Class as the Basis of All Computation
Which keyword makes class members accessible outside the class in which they are declared?
- Private
- Protected
- Public
- Hidden
Answer
Public
Reason — Public keyword makes class members accessible outside the class in which they are declared.
Find the access specifier which prohibits a class member from being used outside a class:
- Private
- Public
- Protected
- None
Answer
Private
Reason — Private prohibits a class member from being used outside a class.
A class object is also known as:
- Identifier
- Instance variable
- Specifier
- Modifier
Answer
Instance variable
Reason — A class object is also known as instance variable.
Which of the following statements is the most appropriate for the private members?
- They are visible out of the class in which they are defined.
- They can be used in the sub-classes.
- They are only visible in the class in which they are declared.
- None of the above.
Answer
They are only visible in the class in which they are declared.
Reason — Private data members and member methods can only be used within the scope of a class.
Which of the following keywords are used to control access to a class member?
- Default
- Abstraction
- Protected
- Interface
Answer
Protected
Reason — The access specifier 'protected' is used to control access to a class member.
Which of the members can be accessed globally?
- Private
- Public
- Protected
- All of the above
Answer
Public
Reason — Public data members can be accessed globally.
The maximum number of objects of a class can be created as:
- 1
- 2
- On the user's choice
- Number of variables
Answer
On the user's choice
Reason — A user can create any number of objects of a class.
A class contains:
- Attributes and methods
- A number of object of same types
- Data and member function
- All of the above
Answer
All of the above
Reason — A class contains attributes and methods, a number of object of same types, data and member functions.
Which of the following features is not the principle of OOP?
- Encapsulation
- Transparency
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
Answer
Transparency
Reason — Transparency is not the principle of OOP.
A package is a:
- collection of data.
- collection of functions.
- collection of classes.
- a nested class.
Answer
collection of classes.
Reason — A package is a collection of classes.
Primitive data types are also called as fundamental data types.
A user defined data type can be created by using a/an object.
this keyword represents the current object in the member method.
public members are accessible from anywhere in the program.
If no access specifier is mentioned then default specifier is referred by default.
private members are accessible only within the same class.
protected members are accessible in its own class as well as in a sub class.
Given below is a class based program to accept name and price of an article and find the amount after 12% discount if the price exceeds 10,000 otherwise, discount is nil. There are some places in the program left blank marked with ?1?, ?2?, ?3? and ?4? to be filled with appropriate keyword/expression.
class Discount
(
int pr; double d, amt; String nm;
Scanner ob = ...?1?... Scanner(System.in);
void input( ) {
System.out.println("Enter customer's name:");
nm = ...?2?... ;
System.out.println("Enter price of the article:");
pr = ob.nextInt( );
}
void calculate() {
if (...?3?...)
d= ...?4?... ;
else
d = 0;
amt = pr - d;
}
void print() {
System.out.println("Name =" + nm);
System.out.println("Amount to be paid=" + amt);
}
}Based on the above discussion, answer the following questions:
(a) What will be keyword /expression filled in place of ?1?
(b) What will be keyword/expression filled in place of ?2?
(c) What will be keyword /expression filled in place of ?3?
(d) What will be keyword /expression filled in place of ?4?
Answer
(a) new
(b) ob.nextLine()
(c) pr > 10000
(d) 12.0 / 100.0 * pr
The complete program is as follows:
class Discount
(
int pr; double d, amt; String nm;
Scanner ob = new Scanner(System.in);
void input( ) {
System.out.println("Enter customer's name:");
nm = ob.nextLine();
System.out.println("Enter price of the article:");
pr = ob.nextInt( );
}
void calculate() {
if (pr > 10000)
d= 12.0 / 100.0 * pr;
else
d = 0;
amt = pr - d;
}
void print() {
System.out.println("Name =" + nm);
System.out.println("Amount to be paid=" + amt);
}
}Why is a class known as composite data type?
Answer
A composite data type is one which is composed with various primitive data types. A class can contain various primitive data types as its data members so it is known as a composite data type.
Name the types of data used in a class.
Answer
The types of data used in a class are as follows:
- Access Specifiers
- Instance Variables
- Class Variables
- Local Variables
- Constructors
- Member Methods
What is the purpose of the new operator?
Answer
The purpose of new operator is to instantiate an object of the class by dynamically allocating memory for it.
Can a class be referred to as user defined data type?
Answer
Yes, a class be referred to as user defined data type since a class is created by the user.
What is public access of a class?
Answer
When a class is declared with public access specifier it is said that the class is publicly accessible. A publicly accessible class is visible everywhere both within and outside its package. For example:
public class Example {
//Class definition
}How are private members of a class different from public members?
Answer
The private members of a class are accessible only within the class in which they are declared while the public members of the class are accessible both within and outside their class.
Mention any two attributes required for class declaration.
Answer
Two attributes required for class declaration are the keyword 'class' and the name of the class.
Explain instance variables. Give an example.
