String Handling
A string is:
- A set of letters
- A set of letters and digits
- A set of letters, digits and special characters
- All the above
Answer
All the above
Reason — A string literal may consist of a set of letters, a set of letters and digits or a set of letters, digits and special characters.
A string internally creates:
- An integer array
- A numeric array
- A character array
- A double type array
Answer
A character array
Reason — String data type creates a character array to store a set of characters in different cells.
If a string contains 12 characters, what will be the index of the last character?
- 12
- 11
- 10
- 0
Answer
11
Reason — A String data type manages character array for storing a string character-wise starting from 0th subscript. Hence, the index number of the characters starts from 0 (zero) and ends with (k-1), if k is length of the string. Hence, the last index will be 11 (12-1), as 12 is the size of the string.
What will be the value stored in the variable 'c' if the following statement is executed?
c = "COMPUTER".charAt("COMPUTER ".indexOf('P'))
- 3
- 4
- P
- M
Answer
P
Reason — charAt(int index) returns a character from the given index of the string and indexOf(char ch) returns the index of first occurrence of a character in the string.
Since P is at 3rd position so indexOf('P') will return 3 and charAt(3) function will return the character at the third index i.e., 'P'. So, the given statement is solved as follows:
c = "COMPUTER".charAt("COMPUTER ".indexOf('P'))
⇒ c = "COMPUTER".charAt(3)
⇒ c = 'P'
Which of the following functions is used to remove leading and trailing white spaces from the string?
- trim( )
- trail( )
- truncate( )
- slice( )
Answer
trim( )
Reason — trim( ) function is used to remove leading and trailing white spaces from the string.
What will be the output of the following program snippet?
s1 = "COMPUTER";
s2 = "computer";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
- True
- False
- 0
- 1
Answer
False
Reason — equals() method treats uppercase and lowercase characters differently. So, the two strings will not be considered equal and the boolean value 'false' will be returned.
What will be the output of the following program snippet?
str1 = "AMAN";
str2 = "AMIT";
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));
- 8
- 0
- -8
- 2
Answer
-8
Reason — compareTo() returns a negative value if the first string is smaller than the second string in terms of the ASCII values of the corresponding characters.
"AMAN" and "AMIT" differ at the third character with 'A' and 'I', respectively. So, output of compareTo() method will be ASCII Code of 'A' - ASCII Code of 'I' ⇒ 65 - 73 ⇒ -8.
Which of the following packages contain string functions?
- java.awt
- java.string
- java.math
- java.lang
Answer
java.lang
Reason — Java Class Library contains a class called String which is available under java.lang package.
concat() method is used to join two strings.
The output of the following statement, when executed:
System.out.println("COMPUTER".charAt(4)); is U.
The output of the statement, when executed:
System.out.println("Object Oriented".length()); is 15.
Plus ( + ) operator is used to concatenate two strings.
String declaration is terminated by the symbol semicolon ( ; ).
Character literal is enclosed within single quotes (').
The return type of the statement equals( ) is boolean.
The output of "VIDYALAYA".substring(2,5) will result in DYA
To check whether a character(chr) is in upper case or not.
Answer
boolean res = Character.isUpperCase(chr);To compare two Strings(str1, str2) are same or not.
Answer
boolean res = str1.equals(str2);To extract the last character of a word(wd) stored in the variable chr.
Answer
char chr = wd.charAt(wd.length() - 1);To return the first occurrence of 'a' in the word "applications".
Answer
int res = "applications".indexOf('a');To replace the word "old" with the word "new" in a given String st = "old is always old"
Answer
String str = st.replace("old", "new");To check if the second character of a String(str) is in upper case.
Answer
boolean res = Character.isUpperCase(str.charAt(1));String str = "Computer Applications" + 1 + 0;
System.out.println("Understanding" + str);Answer
UnderstandingComputer Applications10In the first line, + operator concatenates 1 and 0 to the end of "Computer Applications" so str becomes "Computer Applications10". Next line prints "UnderstandingComputer Applications10" to the console.
String n1 = "46", n2 = "64";
int total = Integer.parseInt(n1) + Integer.parseInt(n2);
System.out.println("The sum of " + "46 " + "and" + " 64" + " is " + total);Answer
The sum of 46 and 64 is 110Integer.parseInt() method will convert the strings n1 and n2 to their corresponding numerical integers. So, 46 and 64 are added as numerical values and the result 110 is stored in int variable total.
boolean p;
p = ("BLUEJ".length() > "bluej".length()) ? true: false;Answer
falseBoth "BLUEJ" and "bluej" have the same length 5. So, condition of ternary operator is false and false is assigned to boolean variable p.
String str = "Information Technology";
int p;
p = str.indexOf('n');
System.out.println(p);Answer
1str.indexOf('n') will return the first index of n in str which is 1. So, the output of this program is 1.
String str1 = "Information Technology";
String str2 = "information technology";
boolean p = str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2);
System.out.println("The result is " + p);Answer
The result is truestr1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2) will do a case insensitive comparison of str1 and str2. As both strings contain the same characters if we ignore the case so it returns true which is stored in boolean variable p.
What do the following functions return?
String x = "Vision";
String y = "2020";
(a) System.out.println(x + y);
(b) System.out.println(x.length());
(c) System.out.println(x.charAt(3));
(d) System.out.println(x.equals(y));
Answer
(a) System.out.println(x + y);
Vision2020x and y are concatenated and printed.
(b) System.out.println(x.length());
6x.length() will give the number of characters in string x which is 6.
(c) System.out.println(x.charAt(3));
ix.charAt(3) will return the character at index 3 of string x which is i.
(d) System.out.println(x.equals(y));
falsex.equals(y) will return false as x and y contains different characters.
String S1 = "Computer World";
String S2 = "COMPUTER WORLD";
String S3 = "Computer world";
String S4 = "computer world";
System.out.println(S1 + " equals "+ S2 + " " + S1.equals(S2));
System.out.println(S1 + " equals "+ S3 + " " + S1.equals(S3));
System.out.println(S1 + " equals "+ S4 + " " + S1.equals(S4));
System.out.println(S1 + " equalsIgnoreCase "+ S4 + " " + S1.equalsIgnoreCase(S4));Answer
Computer World equals COMPUTER WORLD false
Computer World equals Computer world false
Computer World equals computer world false
Computer World equalsIgnoreCase computer world trueAs the strings S1, S2, S3 and S4 differ in the case of the characters so equals() method will return false but equalsIgnoreCase() method will return true.
If:
String x = "Computer";
String y = "Applications";
What do the following functions return?
(i) System.out.println(x.substring(1,5));
(ii) System.out.println(x.indexOf(x.charAt(4)));
(iii) System.out.println(y + x.substring(5));
(iv) System.out.println(x.equals(y));
Answer
(i) System.out.println(x.substring(1,5));
ompu
x.substring(1,5) will return a substring of x starting at index 1 till index 4 (i.e. 5 - 1 = 4).
(ii) System.out.println(x.indexOf(x.charAt(4)));
4
x.charAt(4) returns the character at index 4 of string x which is 'u'. First index of 'u' in x is 4 so output is 4.
(iii) System.out.println(y + x.substring(5));
Applicationster
x.substring(5) will return the substring of x starting at index 5 till the end of the string. It is "ter". This is added to the end of string y and printed to the console as output.
(iv) System.out.println(x.equals(y));
false
As strings x and y are not equal so x.equals(y) returns false.
