Acids, Bases and Salts
(a) What to you understand by the term acid?
(b) Name the positive ion formed when an acid is dissolved in water.
(c) Draw the structure of this ion.
Answer
(a) Acids are defined as compounds which contain one or more hydrogen atoms, and when dissolved in water, they produce hydronium ions (H3O+) as the only positively charged ions.
(b) Hydronium ion (H3O+)
(c) The structure of hydronium ion is shown below:
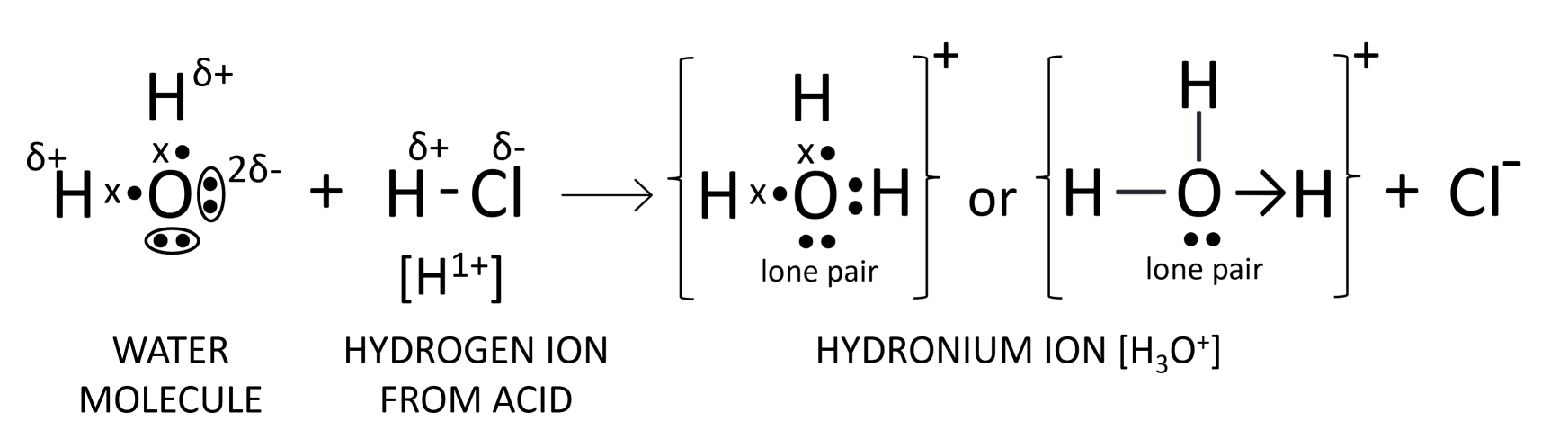
Write the ionisation of sulphuric acid showing the formation of hydronium ion.
Answer
H2SO4 + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + HSO4-
HSO4- + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + SO42-
Water is never added to acid in order to dilute it. Why?
Answer
Water is not added to acid as it is an exothermic process and in this process so much heat is produced that splashing of acidic acid solution may occur, also the container may break which can be fatal to the person.
Define the term 'basicity' of an acid. Give the basicity of: nitric acid, sulphuric acid and phosphoric acid.
Answer
The basicity of an acid is defined as the number of hydronium ions (H3O+) that can be produced by the ionization of one molecule of that acid in aqueous solution.
The basicity of following compounds are:
Basicity of Nitric acid = 1
Basicity of Sulphuric acid = 2
Basicity of Phosphoric acid = 3
Give two examples of each of the following :
(a) oxy-acid
(b) hydracid
(c) tribasic acid
(d) dibasic acid
Answer
(a) Oxyacids — Nitric acid [HNO3] and Sulphuric acid [H2SO4]
(b) Hydracid — Hydrochloric acid [HCl] and Hydrobromic acid [HBr]
(c) Tribasic acid — Phosphoric acid [H3PO4] and Citric acid [C6H8O7]
(d) Dibasic acid — Sulphuric acid [H2SO4] and Carbonic acid [H2CO3]
Name the :
(a) acidic anhydride of the following acids:
- sulphurous acid
- nitric acid
- phosphoric acid
- carbonic acid
(b) acid present in vinegar, grapes and lemons.
Answer
(a) Below are the acidic anhydride of the given acids:
- Sulphurous acid — SO2
- Nitric acid — N2O5
- Phosphoric acid — P2O5
- Carbonic acid — CO2
(b) Acids present in following are:
- Vinegar — Acetic acid
- Grapes — Tartaric acid
- Lemon — Citric acid
What do you understand by the statement 'acetic acid is a monobasic acid'?
