Nested Loop
A loop within another loop is called a:
- double loop
- embedded loop
- circular loop
- nested loop
Answer
nested loop
Reason — A loop within another loop is called a nested loop.
The ............... break is used to terminate the outer loop from the block of inner loop.
- level
- labelled
- unlabelled
- forced
Answer
labelled
Reason — The labelled break is used to terminate the outer loop from the block of inner loop.
Which of the following keywords can be used to terminate a switch case as well as a loop construct?
- continue
- void
- break
- stop
Answer
break
Reason — break can be used to terminate a switch case as well as a loop construct.
Given: for(i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++)
for(j = 1 ; j < 4 ; j++)
...............
Statement
...............
How many times the above nested loop will iterate?
- 12 times
- 8 times
- 4 times
- 16 times
Answer
12 times
Reason — The outer loop will execute 4 times. For each iteration of outer loop, the inner loop will execute 3 times. Therefore, total iterations of nested loop will be 4 x 3 = 12 times. The below table summarizes the iteration of nested loops:
| Value of i | Value of j |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | 1 |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | 1 |
| 2 | |
| 3 |
Which of the following statements is not valid for a nested loop?
- The break statement can be used to terminate inner as well as outer loop.
- The outer loop can be terminated from the block of inner loop.
- The inner loop can be terminated from the block of outer loop.
- The inner loop repeats the execution a number of times for each iteration of the outer loop.
Answer
The inner loop can be terminated from the block of outer loop.
Reason — The inner loop cannot be terminated from the block of outer loop.
Nested loop contains a single loop.
False
When break statement is applied, it terminates the loop.
True
The outer loop follows next iteration when iterations of inner loop is over.
True
Nested loop means the using of two or more loops in a program.
False
Labelled break statement allows the next iteration of the loop from any place of looping structure.
False
In a nested loop, break and continue can be used simultaneously.
False
What is a nested loop?
Answer
When we use a loop within another loop, it is said to be a nested loop. The inner loop repeats a number of times for each repetition of the outer loop.
Write down the syntax of a nested for loop.
Answer
The syntax of nested loop is as follows:
for (<initial value>; <test condition>; <update value>) {
for (<initial value>; <test condition>; <update value>) {
executable statement(s)
}
}
What action will you take to terminate an outer loop from the block of an inner loop?
Answer
An outer loop can be terminated from the block of an inner loop by using labelled break statement as shown in the example given below:
outer: for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 10; j++) {
System.out.println(j);
if (i == 3)
break outer;
}
}
System.out.println("Outside outer loop");What is significance of break outer and continue outer in a nested loop?
Answer
break outer will terminate the loop that is labelled as outer in a nested loop and transfer the program control to the statement just after the loop labelled as outer.
continue outer will skip the remaining statements of the nested loop and start the next iteration of the loop that is labelled as outer.
Write down the constructs (syntax) of:
(a) Nested do-while loop
(b) Nested while loop
Answer
(a) Construct of Nested do-while loop
do {
//statements of outer do-while loop
..
..
do {
//statements of inner do-while loop
} while (<condition>);
..
..
} while (<condition>);
(b) Construct of Nested while loop
while (<condition>) {
//statements of outer while loop
..
..
while (<condition>) {
//statements of inner while loop
}
..
..