Give the output of the following:
String n = "Computer Knowledge";
String m = "Computer Applications";
System.out.println(n.substring(0,8).concat(m.substring(9)));
System.out.println(n.endsWith("e"));Answer
ComputerApplications
truen.substring(0,8) returns the substring of n starting at index 0 till 7 (i.e. 8 - 1 = 7) which is "Computer". m.substring(9) returns the substring of m starting at index 9 till the end of the string which is "Applications". concat() method joins "Computer" and "Applications" together to give the output as ComputerApplications.
Give the output of the following statements:String x[] = {"SAMSUNG", "NOKIA", "SONY", "MICROMAX", "BLACKBERRY"};
(i) System.out.println(x[1]);
(ii) System.out.println(x[3].length());
Answer
(i) System.out.println(x[1]);
NOKIA
x[1] gives the second element of the array x which is "NOKIA"
(ii) System.out.println(x[3].length());
8
x[3].length() gives the number of characters in the fourth element of the array x.
Give the output of the following string functions:
(i) "ACHIEVEMENT".replace('E', 'A')
(ii) "DEDICATE".compareTo("DEVOTE")
Answer
(i) "ACHIEVEMENT".replace('E', 'A')
ACHIAVAMANT
All 'E's are replaced with 'A's.
(ii) "DEDICATE".compareTo("DEVOTE")
-18
"DEDICATE" and "DEVOTE" differ at the third character with 'D' and 'V', respectively. So, output of compareTo() method will be ASCII Code of 'D' - ASCII Code of 'V' ⇒ 68 - 86 ⇒ -18.
Consider the following String array and give the output
String arr[]= {"DELHI", "CHENNAI", "MUMBAI", "LUCKNOW", "JAIPUR"};
System.out.println(arr[0].length() > arr[3].length());
System.out.print(arr[4].substring(0,3));false
JAI
As length of the string "DELHI" is less than that of "LUCKNOW" so first output is false.arr[4].substring(0,3) will return the substring of "JAIPUR" starting at index 0 till index 2 (i.e. 3 - 1 = 2).
Your friend is trying to write a program to find and display the frequency of vowels in a string. Due to confusion in the syntax of some of the statements, he could not complete the program and has left some places blank marked with ?1?, ?2?, ?3? and ?4? to be filled with expression/function. The incomplete program is shown below:
import java.util.*;
class Vowels
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner ...?1?... = new Scanner(System.in);
String st;
int i, b, v = 0;
char chr;
System.out.println("Enter a string");
st = ............?2?............; // to input a string
st = ............?3?...........; // to convert the string into uppercase
b = st.length();
for( i = 0 ; i < b ; i++)
{
chr = ............?4?............; // to extract a character
if(chr == 'A' || chr == 'E' || chr == 'I' || chr == 'O' || chr == 'U')
v = v + 1;
}
System.out.println("No. of Vowels = " + v);
}
}Based on the above discussion, answer the following questions:
(a) What expression/function will be filled in place of ?1?
(b) What expression/function will be filled in place of ?2?
(c) What expression/function will be filled in place of ?3?
(d) What expression/function will be filled in place of ?4?
Answer
(a) in
(b) in.nextLine();
(c) st.toUpperCase();
(d) st.charAt(i);
The completed program is given below for reference:
import java.util.*;
class Vowels
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String st;
int i, b, v = 0;
char chr;
System.out.println("Enter a string");
st = in.nextLine(); // to input a string
st = st.toUpperCase(); // to convert the string into uppercase
b = st.length();
for( i = 0 ; i < b ; i++)
{
chr = st.charAt(i); // to extract a character
if(chr == 'A' || chr == 'E' || chr == 'I' || chr == 'O' || chr == 'U')
v = v + 1;
}
System.out.println("No. of Vowels = " + v);
}
}equals() and ==
Answer
| equals() | == |
|---|---|
| It is a method. | It is a relational operator. |
| It is used to check if the contents of two strings are same or not. | It is used to check if two variables refer to the same object in memory. |
| Example: String s1 = new String("hello"); String s2 = new String("hello"); boolean res = s1.equals(s2); System.out.println(res); The output of this code snippet is true as contents of s1 and s2 are the same. | Example: String s1 = new String("hello"); String s2 = new String("hello"); boolean res = s1 == s2; System.out.println(res); The output of this code snippet is false as s1 and s2 point to different String objects. |
compareTo() and equals()
Answer
| compareTo() | equals() |
|---|---|
| It compares two strings lexicographically. | It checks if contents of two strings are same or not. |
| The result is a negative, positive or zero integer value depending on whether the String object precedes, follows or is equal to the String argument. | The result is true if the contents are same otherwise it is false. |
toLowerCase() and toUpperCase()
Answer
| toLowerCase() | toUpperCase() |
|---|---|
| Converts all characters of the String object to lower case. | Converts all characters of the String object to upper case. |
| Example: String str = "HELLO"; System.out.println(str.toLowerCase()); Output of this code snippet will be hello. | Example: String str = "hello"; System.out.println(str.toUpperCase()); Output of this code snippet will be HELLO. |
charAt() and substring()
Answer
| charAt() | substring() |
|---|---|
| It returns a character from the string at the index specified as its argument. | It extracts a part of the string as specified by its arguments and returns the extracted part as a new string. |
| Its return type is char. | Its return type is String. |
| Example: String str = "Hello"; char ch = str.charAt(1); System.out.println(ch); Output of this code snippet is e. | Example: String str = "Hello"; String subStr = str.substring(1); System.out.println(subStr); Output of this code snippet is ello. |
What is exception? Name two exception handling blocks.
Answer
An exception is an event, which occurs during the execution of a program, that disrupts the normal flow of the program's instructions. Two exception handling blocks are try and catch.
State the purpose and return data type of the following String functions:
(a) indexOf( )
(b) compareTo( )
Answer
(a) indexOf( ) — It returns the index within the string of the first occurrence of the specified character or -1 if the character is not present. Its return type is int.
(b) compareTo( ) — It compares two strings lexicographically. It results in the difference of the ASCII codes of the corresponding characters. Its return type is int.
Write a statement for each to perform the following task on a string:
(i) Extract the second last character of a word stored in the variable wd.
(ii) Check if the second character of a string str is in upper case.
Answer
(i) Extract the second last character of a word stored in the variable wd.
char ch = wd.charAt(wd.length() - 2);(ii) Check if the second character of a string str is in upper case.
boolean res = Character.isUpperCase(str.charAt(1));Write a statement each to perform the following task on a string:
(i) Find and display the position of the last space in a string s.
(ii) Convert a number stored in a string variable x to double data type.
Answer
(i) Find and display the position of the last space in a string s.
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf(' '));(ii) Convert a number stored in a string variable x to double data type.
double a = Double.parseDouble(x);How does endsWith() and startsWith() differ? Explain with an example.
Answer
endsWith() tests if the string object ends with the string specified as its argument. startsWith() tests if the string object starts with the string specified as its argument. Consider the below example:
public class Example {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "ICSE Computer Applications";
System.out.println("Does " + str + " starts with ICSE? " + str.startsWith("ICSE"));
System.out.println("Does " + str + " ends with tions? " + str.endsWith("tions"));
}
}Here, both str.startsWith("ICSE") and str.endsWith("tions") returns 'true' as str starts with "ICSE" and ends with "tions".
toUpperCase()
Answer
It converts a string into upper case characters. If any character is already in uppercase or is a special character then it will remain same.