Answer
Variables that are declared inside a class without using the keyword 'static' and outside any member methods are termed instance variables. Each object of the class gets its own copy of instance variables. Consider the example given below:
class Cuboid {
private double height;
private double width;
private double depth;
private double volume;
public void input(int h, int w, int d) {
height = h;
width = w;
depth = d;
}
public void computeVolume() {
volume = height * width * depth;
System.out.println("Volume = " + volume);
}
}Here, the data members — height, width, depth and volume are instance variables.
Explain any two types of access specifiers.
Answer
Two types of access specifiers are as follows:
private — A data member or member method declared as private is only accessible inside the scope of a class in which it is declared.
public — A data member or member method declared as public is accessible inside as well as outside of the class in which it is declared.
What is meant by private visibility of a method?
Answer
A member method of a class declared with private access specifier is said to have private visibility. Only the member methods of its own class can call this method.
'Object is an instance of a class.' Explain this statement.
Answer
Class is a blueprint of an object. When a class is defined, it doesn't acquire any space in memory, it is only the attributes that must be common to all the objects of that class. Moreover, when an object of a class is created, it includes instance variables described within the class. This is the reason why an object is called an instance of a class.
Differentiate between built-in data types and user defined data types.
Answer
| Built-In Data Types | User Defined Data Types |
|---|---|
| Built-In Data Types are fundamental data types defined by Java language specification. | User Defined Data Types are created by the user. |
| Sizes of Built-In Data Types are fixed. | Sizes of User Defined data types depend upon their constituent members. |
| Built-In Data Types are available in all parts of a Java program. | Availability of User Defined data types depends upon their scope. |
| Built-In Data Types are independent components. | User Defined data types are composed of Built-In Data Types. |
Which of the following declarations are illegal and why?
(a) class abc{...}
(b) public class NumberOfDaysWorked{...}
(c) private int x;
(d) private class abc{...}
(e) default key getkey(...)
Answer
(a) Legal
(b) Legal
(c) Legal
(d) Illegal — only 'public' or no access specifier are allowed for class declaration
(e) Illegal — member method can't be explicitly marked 'default'
Why can't every class be termed as user defined data type?
Answer
The classes that contain public static void main(String args[]) method are not considered as user defined data type. Only the classes that don't contain this method are called user defined data type. The presence of public static void main(String args[]) method in a class, converts it into a Java application so it is not considered as a user defined data type.
Differentiate between static data members and non-static data members.
Answer
| Static Data Members | Non-Static Data Members |
|---|---|
| They are declared using keyword 'static'. | They are declared without using keyword 'static'. |
| All objects of a class share the same copy of static data members. | Each object of the class gets its own copy of non-static data members. |
| They can be accessed using the class name or object. | They can be accessed only through an object of the class. |
Differentiate between private and protected visibility modifiers.
Answer
Private members are only accessible inside the class in which they are defined and they cannot be inherited by derived classes. Protected members are also only accessible inside the class in which they are defined but they can be inherited by derived classes.
Differentiate between instance variable and class variable.
Answer
| Instance Variable | Class Variable |
|---|---|
| They are declared without using keyword 'static'. | They are declared using keyword 'static'. |
| Each object of the class gets its own copy of instance variables. | All objects of a class share the same copy of class variables. |
| They can be accessed only through an object of the class. | They can be accessed using the class name or object. |
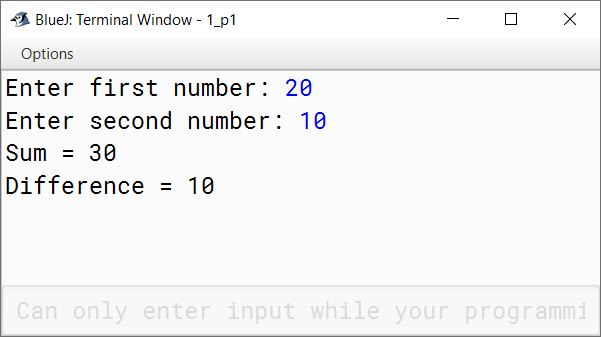
Define a class Calculate to accept two numbers as instance variables. Use the following member methods for the given purposes:
Class name — Calculate
Data members — int a, int b
Member methods:
void inputdata() — to input both the values
void calculate() — to find sum and difference
void outputdata() — to print sum and difference of both the numbers
Use a main method to call the functions.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Calculate
