
=
= 484 Ω
R2 =
=
=
= 806.6 Ω
Total resistance = 484 + 806.6 = 1290.6 Ω
∴ Total power consumption in series = Ptotal =
= = 37.5 W
Hence, total power consumed = 37.5 W.
(b) When the appliances are connected in parallel,
Ptotal = P1 + P2 = 100 W + 60 W = 160 W
(c) Parallel configuration.
Question 8(ii)
(a) State two common properties of γ-rays and X-rays.
(b) Name two main sources of nuclear radiations. How are the nuclear radiations harmful?
Answer
(a) Both γ-rays and X-rays are
- electromagnetic rays.
- undeflected by electric and magnetic fields.
(b) Two main sources of nuclear radiations are:
- Radioactive fall out from nuclear plants — The nuclear power plants are now a major source of electricity in the world. If somehow, there is an accident in the reactor of power plant, a large amount of radioactive material and radiations will escape out into the atmosphere. This will not only affect the population around the plant, but will also affect the life at far off places where they will reach due to air currents.
- Nuclear waste — The nuclear waste are still very radioactive and are a source of harmful radiations therefore, they should not be dumped in the open garbage. They can contaminate water and soil and affect the human and living organisms.
The harmful biological effects of nuclear radiations are of three types:
- Short term recoverable effects like diarrhea, sore throat, loss of hair, nausea, etc.
- Long term irrecoverable effects like leukemia and cancer.
- Genetic effects that appear in the later generations of the person exposed to the radiation as the genes in the living cell get modified.
Question 8(iii)
Five resistors of different resistances are connected together as shown in the figure.
A 12 V battery is connected to the arrangement.

Calculate
(a) total resistance in the circuit.
(b) the total current flowing in the circuit.
Answer
(a) In the circuit, there are three parts. In the first part two resistors of 10 Ω and 40 Ω are connected in parallel. In parallel, the equivalent resistance is Rp, then
In the second part three resistors of 30, 20 and 60 Ω are connected in parallel. In parallel, the equivalent resistance is R'p, then
In the third part, Rp and R'p are in series, the equivalent resistance is R then 8 + 10 = 18 Ω
Hence, total resistance = 18 Ω
(b) From Ohm's Law : V = IR
Substituting the values we get, 12 = I x 18
∴ I = = 0.67 A.
Hence, total current = 0.67 A
Question 9(i)
An electric heater of power 780 W raises the temperature of 5.5 kg of a lab-chemical from 30°C to 41°C in 1.5 min.
Calculate
(a) energy supplied by heater,
(b) heat capacity and
(c) the specific heat capacity of the lab-chemical.
Answer
(a) Given,
t = 1.5 min
converting min to sec
1 min = 60 sec
so 1.5 min = 60 x 1.5 = 90 sec
Rise in temperature = 41 - 30 = 11°C
Mass of liquid = 5.5 kg
Energy supplied by heater (E) = P x t
E = 780 x 90 = 70200 J = 70.2 kJ
(b) From relation, Heat capacity (C)
C =
Substituting we get,
C = = 6381.8 J
(c) From formula, Specific heat capacity (s)
s =
Substituting we get,
s = = 1160.3 J
Question 9(ii)
If a block (made of lead) of mass 500 g at 127°C is heated in a furnace till it completely melts. Determine the quality of heat required.
(a) to bring the block upto its melting point.
(b) total heat energy required to melt the block to its melting point.
(c) total heat energy required.
(Take, melting point of lead = 327°C, specific heat capacity = 0.13 Jg-1°C-1 and specific latent heat of fusion = 26 Jg-1)
Answer
(a) Given,
Mass of lead = 500 g
Change in temperature of water = (327 - 127 ) = 200°C
specific heat capacity of lead = 0.13 Jg-1°C-1
specific latent heat of fusion = 26 Jg-1
melting point of lead = 327°C
Amount of heat required to raise its temperature :
mc△t = 500 x 0.13 x 200 = 13000 J = 13 kJ
(b) Heat required to melt the lead = mc = 500 x 26 = 13000 J = 13 kJ
(c) Therefore, total heat required = 13 + 13 = 26 kJ
Question 9(iii)
(a) List three methods of producing magnetic fields.
(b) Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field?
(c) Which rule is used to find the direction of magnetic field due to a current carrying conductor?
Answer
(a) Three methods are:
- Passing electric field through a straight conductor/circuit.
- Passing electric current through a circular loop.
- Passing electric current through a solenoid.
(b) According to Fleming's left hand rule, the direction of magnetic is vertically downwards, as the current is flowing in clockwise direction.
(c) Right hand thumb rule.