Syntax:
String <variable-name> = <string-variable>.toUpperCase();trim()
Answer
It removes all leading and trailing space from the string.
Syntax:
String <variable-name> = <string-variable>.trim();toLowerCase()
Answer
It converts a string into lowercase characters. If any character is already in lowercase or is a special character then it will remain same.
Syntax:
String <variable-name> = <string-variable>.toLowerCase();length()
Answer
It returns the length of the string i.e. the number of characters present in the string.
Syntax:
int <variable-name> = <string-variable>.length();replace()
Answer
It replaces a character with another character or a substring with another substring at all its occurrences in the given string.
Syntax:
String <variable-name> = <string-variable>.replace(<character or substring to replace>, <new character or substring>);compareTo()
Answer
It compares two strings lexicographically. It results in the difference of the ASCII codes of the corresponding characters. Its return type is int.
Syntax:
int <variable-name> = <string-variable>.compareTo(<string-variable2>);reverse()
Answer
It is a method of StringBuffer class and it is used to reverse the sequence of characters.
Syntax:
<StringBuffer-Variable>.reverse(); indexOf()
Answer
It returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified character within the string or -1 if the character is not present.
Syntax:
int <variable-name> = <string-variable>.indexOf(<character>);startWith()
Answer
It tests if the string object starts with the string specified as its argument.
Syntax:
boolean <variable-name> = <string-variable>.startWith(<string>);equalsIgnoreCase()
Answer
It ignores the case of the characters and checks if the contents of two strings are same or not.
Syntax:
boolean <variable-name> = <string-variable>.equalsIgnoreCase(<string>);Write a program to input a sentence. Find and display the following:
(i) Number of words present in the sentence
(ii) Number of letters present in the sentence
Assume that the sentence has neither include any digit nor a special character.
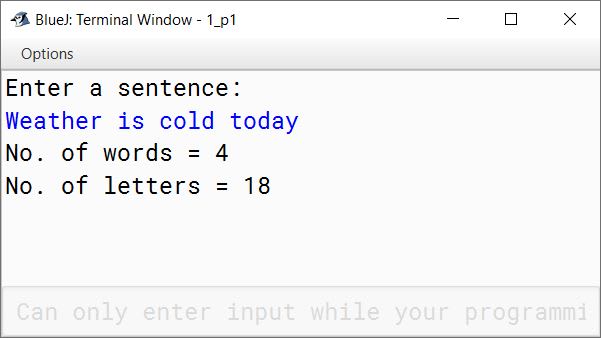
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatWordsNLetters
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a sentence:");
String str = in.nextLine();
int wCount = 0, lCount = 0;
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (ch == ' ')
wCount++;
else
lCount++;
}
/*
* Number of words in a sentence are one more than
* the number of spaces so incrementing wCount by 1
*/
wCount++;
System.out.println("No. of words = " + wCount);
System.out.println("No. of letters = " + lCount);
}
}
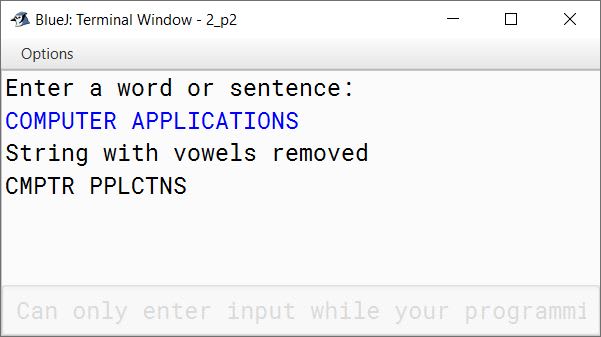
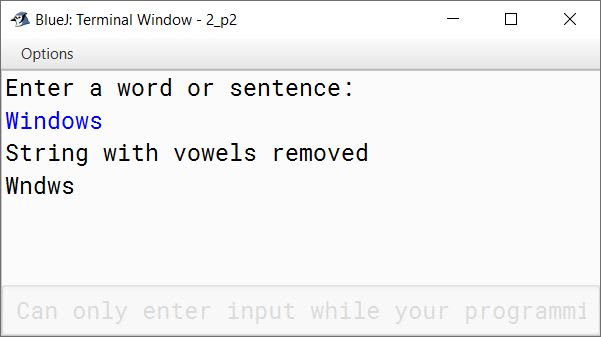
Write a program in Java to accept a word/a String and display the new string after removing all the vowels present in it.
Sample Input: COMPUTER APPLICATIONS
Sample Output: CMPTR PPLCTNS
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatVowelRemoval
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a word or sentence:");
String str = in.nextLine();
int len = str.length();
String newStr = "";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = Character.toUpperCase(str.charAt(i));
if (ch == 'A' ||
ch == 'E' ||
ch == 'I' ||
ch == 'O' ||
ch == 'U') {
continue;
}
newStr = newStr + ch;
}
System.out.println("String with vowels removed");
System.out.println(newStr);
}
}
Write a program in Java to accept a name(Containing three words) and display only the initials (i.e., first letter of each word).
Sample Input: LAL KRISHNA ADVANI
Sample Output: L K A
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatNameInitials
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a name of 3 or more words:");
String str = in.nextLine();
int len = str.length();
System.out.print(str.charAt(0) + " ");
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (ch == ' ') {
char ch2 = str.charAt(i + 1);
System.out.print(ch2 + " ");
}
}
}
}
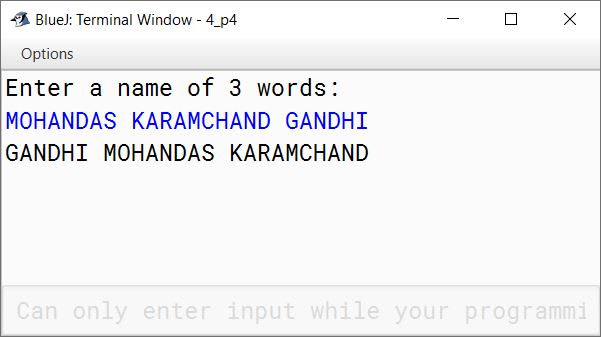
Write a program in Java to accept a name containing three words and display the surname first, followed by the first and middle names.
Sample Input: MOHANDAS KARAMCHAND GANDHI
Sample Output: GANDHI MOHANDAS KARAMCHAND
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSurnameFirst
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a name of 3 words:");
String name = in.nextLine();
/*
* Get the last index
* of space in the string
*/
int lastSpaceIdx = name.lastIndexOf(' ');
String surname = name.substring(lastSpaceIdx + 1);
String initialName = name.substring(0, lastSpaceIdx);
System.out.println(surname + " " + initialName);
}
}
Write a program in Java to enter a String/Sentence and display the longest word and the length of the longest word present in the String.
Sample Input: “TATA FOOTBALL ACADEMY WILL PLAY AGAINST MOHAN BAGAN”
Sample Output: The longest word: FOOTBALL: The length of the word: 8
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatLongestWord
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a word or sentence:");
String str = in.nextLine();
str += " "; //Add space at end of string
String word = "", lWord = "";
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (ch == ' ') {
if (word.length() > lWord.length())
lWord = word;
word = "";
}
else {
word += ch;
}
}
System.out.println("The longest word: " + lWord +
": The length of the word: " + lWord.length());
}
}
Write a program in Java to accept a word and display the ASCII code of each character of the word.