{
private int a;
private int b;
private int sum;
private int diff;
public void inputdata() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter first number: ");
a = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter second number: ");
b = in.nextInt();
}
public void calculate() {
sum = a + b;
diff = a - b;
}
public void outputdata() {
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
System.out.println("Difference = " + diff);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Calculate obj = new Calculate();
obj.inputdata();
obj.calculate();
obj.outputdata();
}
}
Define a class Triplet with the following specifications:
Class name — Triplet
Data Members — int a, int b, int c
Member Methods:
void getdata() — to accept three numbers
void findprint() — to check and display whether the numbers are Pythagorean Triplets or not.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Triplet
{
private int a;
private int b;
private int c;
public void getdata() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a: ");
a = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter b: ");
b = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter c: ");
c = in.nextInt();
}
public void findprint() {
if ((Math.pow(a, 2) + Math.pow(b, 2)) == Math.pow(c, 2)
|| (Math.pow(b, 2) + Math.pow(c, 2)) == Math.pow(a, 2)
|| (Math.pow(a, 2) + Math.pow(c, 2)) == Math.pow(b, 2))
System.out.print("Numbers are Pythagorean Triplets");
else
System.out.print("Numbers are not Pythagorean Triplets");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Triplet obj = new Triplet();
obj.getdata();
obj.findprint();
}
}

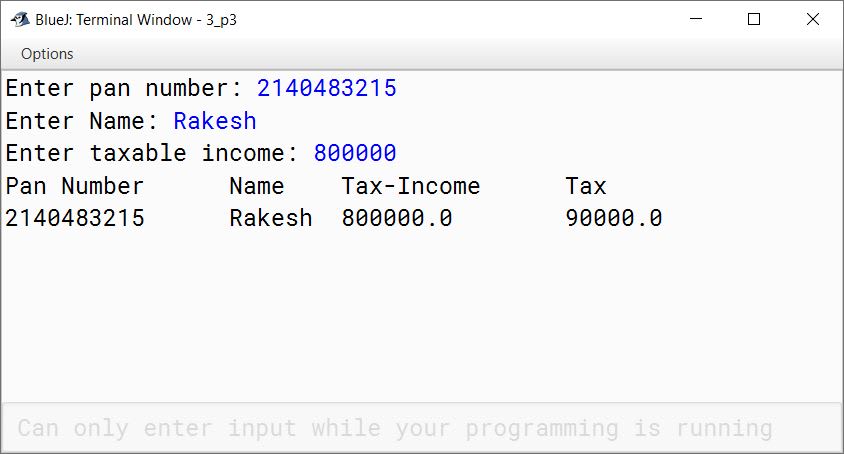
Define a class Employee having the following description:
Class name : Employee
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| int pan | To store personal account number |
| String name | To store name |
| double taxincome | To store annual taxable income |
| double tax | To store tax that is calculated |
| Member functions | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void input() | Store the pan number, name, taxable income |
| void cal() | Calculate tax on taxable income |
| void display() | Output details of an employee |
Calculate tax based on the given conditions and display the output as per the given format.
| Total Annual Taxable Income | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to ₹2,50,000 | No tax |
| From ₹2,50,001 to ₹5,00,000 | 10% of the income exceeding ₹2,50,000 |
| From ₹5,00,001 to ₹10,00,000 | ₹30,000 + 20% of the income exceeding ₹5,00,000 |
| Above ₹10,00,000 | ₹50,000 + 30% of the income exceeding ₹10,00,000 |
Output:
Pan Number Name Tax-Income Tax
.......... .... .......... ...
.......... .... .......... ...import java.util.Scanner;
public class Employee
{
private int pan;
private String name;
private double taxincome;
private double tax;
public void input() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter pan number: ");
pan = in.nextInt();
in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter Name: ");
name = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter taxable income: ");
taxincome = in.nextDouble();
}
public void cal() {
if (taxincome <= 250000)
tax = 0;
else if (taxincome <= 500000)
tax = (taxincome - 250000) * 0.1;
else if (taxincome <= 1000000)
tax = 30000 + ((taxincome - 500000) * 0.2);
else
tax = 50000 + ((taxincome - 1000000) * 0.3);
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Pan Number\tName\tTax-Income\tTax");
System.out.println(pan + "\t" + name + "\t"
+ taxincome + "\t" + tax);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Employee obj = new Employee();
obj.input();
obj.cal();
obj.display();
}
}
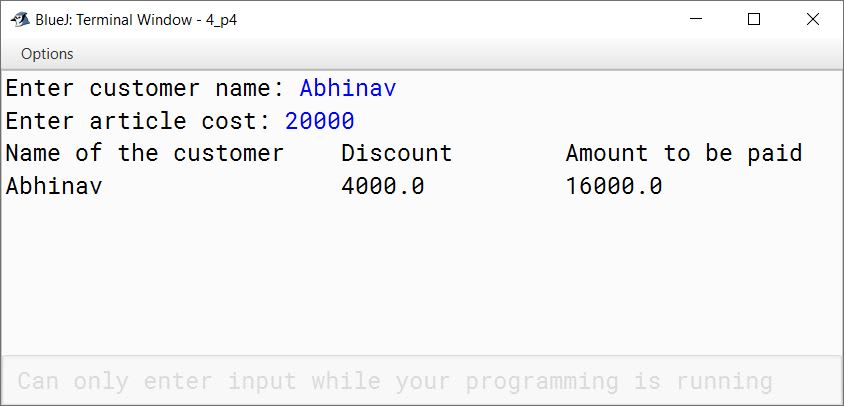
Define a class Discount having the following description:
Class name : Discount
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| int cost | to store the price of an article |
| String name | to store the customer's name |
| double dc | to store the discount |
| double amt | to store the amount to be paid |
| Member methods | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void input() | Stores the cost of the article and name of the customer |
| void cal() | Calculates the discount and amount to be paid |
| void display() | Displays the name of the customer, cost, discount and amount to be paid |
Write a program to compute the discount according to the given conditions and display the output as per the given format.
| List Price | Rate of discount |
|---|---|
| Up to ₹5,000 | No discount |
| From ₹5,001 to ₹10,000 | 10% on the list price |
| From ₹10,001 to ₹15,000 | 15% on the list price |
| Above ₹15,000 | 20% on the list price |
Output:
Name of the customer Discount Amount to be paid
.................... ........ .................
