Library Classes
A package contains:
- tags
- classes
- data
- arrays
Answer
classes
Reason — A package is a collection of Java classes.
Each primitive data type belongs to a specific
- block
- object
- wrapper class
- none
Answer
wrapper class
Reason — A wrapper class is a class that contains a primitive data type.
Automatic conversion of primitive data into an object of wrapper class is called
- autoboxing
- explicit conversion
- shifting
- none
Answer
autoboxing
Reason — Automatic conversion of primitive data into an object of its equivalent wrapper class is called autoboxing.
The parseInt() function is a member of
- integer wrapper class
- character wrapper class
- boolean wrapper class
- none
Answer
integer wrapper class
Reason — The parseInt() function is a member of integer wrapper class.
valueOf() function converts
- Primitive type to String
- String to primitive type
- character to String
- None
Answer
String to primitive type
Reason — valueOf() function converts String to primitive type.
Which of the following functions checks whether a character is a blank or not?
- Character.isBlankSpace( )
- Character.isWhiteSpace( )
- Character.isEmptySpace( )
- Character.isNull( )
Answer
Character.isWhiteSpace( )
Reason — Character.isWhiteSpace( ) returns a boolean type value true if the given argument is a white space and otherwise, it returns false.
Which of the following statements is true?
- Character.isLowerCase( ) and Character.toLowerCase( ) are same.
- Character.isLetter( ) and Character.isAlphabet( ) are same.
- parse and valueOf functions are same.
- Character.isDigit( ) and Character.isNumber( ) are same.
Answer
parse and valueOf functions are same.
Reason — parse and valueOf functions are used to convert a string to a primitive data type.
The variable must be declared ........ type, if a character is to be assigned to it.
- char
- ch
- character
- alphanumeric
Answer
char
Reason — The variable must be declared 'char' type, if a character is to be assigned to it.
Package is a collection of classes.
By default, java.lang package is imported in a Java program.
The user can create a data type by using a class.
The data type int is included in Integer wrapper class.
Wrapper class uses first letter in upper case.
String data is converted to float type by using Float.parseFloat(String) function.
Conversion from primitive type to wrapper object is called as autoboxing.
Each character oriented function uses a wrapper tag Character.
Java class library includes all the packages.
True
Wrapper classes belong to java.util package.
False
Array is a non-primitive data type.
True
Class is a composite data type.
True
Integer.toString() converts integer data to String.
True
char ch = '*';
boolean b = Character.isLetter(ch);
System.out.println(b);Answer
false
As Asterisk (*) is not a letter so Character.isLetter() method returns false.
char c = 'A';
int n = (int) c + 32;
System.out.println((char)n);Answer
a
int n = (int) c + 32 ⇒ 65 + 32 ⇒ 97
So, variable n get the value of 97. 97 is the ASCII code of small 'a' so casting n to char, prints 'a' to the console.
String s= "7";
int t =Integer.parseInt(s);
t = t + 1000;
System.out.println(t);Answer
1007
Integer.parseInt() converts "7" into an int value i.e. the decimal number 7. t + 1000 adds the number 7 to 1000 giving 1007 as the output.
char c = 'B';
int i = 4;
System.out.println(c + i);
System.out.println((int)c + i);Answer
70
70
In the expression c + i, c is of type char and i is of type int. As int is the higher type so char gets promoted to int. Thus, ASCII code of 'B' which is 66 is added to 4 giving the output as 70. This is an example of implicit type conversion.
In the next expression (int)c + i, c which is of char type is explicitly casted to int. Again, ASCII code of 'B' which is 66 is added to 4 giving the output as 70. This is an example of explicit type conversion.
char ch = 'y';
char chr = Character.toUpperCase(ch);
int p = (int) chr;
System.out.println(chr + "\t" + p);Answer
Y 89
Character.toUpperCase()method converts small y to capital Y so chr gets the value of 'Y'. Casting chr to int gives the ASCII code of 'Y' which is 89.
int n = 97;
char ch = Character.toUpperCase((char)n);
System.out.println(ch + " Great Victory");Answer
A Great Victory
97 is the ASCII code of small a so Character.toUpperCase((char)n) returns capital A which is stored in ch.