}
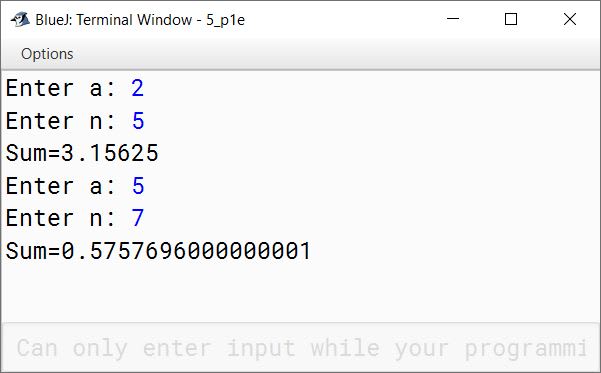
Write programs to find the sum of the following series:
(a) S = 1 + (3/2!) + (5/3!) + (7/4!) + ....... to n
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSeries
{
public void computeSum() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter n: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
double sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 1, j = 1; i <= n; i++, j = j + 2) {
double f = 1;
for (int k = 1; k <= i; k++) {
f *= k;
}
sum += j / f;
}
System.out.println("Sum=" + sum);
}
}
(b) S = a + (a/2!) + (a/3!) + (a/4!) + ....... + (a/n!)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSeries
{
public void computeSum() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a: ");
int a = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter n: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
double f = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
f *= j;
}
sum += a / f;
}
System.out.println("Sum=" + sum);
}
}
(c) S = a - (a/2!) + (a/3!) - (a/4!) + ....... to n
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSeries
{
public void computeSum() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a: ");
int a = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter n: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
double f = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
f *= j;
}
if (i % 2 == 0)
sum -= a / f;
else
sum += a / f;
}
System.out.println("Sum=" + sum);
}
}
(d) S = (a/2!) - (a/3!) + (a/4!) - (a/5!) + ....... + (a/10!)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSeries
{
public void computeSum() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a: ");
int a = in.nextInt();
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= 10; i++) {
double f = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
f *= j;
}
if (i % 2 == 0)
sum += a / f;
else
sum -= a / f;
}
System.out.println("Sum=" + sum);
}
}
(e) S = (2/a) + (3/a2) + (5/a3) + (7/a4) + ....... to n
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSeries
{
public void computeSum() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a: ");
int a = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter n: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
double sum = 0;
int lastPrime = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = lastPrime + 1; j <= Integer.MAX_VALUE; j++) {
boolean isPrime = true;
for (int k = 2; k <= j / 2; k++) {
if (j % k == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
if (isPrime) {
sum += j / Math.pow(a, i);
lastPrime = j;
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println("Sum=" + sum);
}
}
Write a program to input two numbers and check whether they are twin prime numbers or not.
Hint: Twin prime numbers are the prime numbers whose difference is 2.
For example: (5,7), (11,13), ....... and so on.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatTwinPrime
{
public void twinPrimeCheck() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter first number: ");
int a = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter second number: ");
int b = in.nextInt();
boolean isAPrime = true;
for (int i = 2; i <= a / 2; i++) {
if (a % i == 0) {
isAPrime = false;
break;
}
}
if (isAPrime && Math.abs(a - b) == 2) {
boolean isBPrime = true;
for (int i = 2; i <= b / 2; i++) {
if (b % i == 0) {
isBPrime = false;
break;
}
}
if (isBPrime)
System.out.println(a + " and " + b + " are twin prime");
else
System.out.println(a + " and " + b + " are not twin prime");
}
else
System.out.println(a + " and " + b + " are not twin prime");
}
}
Write a program to display all the numbers between 100 and 200 which don't contain zeros at any position.
For example: 111, 112, 113, ....... , 199
public class KboatNoZero
{
public void display() {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 100; i <= 200; i++) {
boolean isNoZero = true;
int t = i;
while (t > 0) {
if (t % 10 == 0) {
isNoZero = false;
break;
}
t /= 10;
}
if (isNoZero) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
count++;
}
//This will print 10 numbers per line
if (count == 10) {
System.out.println();
count = 0;
}
}
}
}
Write a program to display all prime palindrome numbers between 10 and 1000.
[Hint: A number which is prime as well a palindrome is said to be 'Prime Palindrome' number.]