.................... ........ .................import java.util.Scanner;
public class Discount
{
private int cost;
private String name;
private double dc;
private double amt;
public void input() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter customer name: ");
name = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter article cost: ");
cost = in.nextInt();
}
public void cal() {
if (cost <= 5000)
dc = 0;
else if (cost <= 10000)
dc = cost * 0.1;
else if (cost <= 15000)
dc = cost * 0.15;
else
dc = cost * 0.2;
amt = cost - dc;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Name of the customer\tDiscount\tAmount to be paid");
System.out.println(name + "\t" + dc + "\t" + amt);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Discount obj = new Discount();
obj.input();
obj.cal();
obj.display();
}
}
Define a class Telephone having the following description:
Class name : Telephone
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| int prv, pre | to store the previous and present meter readings |
| int call | to store the calls made (i.e. pre - prv) |
| String name | to store name of the consumer |
| double amt | to store the amount |
| double total | to store the total amount to be paid |
| Member functions | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void input() | Stores the previous reading, present reading and name of the consumer |
| void cal() | Calculates the amount and total amount to be paid |
| void display() | Displays the name of the consumer, calls made, amount and total amount to be paid |
Write a program to compute the monthly bill to be paid according to the given conditions and display the output as per the given format.
| Calls made | Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to 100 calls | No charge |
| For the next 100 calls | 90 paise per call |
| For the next 200 calls | 80 paise per call |
| More than 400 calls | 70 paise per call |
However, every consumer has to pay ₹180 per month as monthly rent for availing the service.
Output:
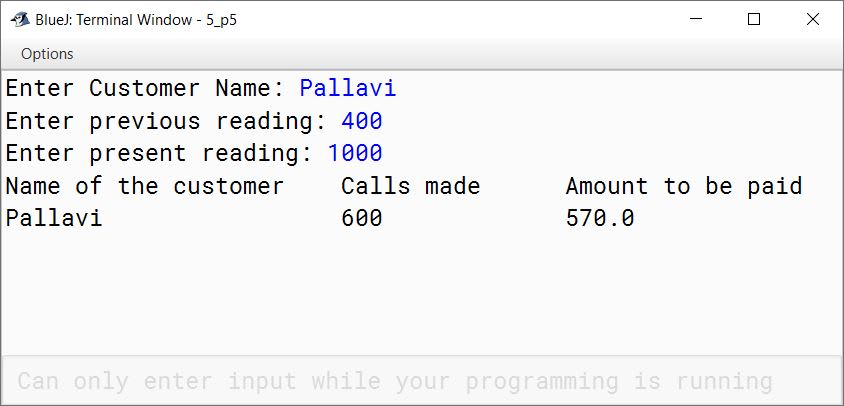
Name of the customer Calls made Amount to be paid
.................... .......... .................
.................... .......... .................import java.util.Scanner;
public class Telephone
{
private int prv;
private int pre;
private int call;
private String name;
private double amt;
private double total;
public void input() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter Customer Name: ");
name = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter previous reading: ");
prv = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter present reading: ");
pre = in.nextInt();
}
public void cal() {
call = pre - prv;
if (call <= 100)
amt = 0;
else if (call <= 200)
amt = (call - 100) * 0.9;
else if (call <= 400)
amt = (100 * 0.9) + (call - 200) * 0.8;
else
amt = (100 * 0.9) + (200 * 0.8) + ((call - 400) * 0.7);
total = amt + 180;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Name of the customer\tCalls made\tAmount to be paid");
System.out.println(name + "\t" + call + "\t" + total);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Telephone obj = new Telephone();
obj.input();
obj.cal();
obj.display();
}
}
Define a class Interest having the following description:
Class name : Interest
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| int p | to store principal (sum) |
| int r | to store rate |
| int t | to store time |
| double interest | to store the interest to be paid |
| double amt | to store the amount to be paid |
| Member functions | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void input() | Stores the principal, rate, time |
| void cal() | Calculates the interest and amount to be paid |
| void display() | Displays the principal, interest and amount to be paid |
Write a program to compute the interest according to the given conditions and display the output.
| Time | Rate of interest |
|---|---|
| For 1 year | 6.5% |
| For 2 years | 7.5% |
| For 3 years | 8.5% |
| For 4 years or more | 9.5% |
(Note: Time to be taken only in whole years)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Interest
{
private int p;
private float r;
private int t;
private double interest;
private double amt;
public void input() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter principal: ");
p = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter time: ");
t = in.nextInt();
}
public void cal() {
if (t == 1)
r = 6.5f;
else if (t == 2)
r = 7.5f;
else if (t == 3)
r = 8.5f;
else
r = 9.5f;
interest = (p * r * t) / 100.0;
amt = p + interest;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Principal: " + p);
System.out.println("Interest: " + interest);
System.out.println("Amount Payable: " + amt);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Interest obj = new Interest();
obj.input();
obj.cal();
obj.display();
}
}
Define a class Library having the following description:
Class name : Library
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| String name | to store name of the book |
| int price | to store the printed price of the book |
| int day | to store the number of days for which fine is to be paid |
| double fine | to store the fine to be paid |
| Member functions | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void input() | To accept the name of the book and printed price of the book |
| void cal() | Calculates the fine to be paid |
| void display() | Displays the name of the book and fine to be paid |
Write a program to compute the fine according to the given conditions and display the fine to be paid.