Sample Input: BLUEJ
Sample Output:
ASCII of B = 66
ASCII of L = 76
ASCII of U = 85
ASCII of E = 69
ASCII of J = 74
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatASCIICode
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a word:");
String word = in.nextLine();
int len = word.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = word.charAt(i);
System.out.println("ASCII of " + ch
+ " = " + (int)ch);
}
}
}
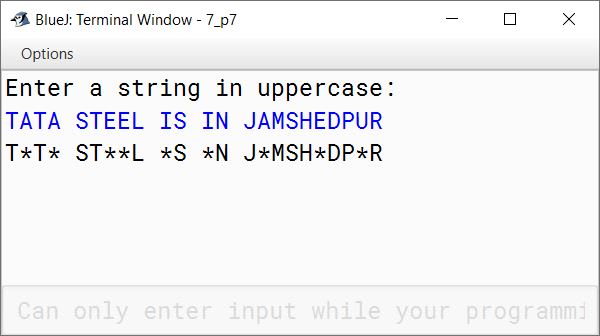
Write a program in Java to accept a String in upper case and replace all the vowels present in the String with Asterisk (*) sign.
Sample Input: "TATA STEEL IS IN JAMSHEDPUR"
Sample output: T*T* ST**L *S *N J*MSH*DP*R
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatVowelReplace
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a string in uppercase:");
String str = in.nextLine();
String newStr = "";
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (ch == 'A' ||
ch == 'E' ||
ch == 'I' ||
ch == 'O' ||
ch == 'U') {
newStr = newStr + '*';
}
else {
newStr = newStr + ch;
}
}
System.out.println(newStr);
}
}
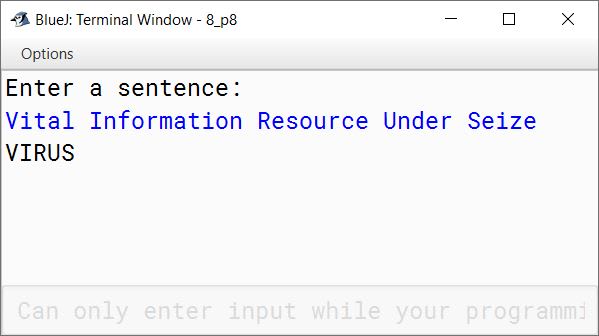
Write a program in Java to enter a sentence. Frame a word by joining all the first characters of each word of the sentence. Display the word.
Sample Input: Vital Information Resource Under Seize
Sample Output: VIRUS
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatFrameWord
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a sentence:");
String str = in.nextLine();
String word = "" + str.charAt(0);
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (ch == ' ')
word += str.charAt(i + 1);
}
System.out.println(word);
}
}
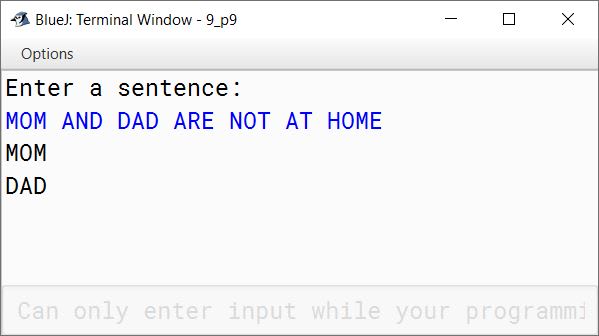
Write a program in Java to enter a sentence. Display the words which are only palindrome.
Sample Input: MOM AND DAD ARE NOT AT HOME
Sample Output: MOM
DAD
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatPalinWords
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a sentence:");
String str = in.nextLine();
str = str + " ";
String word = "";
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (ch == ' ') {
int wordLen = word.length();
boolean isPalin = true;
for (int j = 0; j < wordLen / 2; j++) {
if (word.charAt(j) != word.charAt(wordLen - 1 - j)) {
isPalin = false;
break;
}
}
if (isPalin)
System.out.println(word);
word = "";
}
else {
word += ch;
}
}
}
}
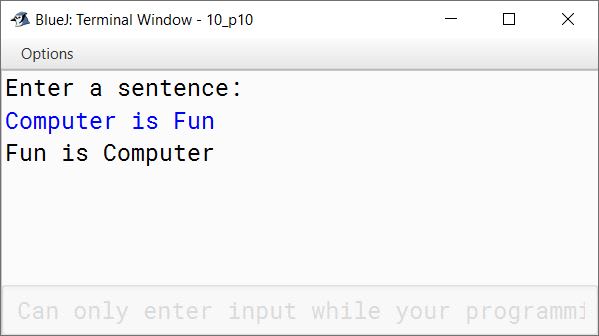
Write a program to accept a sentence. Display the sentence in reversing order of its word.
Sample Input: Computer is Fun
Sample Output: Fun is Computer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatReverseWords
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a sentence:");
String str = in.nextLine();
str = " " + str;
String word = "";
int len = str.length();
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (ch == ' ') {
System.out.print(word + " ");
word = "";
}
else {
word = ch + word;
}
}
}
}
Write a program to input a sentence and display the word of the sentence that contains maximum number of vowels.
Sample Input: HAPPY NEW YEAR
Sample Output: The word with maximum number of vowels: YEAR
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatMaxVowelWord
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a sentence:");
String str = in.nextLine();
str = str + " ";
String word = "", mWord = "";
int count = 0, maxCount = 0;
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = Character.toUpperCase(str.charAt(i));
if (ch == 'A' ||
ch == 'E' ||
ch == 'I' ||
ch == 'O' ||
ch == 'U') {
count++;
}
if (ch == ' ') {
if (count > maxCount) {
maxCount = count;
mWord = word;
}
word = "";
count = 0;
}
else {
word += ch;
}
}
System.out.println("The word with maximum number of vowels: "
+ mWord);
}
}
Consider the sentence as given below:
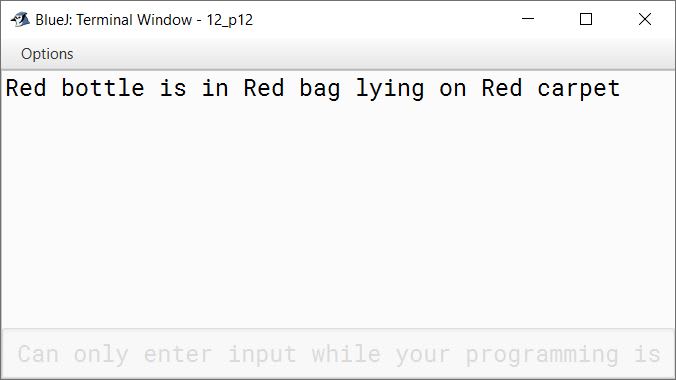
Blue bottle is in Blue bag lying on Blue carpet
Write a program to assign the given sentence to a string variable. Replace the word Blue with Red at all its occurrence. Display the new string as shown below:
Red bottle is in Red bag lying on Red carpet
public class KboatStringReplace
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "Blue bottle is in Blue bag lying on Blue carpet";
str += " ";
String newStr = "";
String word = "";
String target = "Blue";
String newWord = "Red";
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (ch == ' ') {
if (target.equals(word)) {
newStr = newStr + newWord + " ";
}
else {
newStr = newStr + word + " ";
}
word = "";
}
else {
word += ch;
}
}
System.out.println(newStr);
}
}
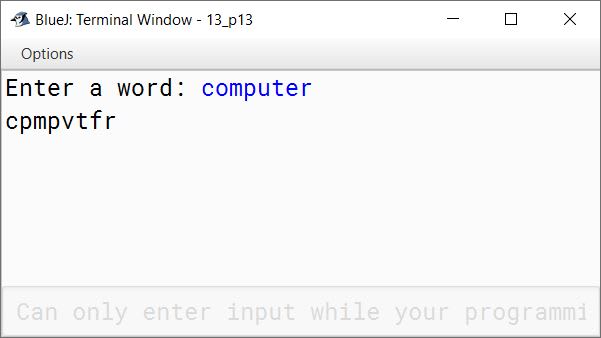
Write a program to accept a word and convert it into lower case, if it is in upper case. Display the new word by replacing only the vowels with the letter following it.