For example: 11, 101, 131, 151,
public class KboatPrimePalindrome
{
public void displayPrimePalindrome() {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 10; i <= 1000; i++) {
int num = i, revNum = 0;
while (num != 0) {
int digit = num % 10;
num /= 10;
revNum = revNum * 10 + digit;
}
if (revNum == i) {
boolean isPrime = true;
for (int j = 2; j <= i / 2; j++) {
if (i % j == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
if (isPrime) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
count++;
if (count == 10) {
System.out.println();
count = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
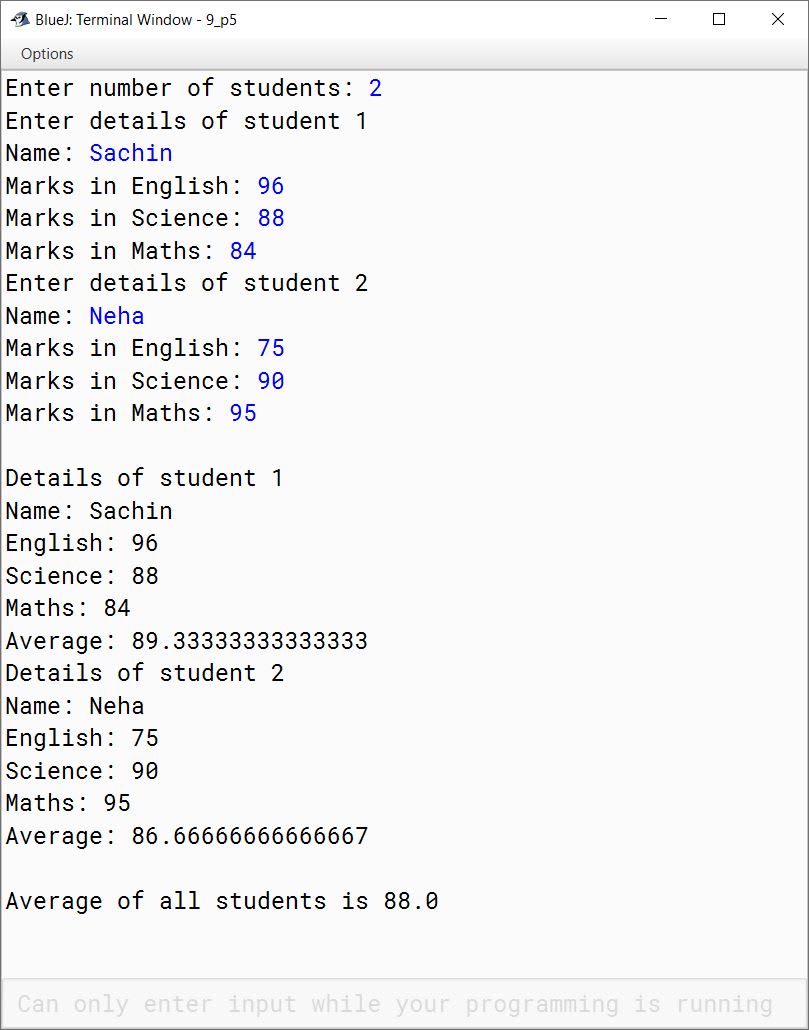
In an entrance examination, students have been appeared in English, Maths and Science papers. Write a program to calculate and display average marks obtained by all the students. Take number of students appeared and marks obtained in all three subjects by every student along with the name as inputs.
Display the name, marks obtained in three subjects and the average of all the students.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatStudentMarks
{
public void studentMarks() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter number of students: ");
int studentCount = in.nextInt();
String names[] = new String[studentCount];
int engMarks[] = new int[studentCount];
int sciMarks[] = new int[studentCount];
int mathsMarks[] = new int[studentCount];
double avgMarks[] = new double[studentCount];
double totalMarks = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < studentCount; i++) {
System.out.println("Enter details of student " + (i + 1));
System.out.print("Name: ");
in.nextLine();
names[i] = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Marks in English: ");
engMarks[i] = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Marks in Science: ");
sciMarks[i] = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Marks in Maths: ");
mathsMarks[i] = in.nextInt();
avgMarks[i] = (engMarks[i] + sciMarks[i] + mathsMarks[i]) / 3.0;
totalMarks += avgMarks[i];
}
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i < studentCount; i++) {
System.out.println("Details of student " + (i + 1));
System.out.println("Name: " + names[i]);
System.out.println("English: " + engMarks[i]);
System.out.println("Science: " + sciMarks[i]);
System.out.println("Maths: " + mathsMarks[i]);
System.out.println("Average: " + avgMarks[i]);
}
double classAvg = totalMarks / studentCount;
System.out.println("\nAverage of all students is " + classAvg);
}
}
Write a program in Java to enter a number containing three digits or more. Arrange the digits of the entered number in ascending order and display the result.