char ch = 'x'; int n = 5;
n = n + (int)ch;
char c = (char)n;
System.out.println((char)((int)c-26));Answer
c
As ASCII code of 'x' is 120, so the expession n + (int)ch ⇒ 5 + 120 ⇒ 125. After that, the expression (char)((int)c-26) ⇒ (char)(125 - 26) ⇒ (char)99 ⇒ 'c' as ASCII code of 'c' is 99. So, c is the final output.
char ch = 'A';
char chr = Character.toLowerCase(ch);
int n = (int)chr-32;
System.out.println((char)n + "\t" + chr);Answer
A a
Character.toLowerCase() converts 'A' to 'a'. ASCII code of 'a' is 97. n becomes 65 — (int)chr-32 ⇒ 97 - 32 ⇒ 65. 65 is the ASCII code of 'A'.
Java language uses each primitive data type under a specific packet. Other than a data type, the packet also contains the functions to convert the primitive type into string and vice versa. The computer uses 128 ASCII characters. Each character is assigned a specific numeric code called ASCII code. Java language also has the facility to convert the characters into the ASCII code and vice versa.
Based on the above discussion, answer the following questions:
(a) What is the name given to the packet containing a primitive data type?
(b) What is the function used to convert a string data into integer type?
(c) Name the term used to convert a primitive data into the object of its wrapper class.
(d) What is the syntax to convert a string "24" into integer data type?
Answer
(a) Wrapper class
(b) parseInt() or valueOf()
(c) Autoboxing
(d) int num = Integer.valueOf("24");
Float.parseFloat()
Answer
It is used to convert string data into float data.
Double.toString()
Answer
It is used to convert double data to a string.
Integer.valueOf()
Answer
It is used to convert string data into the Integer wrapper object.
Character.isDigit()
Answer
It is used to check if the character given as its argument is a digit.
Character.isWhitespace()
Answer
It is used to check if the character given as its argument is a whitespace.
What is a package?
Answer
In Java, a package is used to group related classes. Packages are of 2 types:
- Built-In packages — These are provided by Java API
- User-Defined packages — These are created by the programmers to efficiently structure their code.
java.util, java.lang are examples of built-in packages.
What is the significance of '*' while importing a package?
Answer
The asterisk(*) sign indicates that all the classes of the imported package can be used in the program.
Define a wrapper class.
Answer
The wrapper class is a class that contains a primitive data type. Whenever an object to a wrapper class is created, a field in memory is allocated to contain a primitive data.
Wrapper classes are present in java.lang package. The different wrapper classes provided by Java are Boolean, Byte, Integer, Float, Character, Short, Long and Double.
Differentiate between isUpperCase() and toUpperCase()
Answer
| isUpperCase() | toUpperCase() |
|---|---|
| It is used to check if the character given as its argument is in upper case or not. | It is used to convert the character given as its argument to upper case. |
| Its return type is boolean. | Its return type is char. |
Differentiate between parseInt() and toString() functions
Answer
| parseInt() | toString() |
|---|---|
| It converts a string to an integer. | It converts an integer to a string. |
| Its return type is int. | Its return type is String. |
Differentiate between primitive type and composite type data
Answer
| Primitive Data Types | Composite Data Types |
|---|---|
| Primitive data types are fundamental data types of Java. | Composite data types are created by using primitive data types. |
| Primitive data types are built-in data types defined by Java language specification. | Composite data types are defined by the programmer. |
| Examples of primitive data types are byte, short, int, long, float, double, char, boolean. | Examples of composite data types are Class and Array. |
int res = 'A';
What is the value of res?
Answer
Value of res is 65.
Name the package that contains wrapper classes.
Answer
java.lang package contains wrapper classes.
Write the prototype of a function check which takes an integer as an argument and returns a character.
Answer
char check(int n) takes an integer as an argument and returns a character.