Sample Input: computer
Sample Output: cpmpvtfr
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatVowelReplace
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a word: ");
String str = in.nextLine();
str = str.toLowerCase();
String newStr = "";
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (str.charAt(i) == 'a' ||
str.charAt(i) == 'e' ||
str.charAt(i) == 'i' ||
str.charAt(i) == 'o' ||
str.charAt(i) == 'u') {
char nextChar = (char)(ch + 1);
newStr = newStr + nextChar;
}
else {
newStr = newStr + ch;
}
}
System.out.println(newStr);
}
}
Write a program to input a sentence. Create a new sentence by replacing each consonant with the previous letter. If the previous letter is a vowel then replace it with the next letter (i.e., if the letter is B then replace it with C as the previous letter of B is A). Other characters must remain the same. Display the new sentence.
Sample Input : ICC WORLD CUP
Sample Output : IBB VOQKC BUQ
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatReplaceLetters
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a sentence: ");
String str = in.nextLine();
int len = str.length();
String newStr = "";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
char chUp = Character.toUpperCase(ch);
if (chUp == 'A'
|| chUp == 'E'
|| chUp == 'I'
|| chUp == 'O'
|| chUp == 'U') {
newStr = newStr + ch;
}
else {
char prevChar = (char)(ch - 1);
char prevCharUp = Character.toUpperCase(prevChar);
if (prevCharUp == 'A'
|| prevCharUp == 'E'
|| prevCharUp == 'I'
|| prevCharUp == 'O'
|| prevCharUp == 'U') {
newStr = newStr + (char)(ch + 1);
}
else {
newStr = newStr + prevChar;
}
}
}
System.out.println(newStr);
}
}
A 'Happy Word' is defined as:
Take a word and calculate the word's value based on position of the letters in English alphabet. On the basis of word’s value, find the sum of the squares of its digits. Repeat the process with the resultant number until the number equals 1 (one). If the number ends with 1 then the word is called a 'Happy Word'.
Write a program to input a word and check whether it a ‘Happy Word’ or not. The program displays a message accordingly.
Sample Input: VAT
Place value of V = 22, A= 1, T = 20
[Hint: A = 1, B = 2, ----------, Z = 26]
Solution:
22120 ⇒ 22 + 22 + 12 + 22 + 02 = 13
⇒ 12 + 32 = 10
⇒ 12 + 02 = 1
Sample Output: A Happy Word
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatHappyWord
{
private static boolean isHappyNumber(long num) {
long sum = 0;
long n = num;
do {
sum = 0;
while (n != 0) {
int d = (int)(n % 10);
sum += d * d;
n /= 10;
}
n = sum;
} while (sum > 6);
return (sum == 1);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a word: ");
String word = in.next();
word = word.toUpperCase();
String wordValueStr = "";
int len = word.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
wordValueStr += String.valueOf(word.charAt(i) - 64);
}
long wordValue = Long.parseLong(wordValueStr);
boolean isHappy = isHappyNumber(wordValue);
if (isHappy)
System.out.println("A Happy Word");
else
System.out.println("Not a Happy Word");
}
}

Write a program to input a sentence. Count and display the frequency of each letter of the sentence in alphabetical order.
Sample Input: COMPUTER APPLICATIONS
Sample Output:
| Character | Frequency | Character | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2 | O | 2 |
| C | 2 | P | 3 |
| I | 1 | R | 1 |
| L | 2 | S | 1 |
| M | 1 | T | 2 |
| N | 1 | U | 1 |
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatLetterFreq
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a sentence:");
String str = in.nextLine();
str = str.toUpperCase();
int freqMap[] = new int[26];
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (Character.isLetter(ch)) {
int chIdx = ch - 65;
freqMap[chIdx]++;
}
}
System.out.println("Character\tFrequency");
for (int i = 0; i < freqMap.length; i++) {
if (freqMap[i] > 0) {
System.out.println((char)(i + 65)
+ "\t\t" + freqMap[i]);
}
}
}
}
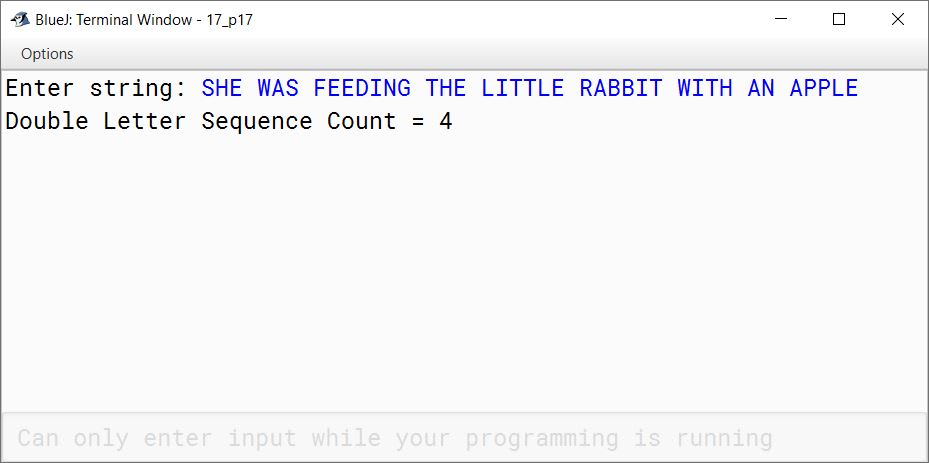
Write a program to accept a string. Convert the string into upper case letters. Count and output the number of double letter sequences that exist in the string.
Sample Input: "SHE WAS FEEDING THE LITTLE RABBIT WITH AN APPLE"
Sample Output: 4
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatLetterSeq
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter string: ");
String s = in.nextLine();
String str = s.toUpperCase();
int count = 0;
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
if (str.charAt(i) == str.charAt(i + 1))
count++;
}
System.out.println("Double Letter Sequence Count = " + count);
}
}
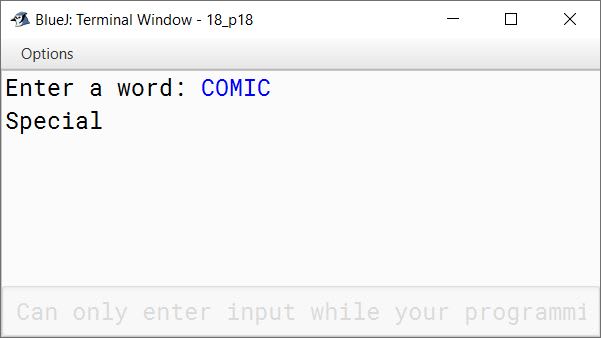
Special words are those words which start and end with the same letter.
Example: EXISTENCE, COMIC, WINDOW
Palindrome words are those words which read the same from left to right and vice-versa.