| Days | Fine |
|---|---|
| First seven days | 25 paise per day |
| Eight to fifteen days | 40 paise per day |
| Sixteen to thirty days | 60 paise per day |
| More than thirty days | 80 paise per day |
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Library
{
private String name;
private int price;
private int day;
private double fine;
public void input() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter name of the book: ");
name = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter printed price of the book: ");
price = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("For how many days fine needs to be paid: ");
day = in.nextInt();
}
public void cal() {
if (day <= 7)
fine = day * 0.25;
else if (day <= 15)
fine = (7 * 0.25) + ((day - 7) * 0.4);
else if (day <= 30)
fine = (7 * 0.25) + (8 * 0.4) + ((day - 15) * 0.6);
else
fine = (7 * 0.25) + (8 * 0.4) + (15 * 0.6) + ((day - 30) * 0.8);
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Name of the book: " + name);
System.out.println("Fine to be paid: " + fine);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Library obj = new Library();
obj.input();
obj.cal();
obj.display();
}
}
Bank charges interest for the vehicle loan as given below:
| Number of years | Rate of interest |
|---|---|
| Up to 5 years | 15% |
| More than 5 and up to 10 years | 12% |
| Above 10 years | 10% |
Write a program to model a class with the specifications given below:
Class name: Loan
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| int time | Time for which loan is sanctioned |
| double principal | Amount sanctioned |
| double rate | Rate of interest |
| double interest | To store the interest |
| double amt | Amount to pay after given time |
| Member Methods | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void getdata() | To accept principal and time |
| void calculate() | To find interest and amount. Interest = (Principal*Rate*Time)/100 Amount = Principal + Interest |
| void display() | To display interest and amount |
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Loan
{
private int time;
private double principal;
private double rate;
private double interest;
private double amt;
public void getdata() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter principal: ");
principal = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter time: ");
time = in.nextInt();
}
public void calculate() {
if (time <= 5)
rate = 15.0;
else if (time <= 10)
rate = 12.0;
else
rate = 10.0;
interest = (principal * rate * time) / 100.0;
amt = principal + interest;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Interest = " + interest);
System.out.println("Amount Payable = " + amt);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Loan obj = new Loan();
obj.getdata();
obj.calculate();
obj.display();
}
}
Hero Honda has increased the cost of its vehicles as per the type of the engine using the following criteria:
| Type of Engine | Rate of increment |
|---|---|
| 2 stroke | 10% of the cost |
| 4 stroke | 12% of the cost |
Write a program by using a class to find the new cost as per the given specifications:
Class name: Honda
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| int type | To accept type of engine 2 stroke or 4 stroke |
| int cost | To accept previous cost |
| Member Methods | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void gettype() | To accept the type of engine and previous cost |
| void find() | To find the new cost as per the criteria given above |
| void printcost() | To print the type and new cost of the vehicle |
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Honda
{
private int type;
private int cost;
private double newCost;
public void gettype() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter type: ");
type = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter cost: ");
cost = in.nextInt();
}
public void find() {
switch (type) {
case 2:
newCost = cost + (cost * 0.1);
break;
case 4:
newCost = cost + (cost * 0.12);
break;
default:
System.out.println("Incorrect type");
break;
}
}
public void printcost() {
System.out.println("Type: " + type);
System.out.println("New cost: " + newCost);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Honda obj = new Honda();
obj.gettype();
obj.find();
obj.printcost();
}
}
Define a class called 'Mobike' with the following specifications:
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| int bno | To store the bike number |
| int phno | To store the phone number of the customer |
| String name | To store the name of the customer |
| int days | To store the number of days the bike is taken on rent |
| int charge | To calculate and store the rental charge |