Answer
Acetic acid is a monobasic acid because it's molecule ionises by liberating only one hydronium ion.
CH3COOH + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + CH3COO-
Give a balanced equation for :
(i) reaction of nitrogen dioxide with water
(ii) preparation of a non volatile acid from a volatile acid.
Answer
(i) 2NO2 + H2O ⟶ HNO2 + HNO3
(ii) S + 6HNO3 ⟶ H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO2
What do you understand by the strength of an acid? On which factor does the strength of an acid depend.
Answer
The strength of an acid is the measure of concentration of hydronium ions [H3O+] produced by that acid in aqueous solution.
Factors on which the strength of an acid depends are:
- Degree of ionisation (α).
- Concentration of hydronium ions [H3O+] produced by that acid in aqueous solution.
Explain the following:
(a) Carbonic acid gives an acid salt but hydrochloric acid does not.
(b) Dil. HCl acid is stronger than highly concentrated acetic acid.
(c) H3PO3 is not a tribasic acid.
(d) Lead carbonate does not react with dil. HCl
(e) Nitrogen dioxide is a double acid anhydride.
Answer
(a) Carbonic acid is a dibasic acid i.e., it has two replaceable hydrogen ions. Hence, it forms one acid salt or one normal salt. On the other hand, hydrochloric acid is a monobasic acid with one replaceable hydrogen ion. Hence, it forms only one normal salt.
(b) Concentration of an acid means the amount of water present in the acid and not at all the strength of an acid. Strength of an acid is the measure of concentration of hydronium ions it produces in its aqueous solution. Thus, dil. HCl is stronger acid than highly concentrated acetic acid.
(c) H3PO3 is not a tribasic acid but dibasic because in oxyacids of phosphorus, hydrogen atoms which are attached to oxygen atoms are replaceable. Hydrogen atoms directly bonded to phosphorus atoms are not replaceable.

(d) Generally, acids liberate carbon dioxide on reaction with metallic carbonates and bicarbonates. But if the salt produced is insoluble, then the reaction does not proceed. So, we do not expect lead carbonate to react with hydrochloric acid.
(e) Nitrogen dioxide is called double acid anhydride because two acids – nitrous acid and nitric acid – are formed when it reacts with water.
2NO2 + H2O ⟶ HNO2 + HNO3
How is an acid prepared from a (a) Non-metal (b) salt ? Give an equation for each.
Answer
(a) A non-metal, e.g., sulphur or phosphorous is oxidised by conc. nitric acid to form to form sulphuric acid or phosphoric acid respectively.
S + 6HNO3 ⟶ H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO2
P + 5HNO3 ⟶ H3PO4 + H2O + 5NO2
(b) Normal salts of more volatile acids are displaced by a less or non-volatile acid.
E.g., Both hydrochloric acid and nitric acid are formed by using sulphuric acid [H2SO4].
NaCl + H2SO4 NaHSO4 + HCl
NaNO3 + H2SO4 NaHSO4 + HNO3
Give equations to show how the following are made from their corresponding anhydrides.
(a) sulphurous acid
(b) phosphoric acid
(c) carbonic acid
(d) sulphuric acid
Answer
(a) SO2 + H2O ⟶ H2SO3
(b) P2O5 + 3H2O ⟶ 2H3PO4
(c) CO2 + H2O ⟶ H2CO3
(d) SO3 + H2O ⟶ H2SO4
Name an acid used:
(a) to flavour and preserve food;
(b) in a drink
(c) to remove ink spots
(d) as an eyewash.
Answer
(a) Citric acid
(b) Carbonic acid
(c) Oxalic acid
(d) Boric acid
Give reaction of acids with
(a) chlorides
(b) nitrates
State the conditions under which they react.
Answer
(a) Chlorides do not react with dilute acids. They react with concentrated sulphuric acid on warming to liberate hydrogen chloride.
(b) Nitrates do not react with dilute acids. When heated with conc. sulphuric acid they produce more volatile nitric acid.
What do you understand by an alkali? Give two examples of :
(a) strong alkalis
(b) weak alkalis
Answer
An alkali is a base soluble in water. All alkalis form hydroxyl (OH-) ions in aqueous solution as the only negative ions. They turn red litmus blue.