Example: MALYALAM, MADAM, LEVEL, ROTATOR, CIVIC
All palindromes are special words but all special words are not palindromes.
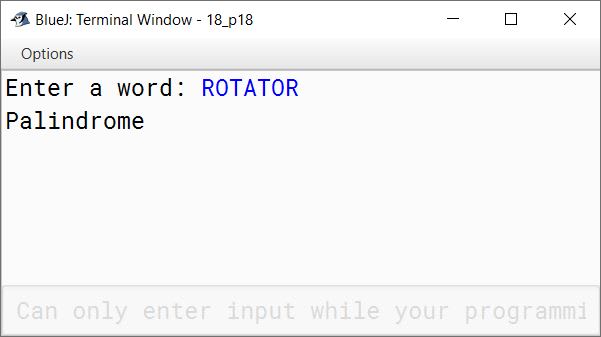
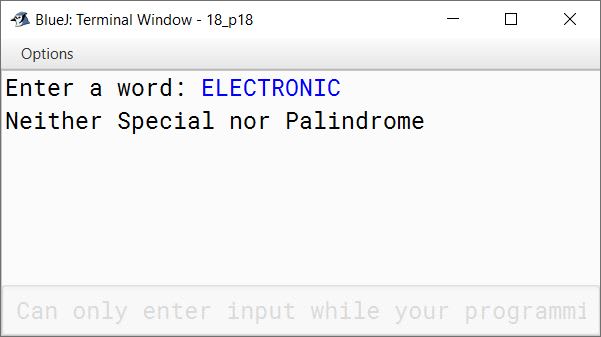
Write a program to accept a word. Check and display whether the word is a palindrome or only a special word or none of them.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSpecialPalindrome
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a word: ");
String str = in.next();
str = str.toUpperCase();
int len = str.length();
if (str.charAt(0) == str.charAt(len - 1)) {
boolean isPalin = true;
for (int i = 1; i < len / 2; i++) {
if (str.charAt(i) != str.charAt(len - 1 - i)) {
isPalin = false;
break;
}
}
if (isPalin) {
System.out.println("Palindrome");
}
else {
System.out.println("Special");
}
}
else {
System.out.println("Neither Special nor Palindrome");
}
}
}
Write a program to input a sentence. Convert the sentence into upper case letters. Display the words along with frequency of the words which have at least a pair of consecutive letters.
Sample Input: MODEM IS AN ELECTRONIC DEVICE
Sample Output:
MODEM
DEVICE
Number of words containing consecutive letters: 2
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatStringConsecutive
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the string: ");
String str = in.nextLine();
str = str.toUpperCase();
str += " ";
String word = "";
int count = 0;
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (str.charAt(i) == ' ') {
int wordLen = word.length();
for (int j = 0; j < wordLen - 1; j++) {
if (word.charAt(j) + 1 == word.charAt(j + 1)) {
count++;
System.out.println(word);
break;
}
}
word = "";
}
else {
word += str.charAt(i);
}
}
System.out.println("Number of words containing consecutive letters: " + count);
}
}
Write a program to accept a word (say, BLUEJ) and display the pattern:
(a)
B L U E J
B L U E
B L U
B L
B
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatStringPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a word: ");
String word = in.nextLine();
int len = word.length();
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
char ch = word.charAt(j);
System.out.print(ch);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(b)
J
E E
U U U
L L L L
B B B B B
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatStringPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a word: ");
String word = in.nextLine();
int len = word.length();
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = len - 1; j >= i; j--) {
char ch = word.charAt(i);
System.out.print(ch);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(c)
B L U E J
L U E J
U E J
E J
J
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatStringPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a word: ");
String word = in.nextLine();
int len = word.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < len; j++) {
char ch = word.charAt(j);
System.out.print(ch);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Write a program to display the pattern:
(a)
A B C D E
B C D E
C D E
D E
E
public class KboatStringPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
String word = "ABCDE";
int len = word.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < len; j++) {
char ch = word.charAt(j);
System.out.print(ch);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(b)
A
B C
D E F
G H I J
K L M N O
public class KboatStringPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
char ch = 'A';
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(ch++);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(c)
A B C D E
A B C D A
A B C A B
A B A B C
A A B C D
public class KboatStringPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
String word = "ABCDE";
int len = word.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < len - i; j++) {
System.out.print(word.charAt(j));
}
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++) {
System.out.print(word.charAt(k));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Write a program to generate a triangle or an inverted triangle till n terms based upon the User’s choice of the triangle to be displayed.
Example 1:
Input: Type 1 for a triangle and
Type 2 for an inverted triangle
Enter your choice 1
Enter the number of terms 5
Sample Output:
* * * * *
* * * *
* * *
* *
*Example 2:
Input: Type 1 for a triangle and
Type 2 for an inverted triangle
Enter your choice 2
Enter the number of terms 5
Sample Output:
A B C D E
A B C D
A B C
A B
Aimport java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatTriangleChoice
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Type 1 for a triangle and");
System.out.println("Type 2 for an inverted triangle of alphabets");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
int choice = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter the number of terms: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
System.out.print(' ');
}
for (int k = i; k <= n; k++) {
System.out.print('*');
}
System.out.println();
}
break;
case 2:
n += 64;
for (int i = n; i >= 65; i--) {
for (int j = 65; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print((char)j);
}
System.out.println();
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Incorrect choice");
break;
}
}
}

Write a program to generate a triangle or an inverted triangle based upon User’s choice.
Example 1:
Input: Type 1 for a triangle and
Type 2 for an inverted triangle
Enter your choice 1
Enter a word : BLUEJ
Sample Output:
B
L L
U U U
E E E E
J J J J J
Example 2:
Input: Type 1 for a triangle and
Type 2 for an inverted triangle
Enter your choice 2
Enter a word : BLUEJ
Sample Output:
B L U E J
B L U E
B L U
B L
B
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatTriangleMenu
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Type 1 for a triangle and");
System.out.println("Type 2 for an inverted triangle");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
int choice = in.nextInt();
in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter a word: ");
String word = in.nextLine();
int len = word.length();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(word.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
break;
case 2:
for(int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(word.charAt(j));
}
System.out.println();
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Incorrect choice");
break;
}
}
}

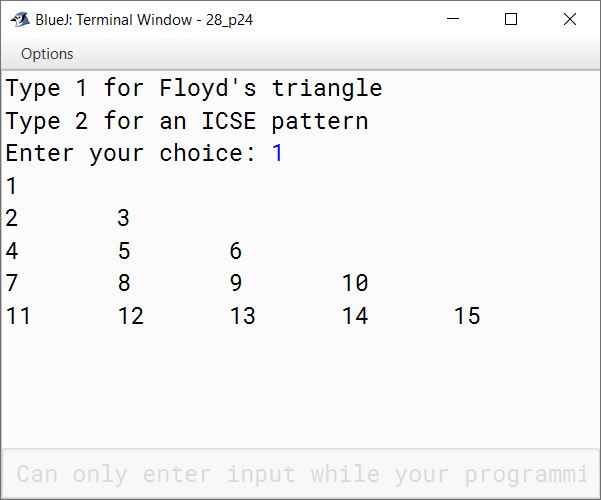
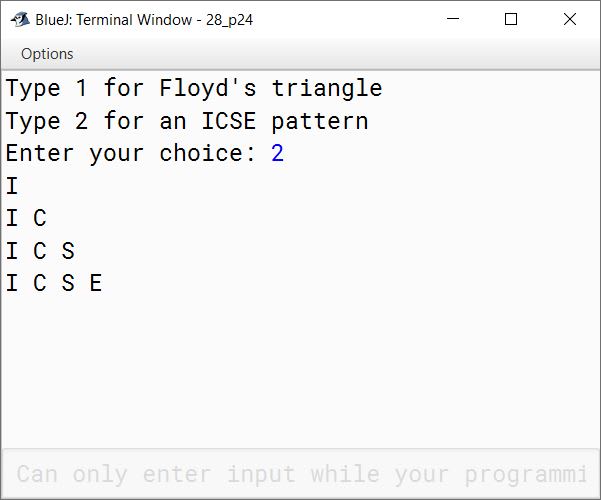
Using the switch statement, write a menu driven program for the following:
(a) To print the Floyd’s triangle:
1
2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15
(b) To display the following pattern:
I
I C
I C S
I C S E
For an incorrect option, an appropriate error message should be displayed.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Type 1 for Floyd's triangle");
System.out.println("Type 2 for an ICSE pattern");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
int ch = in.nextInt();
switch (ch) {
case 1:
int a = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(a++ + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
break;
case 2:
String s = "ICSE";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(s.charAt(j) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Incorrect Choice");
}
}
}
Write a program in Java to store 10 different country names and their capitals in two different Single Dimensional Arrays (SDA). Display the country names (that starts with a vowel) along with their capitals in the given format.