Write a program in Java to input a character. Find and display the next 10th character in the ASCII table.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatTenthChar
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a character: ");
char ch = in.next().charAt(0);
char nextCh = (char)(ch + 10);
System.out.println("Tenth character from "
+ ch + " is " + nextCh);
}
}
Write a program in Java to input a character. Display next 5 characters.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatFiveChars
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a character: ");
char ch = in.next().charAt(0);
System.out.println("Next 5 characters from "
+ ch + " are:");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(++ch);
}
}
}

Write a program in Java to generate all the alternate letters in the range of letters from A to Z.
public class KboatAlternateLetters
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
for (char ch = 'A'; ch <= 'Z'; ch = (char)(ch + 2)) {
System.out.println(ch);
}
}
}
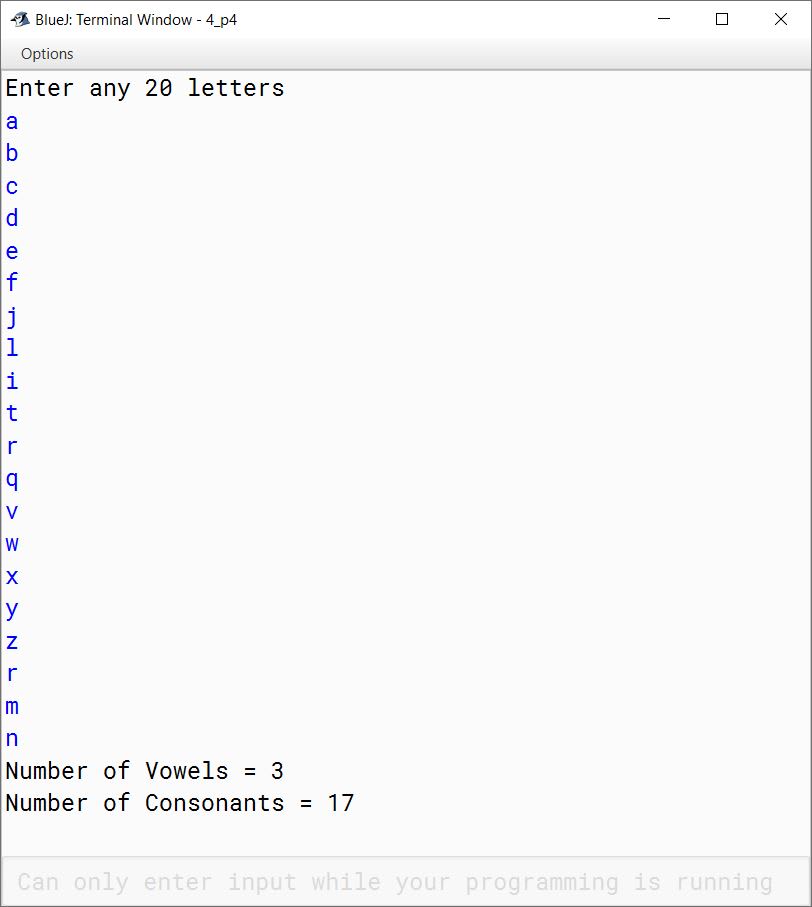
Write a program to input a set of 20 letters. Convert each letter into upper case. Find and display the number of vowels and number of consonants present in the set of given letters.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Kboat20LetterSet
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter any 20 letters");
int vc = 0, cc = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
char ch = in.next().charAt(0);
ch = Character.toUpperCase(ch);
if (ch == 'A' ||
ch == 'E' ||
ch == 'I' ||
ch == 'O' ||
ch == 'U')
vc++;
else if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')
cc++;
}
System.out.println("Number of Vowels = " + vc);
System.out.println("Number of Consonants = " + cc);
}
}
Write a program in Java to accept an integer number N such that 0<N<27. Display the corresponding letter of the alphabet (i.e. the letter at position N).