Sample Input: Enter a number 4972
Sample Output: 2, 4, 7, 9
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatDigitSort
{
public void sortDigits() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number having 3 or more digits: ");
int OrgNum = in.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) {
int num = OrgNum;
int c = 0;
while (num != 0) {
if (num % 10 == i)
c++;
num /= 10;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= c; j++) {
System.out.print(i + ", ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Write a program to input a number and check whether it is 'Magic Number' or not. Display the message accordingly.
A number is said to be a magic number if the eventual sum of digits of the number is one.
Sample Input : 55
Then, 5 + 5 = 10, 1 + 0 = 1
Sample Output: Hence, 55 is a Magic Number.
Similarly, 289 is a Magic Number.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatMagicNum
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter number to check: ");
int num = in.nextInt();
int n = num;
while (n > 9) {
int sum = 0;
while (n != 0) {
int d = n % 10;
n /= 10;
sum += d;
}
n = sum;
}
if (n == 1)
System.out.println(num + " is Magic Number");
else
System.out.println(num + " is not Magic Number");
}
}
A number is said to be Multiple Harshad number, when divided by the sum of its digits, produces another 'Harshad Number'. Write a program to input a number and check whether it is a Multiple Harshad Number or not.
(When a number is divisible by the sum of its digit, it is called 'Harshad Number').
Sample Input: 6804
Hint: 6804 ⇒ 6+8+0+4 = 18 ⇒ 6804/18 = 378
378 ⇒ 3+7+8= 18 ⇒ 378/18 = 21
21 ⇒ 2+1 = 3 ⇒ 21/3 = 7
Sample Output: Multiple Harshad Number
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatMultipleHarshad
{
public void checkMultipleHarshad() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter number to check: ");
int num = in.nextInt();
int dividend = num;
int divisor;
int count = 0;
while (dividend > 1) {
divisor=0;
int t = dividend;
while (t > 0) {
int d = t % 10;
divisor += d;
t /= 10;
}
if (dividend % divisor == 0 && divisor != 1) {
dividend = dividend / divisor;
count++;
}
else {
break;
}
}
if (dividend == 1 && count > 1)
System.out.println(num + " is Multiple Harshad Number");
else
System.out.println(num + " is not Multiple Harshad Number");
}
}
Write the programs to display the following patterns:
(a)
1
3 1
5 3 1
7 5 3 1
9 7 5 3 1
public class KboatPattern
{
public void displayPattern() {
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i = i + 2) {
for (int j = i; j > 0; j = j - 2) {
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(b)
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9
10 11 12
13 14
15
public class KboatPattern
{
public void displayPattern() {
int a = 1;
for (int i = 5; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(a++ + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(c)
15 14 13 12 11
10 9 8 7
6 5 4
3 2
1
public class KboatPattern
{
public void displayPattern() {
int a = 15;
for (int i = 5; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(a-- + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(d)
1
1 0
1 0 1
1 0 1 0
1 0 1 0 1
public class KboatPattern
{
public void displayPattern() {
int a = 1, b = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
if (j % 2 == 0)
System.out.print(b + " ");
else
System.out.print(a + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(e)
5 5 5 5 5
4 4 4 4
3 3 3
2 2
1
public class KboatPattern
{
public void displayPattern() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int k = 5 - i; k > 0; k--) {
System.out.print((5 - i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(f)
1 2 3 4 5
2 2 3 4 5
3 3 3 4 5
4 4 4 4 5
5 5 5 5 5
public class KboatPattern
{
public void displayPattern() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
System.out.print(i + " ");
for (int k = i; k <= 5; k++)
System.out.print(k + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(g)
*
* #
* # *
* # * #
* # * # *
public class KboatPattern
{
public void displayPattern() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
if (j % 2 == 0)
System.out.print("# ");
else
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(h)
5 4 3 2 1
5 4 3 2
5 4 3
5 4
5
public class KboatPattern
{
public void displayPattern() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 5; j >= i; j--) {
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(i)
1
2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15
public class KboatPattern
{
public void displayPattern() {
int a = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(a++ + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Write a program to generate a triangle or an inverted triangle till n terms based upon the user's choice.