| Member Methods | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void input() | To input and store the details of the customer |
| void compute() | To compute the rental charge |
| void display() | To display the details in the given format |
The rent for a mobike is charged on the following basis:
| Days | Charge |
|---|---|
| For first five days | ₹500 per day |
| For next five days | ₹400 per day |
| Rest of the days | ₹200 per day |
Output:
Bike No. Phone No. Name No. of days Charge
xxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxx xxx xxxxxx import java.util.Scanner;
public class Mobike
{
private int bno;
private int phno;
private int days;
private int charge;
private String name;
public void input() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter Customer Name: ");
name = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter Customer Phone Number: ");
phno = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter Bike Number: ");
bno = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter Number of Days: ");
days = in.nextInt();
}
public void compute() {
if (days <= 5)
charge = days * 500;
else if (days <= 10)
charge = (5 * 500) + ((days - 5) * 400);
else
charge = (5 * 500) + (5 * 400) + ((days - 10) * 200);
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Bike No.\tPhone No.\tName\tNo. of days \tCharge");
System.out.println(bno + "\t" + phno + "\t" + name + "\t" + days
+ "\t" + charge);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Mobike obj = new Mobike();
obj.input();
obj.compute();
obj.display();
}
}
Write a program using a class with the following specifications:
Class name: Caseconvert
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| String str | To store the string |
| Member Methods | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void getstr() | to accept a string |
| void convert() | to obtain a string after converting each upper case letter into lower case and vice versa |
| void display() | to print the converted string |
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Caseconvert
{
private String str;
private String convStr;
public void getstr() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the string: ");
str = in.nextLine();
}
public void convert() {
char arr[] = new char[str.length()];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if (Character.isUpperCase(str.charAt(i)))
arr[i] = Character.toLowerCase(str.charAt(i));
else if (Character.isLowerCase(str.charAt(i)))
arr[i] = Character.toUpperCase(str.charAt(i));
else
arr[i] = str.charAt(i);
}
convStr = new String(arr);
}
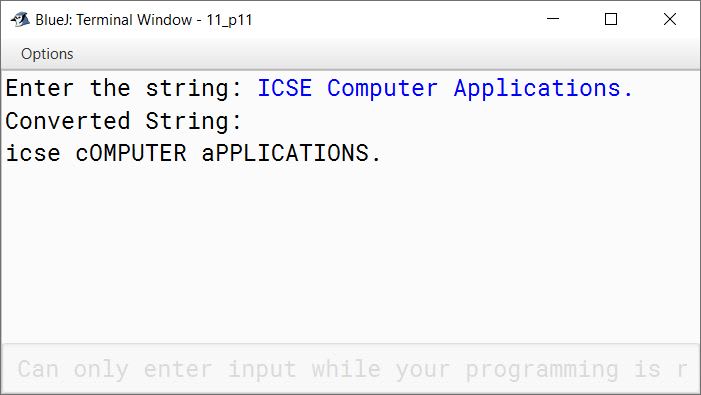
public void display() {
System.out.println("Converted String:");
System.out.println(convStr);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Caseconvert obj = new Caseconvert();
obj.getstr();
obj.convert();
obj.display();
}
}
Write a program by using a class with the following specifications:
Class name: Vowel
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| String s | To store the string |
| int c | To count vowels |
| Member Methods | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void getstr() | to accept a string |
| void getvowel() | to count the number of vowels |
| void display() | to print the number of vowels |
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Vowel
{
private String s;
private int c;
public void getstr() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the string: ");
s = in.nextLine();
}
public void getvowel() {
String temp = s.toUpperCase();
c = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < temp.length(); i++) {
char ch = temp.charAt(i);
if (ch == 'A' || ch == 'E' || ch == 'I' || ch == 'O'
|| ch == 'U')
c++;
}
}
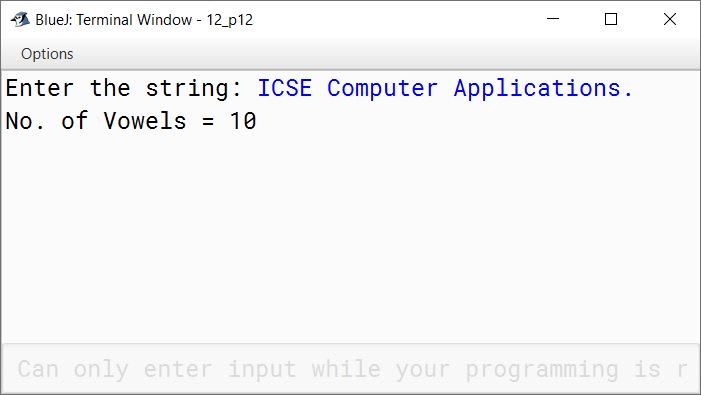
public void display() {
System.out.println("No. of Vowels = " + c);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Vowel obj = new Vowel();
obj.getstr();
obj.getvowel();
obj.display();
}
}
A bookseller maintains record of books belonging to the various publishers. He uses a class with the specifications given below:
Class name — Stock
Data Members:
- String title — Contains title of the book
- String author — Contains author name
- String pub — Contains publisher's name
- int noc — Number of copies
Member Methods:
- void getdata() — To accept title, author, publisher's name and the number of copies.
- void purchase(int t, String a, String p, int n) — To check the existence of the book in the stock by comparing total, author's and publisher's name. Also check whether noc >n or not. If yes, maintain the balance as noc-n, otherwise display book is not available or stock is under flowing.