[Hint: If N =1 then display A]
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatInteger2Letter
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter integer: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
if (n > 0 && n < 27) {
char ch = (char)(n + 64);
System.out.println("Corresponding letter = " + ch);
}
else {
System.out.println("Please enter a number in 1 to 26 range");
}
}
}

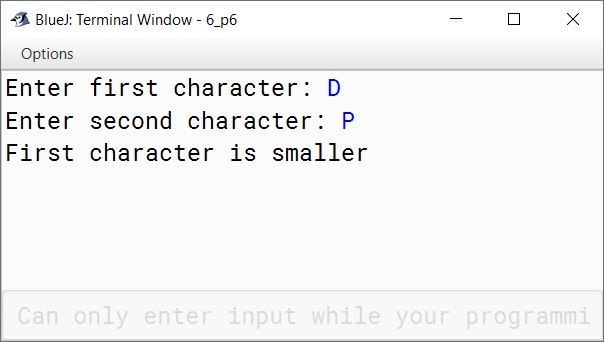
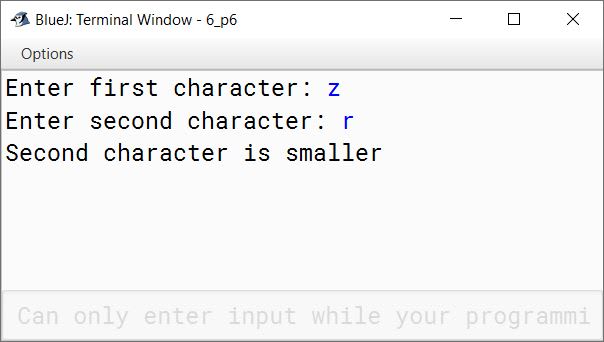
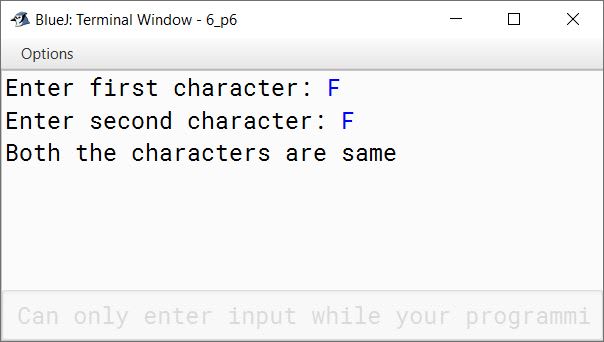
Write a program to input two characters from the keyboard. Find the difference (d) between their ASCII codes. Display the following messages:
If d=0 : both the characters are same.
If d<0 : first character is smaller.
If d>0 : second character is smaller.
Sample Input :
D
P
Sample Output :
d= (68-80) = -12
First character is smaller
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatASCIIDiff
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter first character: ");
char ch1 = in.next().charAt(0);
System.out.print("Enter second character: ");
char ch2 = in.next().charAt(0);
int d = (int)ch1 - (int)ch2;
if (d > 0)
System.out.println("Second character is smaller");
else if (d < 0)
System.out.println("First character is smaller");
else
System.out.println("Both the characters are same");
}
}
Write a program to input a set of any 10 integer numbers. Find the sum and product of the numbers. Join the sum and product to form a single number. Display the concatenated number.
[Hint: let sum=245 and product = 1346 then the number after joining sum and product will be 2451346]
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSumProdConcat
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter 10 integers");
long sum = 0, prod = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int n = in.nextInt();
sum += n;
prod *= n;
}
String s = Long.toString(sum) + Long.toString(prod);
long r = Long.parseLong(s);
System.out.println("Concatenated Number = " + r);