(a) Strong alkalis — Sodium hydroxide [NaOH], Potassium hydroxide [KOH]
(b) Weak alkalis — Calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2], Ammonium hydroxide [NH4OH]
What is the difference between :
(a) an alkali and a base,
(b) the chemical nature of an aqueous solution of HCl and an aqueous solution of NH3
Answer
(a) Difference between an alkali and a base:
| Alkali | Base |
|---|---|
| An alkali is a compound which when dissolved in water yields hydroxyl ions [OH-] as the only negatively charged ions. | A base is either a metallic oxide or a metallic hydroxide or ammonium hydroxide which reacts with hydronium ions of an acid to form salt and water only. |
| Alkalis are soluble in water | Bases may be or may not be soluble in water. |
| All alkalis are bases | All bases are not alkalis. |
(b) Difference between chemical nature of an aq. soln. of HCl and NH3:
| Chemical nature of an aq. soln. of HCl | Chemical nature of an aq. soln. of NH3 |
|---|---|
| The aqueous soln. of HCl is acidic in nature. | The aqueous soln. of NH3 is basic in nature. |
| It can turn blue litmus to red. | It can turn red litmus to blue. |
| It gives hydronium ions in the solution | It gives hydroxyl ions in the solution. |
Name the ions furnished by:
(a) bases in solution
(b) an acid
Answer
(a) bases in solution — Hydroxyl ion [OH-]
(b) an acid — H3O[+] . At first the the hydrogen molecule furnishes hydrogen ion, but this hydrogen ion cannot exist independently. Therefore it combines with water molecule to form hydronium ion H3O[+].
Give one example in case:
(a) A basic oxide which is soluble in water,
(b) A hydroxide which is highly soluble in water,
(c) A basic oxide which is insoluble in water,
(d) A hydroxide which is insoluble in water,
(e) A weak mineral acid
(f) A base which is not an alkali
(g) An oxide which is a base,
(h) A hydrogen containing compound which is not an acid
(i) A base which does not contain a metal ion.
Answer
(a) Sodium oxide [Na2O]
(b) Sodium hydroxide [NaOH]
(c) Copper (II) oxide [CuO]
(d) Aluminium hydroxide [Al(OH)3]
(e) Carbonic acid [H2CO3]
(f) Ferric hydroxide [Fe(OH)3]
(g) Copper (II) oxide [CuO]
(h) Ammonia [NH3]
(i) Ammonium hydroxide [NH4OH]
You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two have an acidic solution and a basic solution respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper, how will you identify the contents of each test tube?
Answer
We take three pieces of red litmus paper. The solution which turns red litmus paper to blue is basic solution. Distilled water (neutral) and acidic solution will not effect red litmus paper.
Now we divide the so formed blue litmus paper into two pieces. The test tube containing distilled water does not change the colour of the blue litmus paper.
The test tube containing acidic solution changes the colour of the blue litmus paper to red. Hence, we can identify the three solutions.
HCl, HNO3, C2H5OH, C6H12O6 all contain H atoms but only HCl and HNO3 show acidic character. Why?
Answer
HCl and HNO3 show acidic character because they ionise in aqueous solution.
Ionisation of HCl in water:
HCl ⟶ H+ + Cl-
H+ + H2O ⟶ H3O+
Ionisation of HNO3 in water:
HNO3 ⟶ H+ + NO3-
H+ + H2O ⟶ H3O+
C2H5OH (Ethanol) and C6H12O6 (Glucose) are covalent compounds. Their H atoms do not ionise in water to form hydronium ions [H3O+]. Hence, they don't show acidic character.
(a) Dry HCl gas does not change the colour of dry litmus paper. Why?
(b) Is PbO2 a base or not? Comment.
(c) Do basic solutions also have H+(aq.) ? Explain why are they basic by taking an example?
Answer
(a) The colour of litmus paper changes only in presence of ions like hydrogen [H+] or hydronium ions [H3O+]. HCl can produce these ions only in the form of aqueous solution. Hence, dry HCl gas does not change the colour of dry litmus paper.
(b) A base reacts with an acid to form salt and water ONLY. The word ONLY is of importance in the definition of a base. Lead oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce lead (II) chloride (a salt) and water, but the word "only" excludes it from the class of bases because chlorine is also produced.
PbO2(s) + 4HCl(aq.) ⟶ PbCl2(aq.) + Cl2(g) + 2H2O
Thus, PbO2 is not a base.
(c) Yes, basic solutions have H+ ions, but the concentration of OH- ions is more than the H+ ions which makes the solution basic in nature.
Example — Sodium hydroxide (NaOH). It has more OH- ions than H+ ions, so it is basic in nature.
How would you obtain:
(a) a base from another base,
(b) an alkali from a base,
(c) salt from another salt?
Answer
(a) A base from another base can obtained by double decomposition. The aqueous solution of salts with base (alkali) precipitates the respective metallic hydroxide.