Example 1:
Input: Type 1 for a triangle and
Type 2 for an inverted triangle
Enter your choice 1
Enter the number of terms 5
Sample Output:
1
2 2
3 3 3
4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5
Example 2:
Input: Type 1 for a triangle and
Type 2 for an inverted triangle
Enter your choice 2
Enter the number of terms 6
Sample Output:
6 6 6 6 6 6
5 5 5 5 5
4 4 4 4
3 3 3
2 2
1
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatPattern
{
public void choosePattern() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Type 1 for a triangle");
System.out.println("Type 2 for an inverted triangle");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
int ch = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter the number of terms: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
switch (ch) {
case 1:
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
break;
case 2:
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Incorrect Choice");
}
}
}

Using the switch statement, write a menu driven program for the following:
(a) To print the Floyd's triangle:
1
2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15
(b) To display the following pattern:
I
I C
I C S
I C S E
For an incorrect option, an appropriate error message should be displayed.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatPattern
{
public void choosePattern() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Type 1 for Floyd's triangle");
System.out.println("Type 2 for an ICSE pattern");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
int ch = in.nextInt();
switch (ch) {
case 1:
int a = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(a++ + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
break;
case 2:
String s = "ICSE";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(s.charAt(j) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Incorrect Choice");
}
}
}

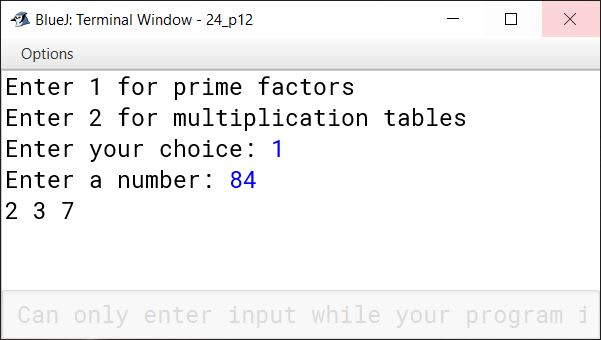
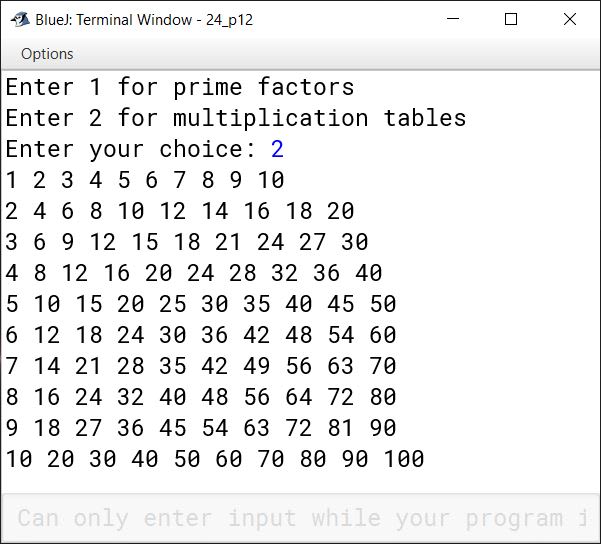
Using the switch case statement, write a menu driven program for the following:
(a) To input a number and display only those factors of the numbers which are prime.
Sample Input: 84
Sample Output: 2, 3, 7
(b) A program that displays the multiplication table from 1 to 10, as shown:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30
...................................
...................................
...................................
9 18 27 36 45 54 63 72 81 90
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatPrimeFactorsNTables
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter 1 for prime factors");
System.out.println("Enter 2 for multiplication tables");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
int ch = in.nextInt();
switch (ch) {
case 1:
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int num = in.nextInt();
for(int i = 2; i <= num/2; i++) {
int c = 0;
if(num % i == 0) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
if(i % j == 0)
c++;
}
if(c == 2)
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
break;
case 2:
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 10; j++)
System.out.print((i * j) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Incorrect Choice");
}
}
}