}
}
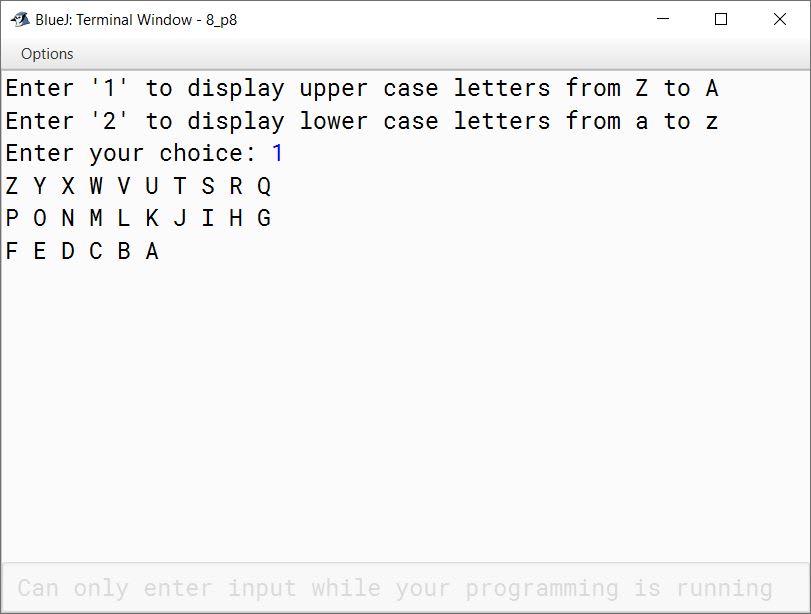
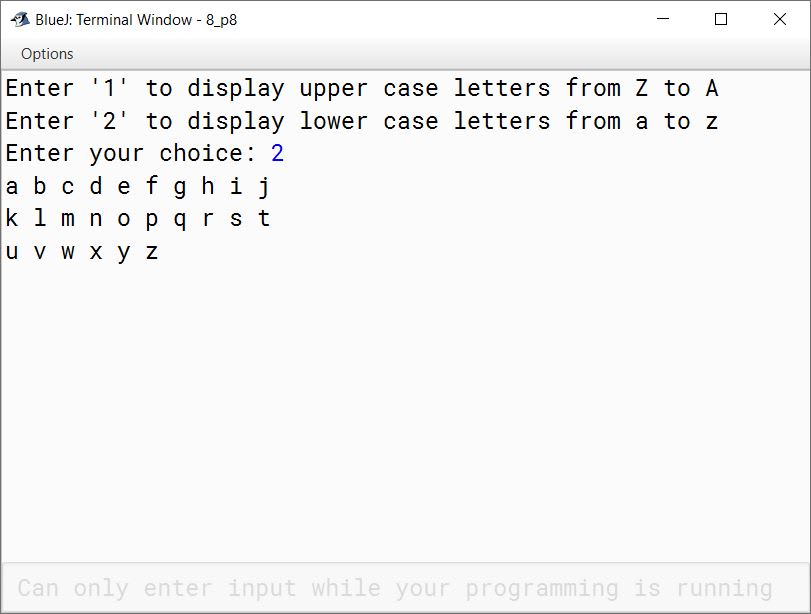
Write a menu driven program to generate the upper case letters from Z to A and lower case letters from 'a' to 'z' as per the user's choice.
Enter '1' to display upper case letters from Z to A and Enter '2' to display lower case letters from a to z.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatLetters
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter '1' to display upper case letters from Z to A");
System.out.println("Enter '2' to display lower case letters from a to z");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
int ch = in.nextInt();
int count = 0;
switch (ch) {
case 1:
for (int i = 90; i > 64; i--) {
char c = (char)i;
System.out.print(c);
System.out.print(" ");
count++;
//Print 10 characters per line
if (count == 10) {
System.out.println();
count = 0;
}
}
break;
case 2:
for (int i = 97; i < 123; i++) {
char c = (char)i;
System.out.print(c);
System.out.print(" ");
count++;
//Print 10 characters per line
if (count == 10) {
System.out.println();
count = 0;
}
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Incorrect Choice");
}
}
}
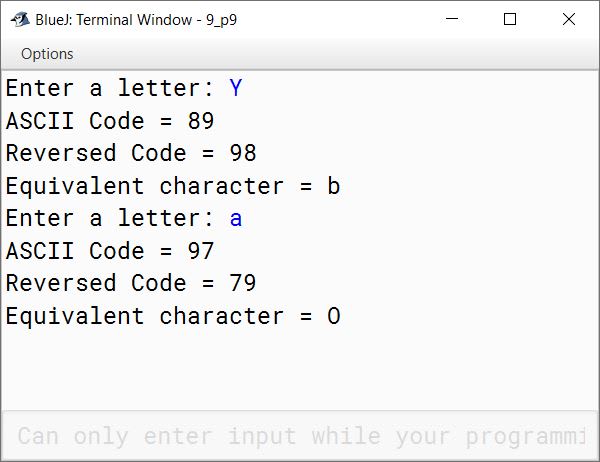
Write a program to input a letter. Find its ASCII code. Reverse the ASCII code and display the equivalent character.
Sample Input: Y
Sample Output: ASCII Code = 89
Reverse the code = 98
Equivalent character: b
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatASCIIReverse
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a letter: ");
char l = in.next().charAt(0);
int a = (int)l;
System.out.println("ASCII Code = " + a);
int r = 0;
while (a > 0) {
int digit = a % 10;
r = r * 10 + digit;
a /= 10;
}
System.out.println("Reversed Code = " + r);
System.out.println("Equivalent character = " + (char)r);
}
}
Write a menu driven program to display
(i) first five upper case letters
(ii) last five lower case letters as per the user's choice.