Write a program to perform the task given above.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Stock
{
private String title;
private String author;
private String pub;
private int noc;
public void getdata() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter book title: ");
title = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter book author: ");
author = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter book publisher: ");
pub = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter no. of copies: ");
noc = in.nextInt();
}
public void purchase(String t, String a, String p, int n) {
if (title.equalsIgnoreCase(t) &&
author.equalsIgnoreCase(a) &&
pub.equalsIgnoreCase(p)) {
if (noc > n) {
noc -= n;
System.out.println("Updated noc = " + noc);
}
else {
System.out.println("Stock is under flowing");
}
}
else {
System.out.println("Book is not available");
}
}
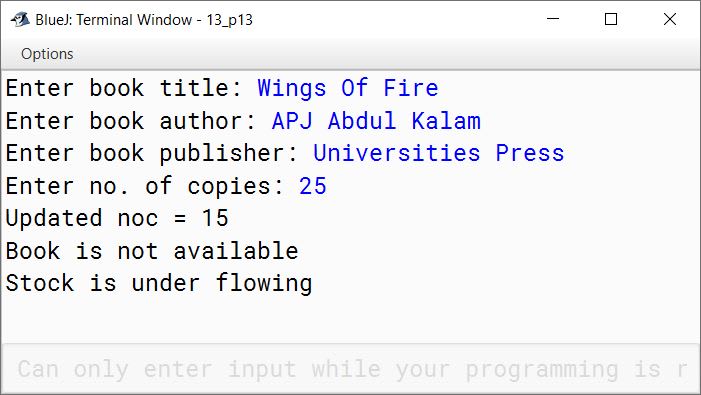
public static void main(String args[]) {
Stock obj = new Stock();
obj.getdata();
obj.purchase("wings of fire", "APJ Abdul Kalam",
"universities press", 10);
obj.purchase("Ignited Minds", "APJ Abdul Kalam",
"Penguin", 5);
obj.purchase("wings of fire", "APJ Abdul Kalam",
"universities press", 20);
}
}
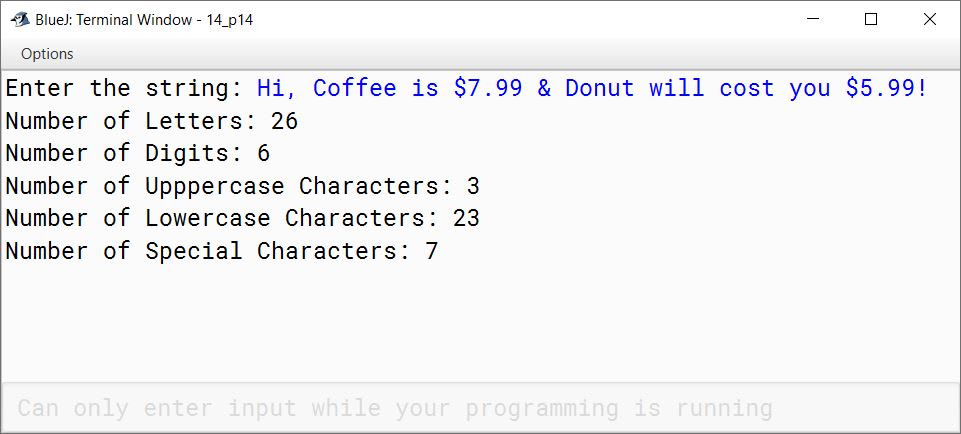
Write a program by using class with the following specifications:
Class name — Characters
Data Members:
- String str — To store the string
Member Methods:
- void input (String st) — to assign st to str
- void check_print() — to check and print the following:
(i) number of letters
(ii) number of digits
(iii) number of uppercase characters
(iv) number of lowercase characters
(v) number of special characters
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Characters
{
private String str;
public void input(String st) {
str = st;
}
public void check_print() {
int cLetters = 0, cDigits = 0, cUpper = 0, cLower = 0,
cSpecial = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') {
cLetters++;
cUpper++;
}
else if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
cLetters++;
cLower++;
}
else if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
cDigits++;
}
else if (!Character.isWhitespace(ch)) {
cSpecial++;
}
}
System.out.println("Number of Letters: " + cLetters);
System.out.println("Number of Digits: " + cDigits);
System.out.println("Number of Upppercase Characters: "
+ cUpper);
System.out.println("Number of Lowercase Characters: "
+ cLower);
System.out.println("Number of Special Characters: "
+ cSpecial);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the string: ");
String s = in.nextLine();
Characters obj = new Characters();
obj.input(s);
obj.check_print();
}
}
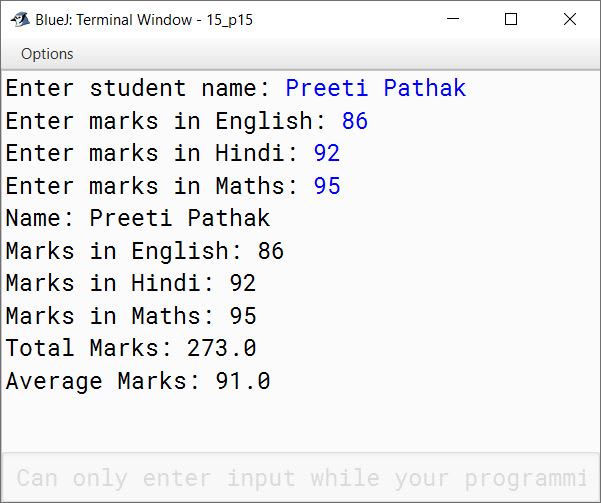
Define a class Student with the following specifications:
Class Name : Student
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| String name | To store the name of the student |
| int eng | To store marks in English |
| int hn | To store marks in Hindi |
| int mts | To store marks in Maths |
| double total | To store total marks |
| double avg | To store average marks |
| Member Methods | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void accept() | To input marks in English, Hindi and Maths |
| void compute() | To calculate total marks and average of 3 subjects |
| void display() | To show all the details viz. name, marks, total and average |
Write a program to create an object and invoke the above methods.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Student
{
private String name;
private int eng;
private int hn;
private int mts;
private double total;
private double avg;
public void accept() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter student name: ");
name = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter marks in English: ");
eng = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter marks in Hindi: ");
hn = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter marks in Maths: ");
mts = in.nextInt();
}
public void compute() {