Country Names Capital
xxxx xxxx
xxxx xxxx
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatCountryCapital
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
final int SIZE = 10;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String countries[] = new String[SIZE];
String capitals[] = new String[SIZE];
System.out.println("Enter " + SIZE
+ " countries and their capitals");
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
System.out.print("Enter country name: ");
countries[i] = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter its capital: ");
capitals[i] = in.nextLine();
}
System.out.println("Country Names\t\tCapital");
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
char ch = Character.toUpperCase(countries[i].charAt(0));
if (ch == 'A' ||
ch == 'E' ||
ch == 'I' ||
ch == 'O' ||
ch == 'U') {
System.out.println(countries[i] + "\t\t" + capitals[i]);
}
}
}
}
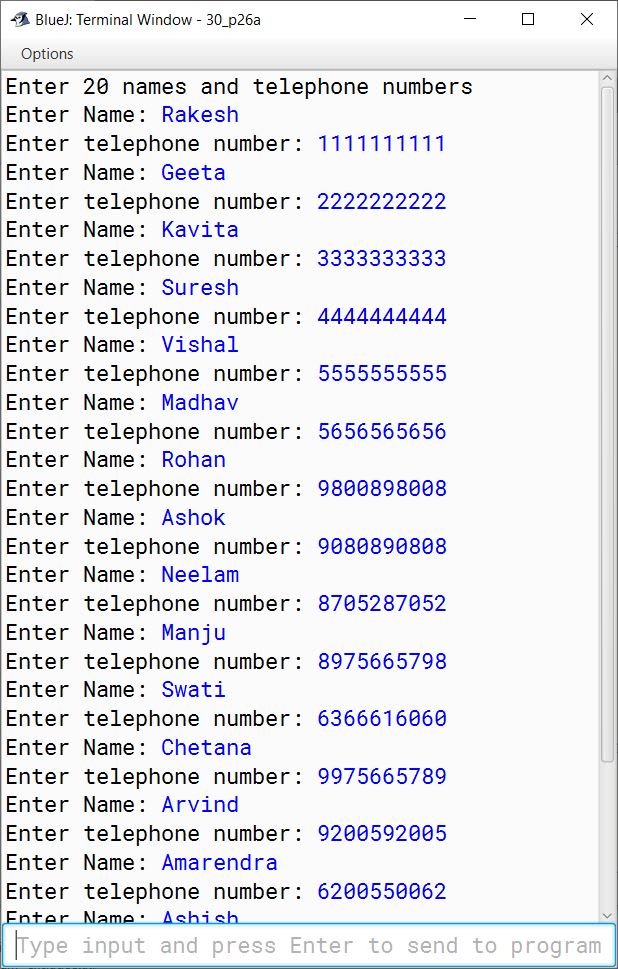
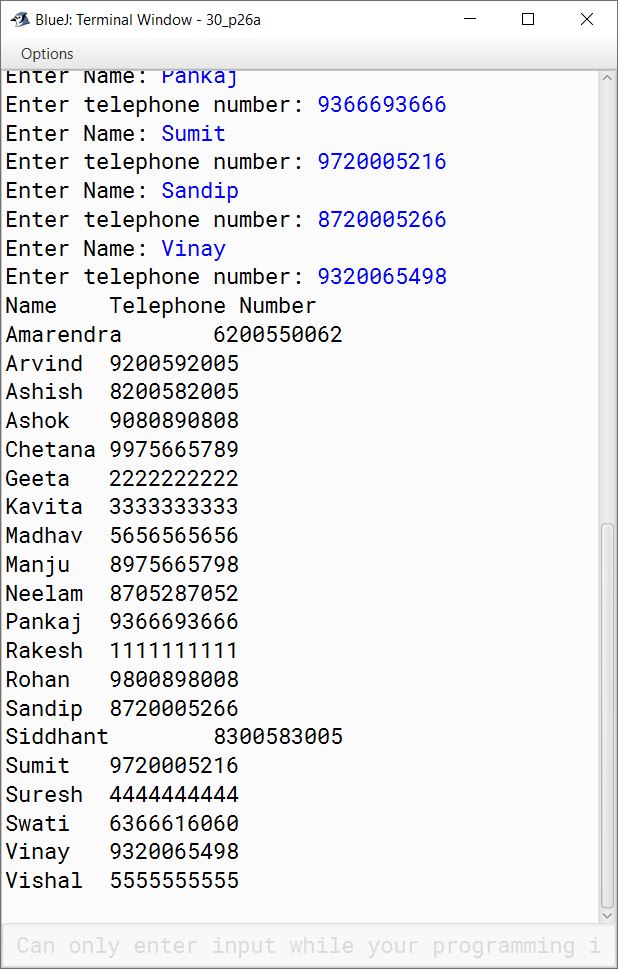
(a) Write a program in Java to store 20 different names and telephone numbers of your friends in two different Single Dimensional Arrays (SDA). Now arrange all the names in alphabetical order and display all the names along with their respective telephone numbers using selection sort technique.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatTelephoneBook
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
final int SIZE = 20;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String names[] = new String[SIZE];
long telNos[] = new long[SIZE];
System.out.println("Enter " + SIZE + " names and telephone numbers");
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
System.out.print("Enter Name: ");
names[i] = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter telephone number: ");
telNos[i] = in.nextLong();
in.nextLine();
}
//Selection Sort
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE - 1; i++) {
int min = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < SIZE; j++) {
if (names[j].compareToIgnoreCase(names[min]) < 0) {
min = j;
}
}
String temp = names[min];
names[min] = names[i];
names[i] = temp;
long t = telNos[min];
telNos[min] = telNos[i];
telNos[i] = t;
}
System.out.println("Name\tTelephone Number");
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
System.out.println(names[i] + "\t" + telNos[i]);
}
}
}
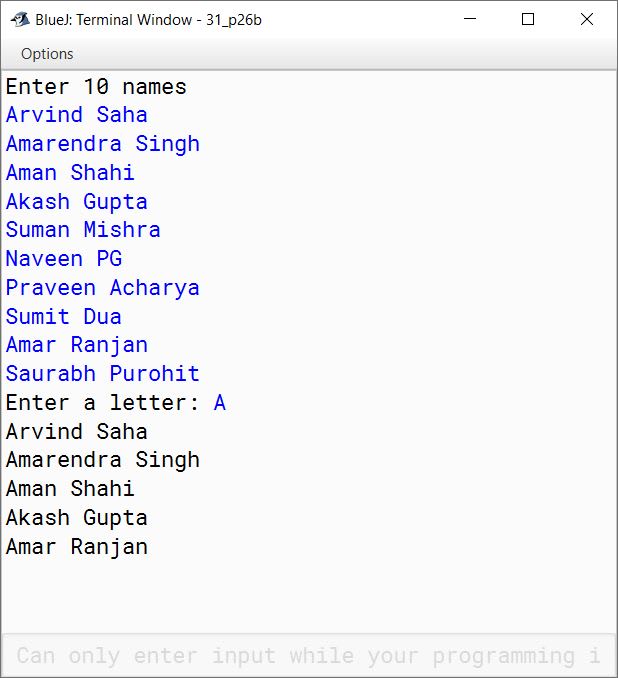
(b) Write a program to accept 10 names in a Single Dimensional Array (SDA). Display the names whose first letter matches with the letter entered by the user.