Enter '1' to display upper case letters and enter '2' to display lower case letters.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatMenuUpLowCase
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter '1' to display upper case letters");
System.out.println("Enter '2' to display lower case letters");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
int ch = in.nextInt();
switch (ch) {
case 1:
for (int i = 65; i <= 69; i++)
System.out.println((char)i);
break;
case 2:
for (int i = 118; i <= 122; i++)
System.out.println((char)i);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}

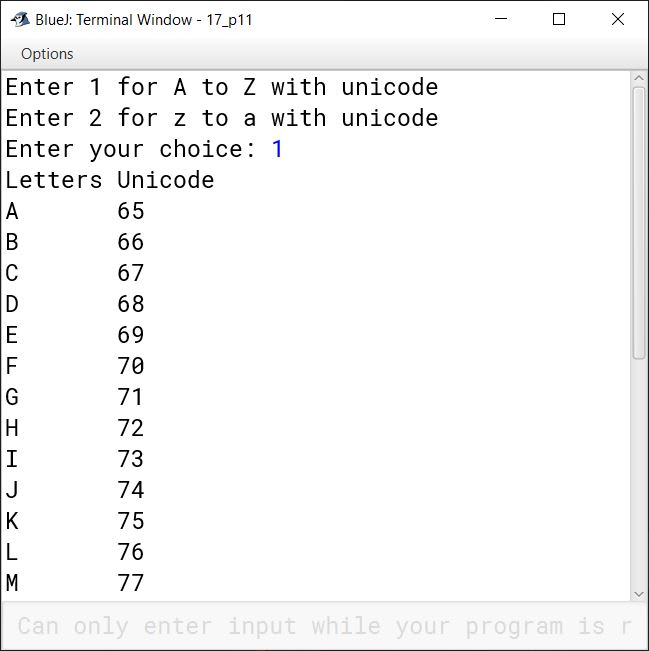
Using switch case statement, write a menu driven program to perform the following tasks:
(a) To generate and print the letters from A to Z along with their Unicode.
Letters Unicode
A 65
B 66
..... ........
..... ........
Z 90
(b) To generate and print the letters from z to a along with their Unicode.
Letters Unicode
z 122
y 121
..... ........
..... ........
a 97
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatLettersNUnicode
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter 1 for A to Z with unicode");
System.out.println("Enter 2 for z to a with unicode");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
int ch = in.nextInt();
switch (ch) {
case 1:
System.out.println("Letters" + "\t" + "Unicode");
for(int i = 65; i <= 90; i++)
System.out.println((char)i + "\t" + i);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Letters" + "\t" + "Unicode");
for (int i = 122; i >= 97; i--)
System.out.println((char)i + "\t" + i);
break;
default:
System.out.println("Incorrect Choice");
}
}
}
Write a program in Java to display the following patterns:
(i)
A
ab
ABC
abcd
ABCDE
public class KboatPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
for (int i = 65; i < 70; i++) {
for (int j = 65; j <= i; j++) {
if (i % 2 == 0)
System.out.print((char)(j+32));
else
System.out.print((char)j);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(ii)
ZYXWU
ZYXW
ZYX
ZY
Z
public class KboatPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
for (int i = 86; i <= 90; i++) {
for (int j = 90; j >= i; j--) {
System.out.print((char)j);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(iii)
ABCDE
ABC
A
public class KboatPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
for (int i = 69; i >= 65; i = i - 2) {
for (int j = 65; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print((char)j);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(iv)
PRTV
PRT
PR
P
public class KboatPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
for (int i = 86; i >= 80; i = i - 2) {
for (int j = 80; j <= i; j = j + 2) {
System.out.print((char)j);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(v)
A*B*C*D*E*
A*B*C*D*
A*B*C*
A*B*
A*
public class KboatPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
for(int i = 69; i >= 65; i--) {
for (int j = 65; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print((char)j + "*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
(vi)
a a a a a
b b b b b
A A A A A
B B B B B
public class KboatPattern
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 97;
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++) {
System.out.print((char)a + " ");
}
a++;
if (i == 2)
a = 65;
System.out.println();
}
}
}