total = eng + hn + mts;
avg = total / 3.0;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Marks in English: " + eng);
System.out.println("Marks in Hindi: " + hn);
System.out.println("Marks in Maths: " + mts);
System.out.println("Total Marks: " + total);
System.out.println("Average Marks: " + avg);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student obj = new Student();
obj.accept();
obj.compute();
obj.display();
}
}
Define a class called ParkingLot with the following description:
Class name : ParkingLot
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| int vno | To store the vehicle number |
| int hours | To store the number of hours the vehicle is parked in the parking lot |
| double bill | To store the bill amount |
| Member Methods | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void input( ) | To input the vno and hours |
| void calculate( ) | To compute the parking charge at the rate ₹3 for the first hour or the part thereof and ₹1.50 for each additional hour or part thereof. |
| void display() | To display the detail |
Write a main method to create an object of the class and call the above methods.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ParkingLot
{
private int vno;
private int hours;
private double bill;
public void input() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter vehicle number: ");
vno = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter hours: ");
hours = in.nextInt();
}
public void calculate() {
if (hours <= 1)
bill = 3;
else
bill = 3 + (hours - 1) * 1.5;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Vehicle number: " + vno);
System.out.println("Hours: " + hours);
System.out.println("Bill: " + bill);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
ParkingLot obj = new ParkingLot();
obj.input();
obj.calculate();
obj.display();
}
}
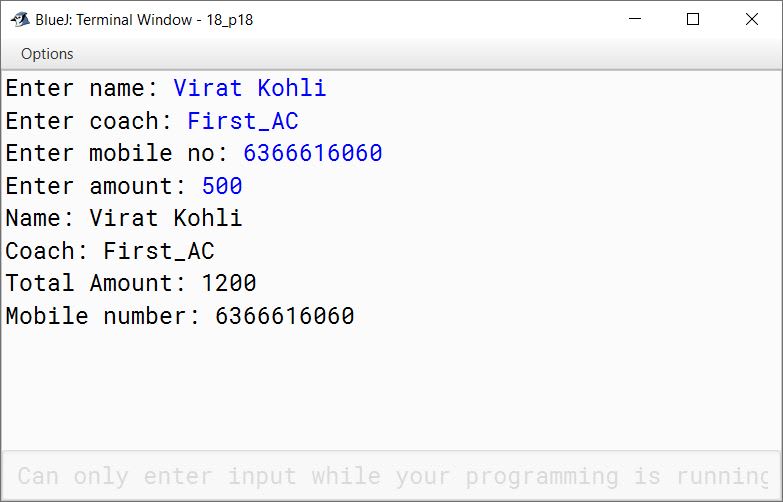
Design a class RailwayTicket with following description:
Class name : RailwayTicket
| Data Members | Purpose |
|---|---|
| String name | To store the name of the customer |
| String coach | To store the type of coach customer wants to travel |
| long mob no | To store customer's mobile number |
| int amt | To store basic amount of ticket |
| int totalamt | To store the amount to be paid after updating the original amount |
| Member Methods | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void accept() | To take input for name, coach, mobile number and amount |
| void update() | To update the amount as per the coach selected (extra amount to be added in the amount as per the table below) |
| void display() | To display all details of a customer such as name, coach, total amount and mobile number |
| Type of Coaches | Amount |
|---|---|
| First_AC | ₹700 |
| Second_AC | ₹500 |
| Third_AC | ₹250 |
| Sleeper | None |
Write a main method to create an object of the class and call the above member methods.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RailwayTicket
{
private String name;
private String coach;
private long mobno;
private int amt;
private int totalamt;
private void accept() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter name: ");
name = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter coach: ");
coach = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter mobile no: ");
mobno = in.nextLong();
System.out.print("Enter amount: ");
amt = in.nextInt();
}
private void update() {
if(coach.equalsIgnoreCase("First_AC"))
totalamt = amt + 700;
else if(coach.equalsIgnoreCase("Second_AC"))
totalamt = amt + 500;
else if(coach.equalsIgnoreCase("Third_AC"))
totalamt = amt + 250;
else if(coach.equalsIgnoreCase("Sleeper"))
totalamt = amt;
}
private void display() {
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Coach: " + coach);
System.out.println("Total Amount: " + totalamt);
System.out.println("Mobile number: " + mobno);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
RailwayTicket obj = new RailwayTicket();
obj.accept();
obj.update();
obj.display();
}
}