Sample Input:
Aman Shahi
Akash Gupta
Suman Mishra
and so on ..........
Sample Output:
Enter the alphabet: A
Aman Shahi
Akash Gupta
.....
.....
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSDANames
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String names[] = new String[10];
System.out.println("Enter 10 names");
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
names[i] = in.nextLine();
}
System.out.print("Enter a letter: ");
char ch = in.next().charAt(0);
ch = Character.toUpperCase(ch);
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
if (Character.toUpperCase(names[i].charAt(0)) == ch) {
System.out.println(names[i]);
}
}
}
}
Write a program to input twenty names in an array. Arrange these names in ascending order of letters, using the bubble sort technique.
Sample Input:
Rohit, Devesh, Indrani, Shivangi, Himanshu, Rishi, Piyush, Deepak, Abhishek, Kunal, .....
Sample Output:
Abhishek, Deepak, Devesh, Himanshu, Indrani, Kunal, Piyush, Rishi, Rohit, Shivangi, .....
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatArrangeNames
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String names[] = new String[20];
System.out.println("Enter 20 names:");
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
names[i] = in.nextLine();
}
//Bubble Sort
for (int i = 0; i < names.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < names.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (names[j].compareToIgnoreCase(names[j + 1]) > 0) {
String temp = names[j + 1];
names[j + 1] = names[j];
names[j] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("\nSorted Names");
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
System.out.println(names[i]);
}
}
}

Write a program in Java to input the names of 10 cities in a Single Dimensional Array. Display only those names which begin with a consonant but end with a vowel.
Sample Input: Kolkata, Delhi, Bengaluru, Jamshedpur, Bokaro, .......
Sample Output: Kolkata
Delhi
Bengaluru
Bokaro
....
....
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatCityName
{
public static boolean isVowel(char ch) {
char letter = Character.toUpperCase(ch);
if (letter == 'A' ||
letter == 'E' ||
letter == 'I' ||
letter == 'O' ||
letter == 'U')
return true;
return false;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
String cities[] = new String[10];
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter 10 city names");
for (int i = 0; i < cities.length; i++) {
cities[i] = in.nextLine();
}
System.out.println("\nCities starting with consonant & ending with vowel:");
for (int i = 0; i < cities.length; i++) {
if (!isVowel(cities[i].charAt(0)) &&
isVowel(cities[i].charAt(cities[i].length() - 1)))
System.out.println(cities[i]);
}
}
}
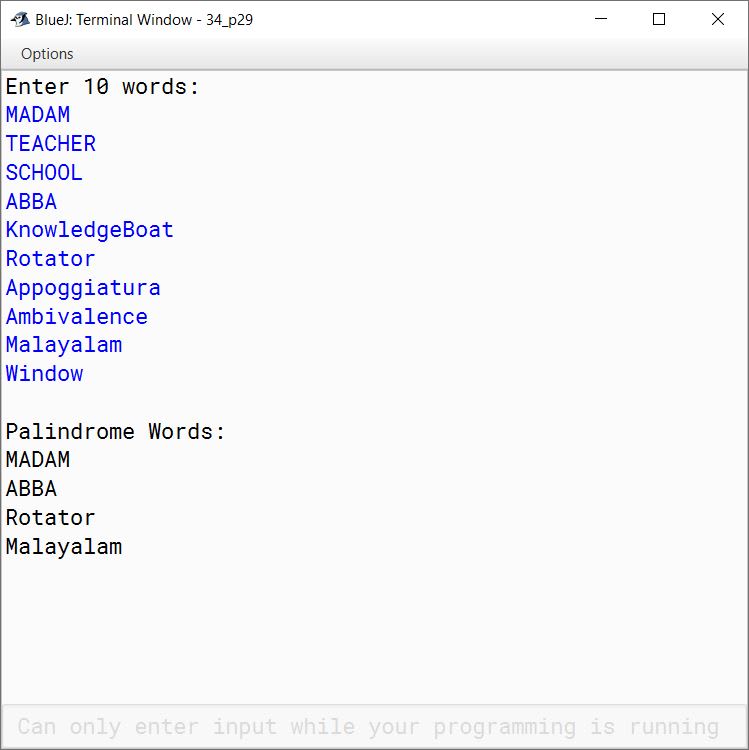
Write a program in Java to store 10 words in a Single Dimensional Array. Display only those words which are Palindrome.
Sample Input: MADAM, TEACHER, SCHOOL, ABBA, .........
Sample Output: MADAM
ABBA
..........
..........
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSDAPalindrome
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String words[] = new String[10];
System.out.println("Enter 10 words:");
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
words[i] = in.nextLine();
}
System.out.println("\nPalindrome Words:");
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
String str = words[i].toUpperCase();
int strLen = str.length();
boolean isPalin = true;
for (int j = 0; j < strLen / 2; j++) {
if (str.charAt(j) != str.charAt(strLen - 1 - j)) {
isPalin = false;
break;
}
}
if (isPalin)
System.out.println(words[i]);
}
}
}
Write a program to accept the names of 10 cities in a single dimensional string array and their STD (Subscribers Trunk Dialling) codes in another single dimension integer array. Search for the name of a city input by the user in the list. If found, display "Search Successful" and print the name of the city along with its STD code, or else display the message "Search unsuccessful, no such city in the list".
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatStdCodes
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
final int SIZE = 10;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String cities[] = new String[SIZE];
String stdCodes[] = new String[SIZE];
System.out.println("Enter " + SIZE +
" cities and their STD codes:");
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
System.out.print("Enter City Name: ");
cities[i] = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter its STD Code: ");
stdCodes[i] = in.nextLine();
}
System.out.print("Enter name of city to search: ");
String city = in.nextLine();
int idx;
for (idx = 0; idx < SIZE; idx++) {
if (city.compareToIgnoreCase(cities[idx]) == 0) {
break;
}
}
if (idx < SIZE) {
System.out.println("Search Successful");
System.out.println("City: " + cities[idx]);
System.out.println("STD Code: " + stdCodes[idx]);
}
else {
System.out.println("Search Unsuccessful");
}
}
}