For example,
FeCl3 + 3NaOH ⟶ 3NaCl + Fe(OH)3 ↓ [red brown ppt.]
(b) An alkali from a base can be obtained by the action of water on soluble metallic oxides like oxides of sodium, potassium and calcium:
CaO + H2O ⟶ Ca(OH)2
(c) A salt from another salt can be obtained by adding an alkali to the solutions of the salts of the heavy metals like copper, iron, zinc, etc.
For example,
FeSO4 [aq.] + 2NaOH [aq.] ⟶ Na2SO4 [aq.] + Fe(OH)2 ↓ [dirty green]
Write balanced equation to satisfy each statement.
(a) Acid + Active metal ⟶ Salt + Hydrogen
(b) Acid + Base ⟶ Salt + Water
(c) Acid + carbonate or bicarbonate ⟶ Salt + water + carbon dioxide
(d) Acid + sulphite or bisulphite ⟶ Salt + water + sulphur dioxide
(e) Acid + sulphide ⟶ Salt + hydrogen sulphide
Answer
(a) Mg + 2HCl ⟶ MgCl2 + H2
(b) HCl + NaOH ⟶ NaCl + H2O
(c) CaCO3 + 2HCl ⟶ CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
(d) CaSO3 + 2HCl ⟶ CaCl2 + H2O + SO2
(e) ZnS + 2HCl ⟶ ZnCl2 + H2S
The skin has and needs natural oils. Why it is advisable to wear gloves while working with strong alkalis?
Answer
Alkalis react with oil to form soap. Since, our skin contains oil hence when we touch strong alkalis, a reaction takes place and soapy solutions are formed. This reaction can be corrosive for skin. Hence we should wear gloves while working with strong alkalis.
Complete the table:
| Indicator | Neutral | Acidic | Alkaline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Litmus | Purple | .......... | .......... |
| Phenolphthalein | Colourless | .......... | .......... |
Answer
Completed table is shown below:
| Indicator | Neutral | Acidic | Alkaline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Litmus | Purple | blue to red | red to blue |
| Phenolphthalein | Colourless | colourless | pink |
What do you understand by pH value? Two solution X and Y have pH values of 4 and 10 respectively. Which one of these two will give a pink colour with phenolphthalein indicator.
Answer
pH of a solution is the negative logarithm to the base 10 of the hydrogen ion concentration expressed in moles per litre.
The solution with pH value 10 [i.e., Y] will give pink colour with phenolphthalein indicator.
You are supplied with five solutions : A, B, C, D and E with pH values as follows:
A = 1.8, B = 7, C = 8.5, D = 13, and E = 5
Classify these solutions as neutral, slightly or strongly acidic and slightly or strongly alkaline.
Which solution would be most likely to liberate hydrogen with:
(a) magnesium powder
(b) powdered zinc metal. Give a word equation for each reaction.
Answer
A = Strongly acidic
B = neutral
C = slightly alkaline
D = Strongly alkaline
E = slightly acidic
(a) Solution A (acidic solution)
Solution A (acidic solution) + magnesium powder ⟶ Hydrogen + Mg salt
(b) Solution A (acidic solution)
Solution A (acidic solution) + powdered zinc metal ⟶ Hydrogen + Zn salt
Distinguish between :
(a) a common acid base indicator and a universal indicator.
(b) acidity of bases and basicity of acids,
(c) acid and alkali (other than indicator)
Answer
(a) Difference between a common acid base indicator and a universal indicator:
| Common acid-base indicator | Universal indicator |
|---|---|
| Common acid-base indicators test whether a solution is acidic, basic or neutral. | Universal indicator gives a spectrum of colours depending upon how acidic or alkaline a solution is. |
| Common acid-base indicators does not give the exact pH value of the solution. | Universal indicator helps to get a reasonably accurate pH value. |
(b) Difference between acidity of bases and basicity of acids:
| Acidity of bases | Basicity of acids |
|---|---|
| The acidity of bases is the number of hydroxyl ions [OH-] which can be produced per molecule of the base in aqueous solution. | The basicity of an acid is defined as the number of hydronium ions [H3O+] that can be produced by the ionisation of one molecule of that acid in aqueous solution. |
| On the basis of their acidity, bases are classified as Monoacidic base, Diacidic base and Triacidic base. | On the basis of their basicity, acids are classified as Monobasic acids, Dibasic acids and Tribasic acids. |
(c) Difference between acid and alkali (other than indicator):
| Acid | Alkali |
|---|---|
| Acids are compounds which contain one or more hydrogen atoms and when dissolved in water, produce hydronium ions [H3O+] as the only positively charged ions. | An alkali is a basic hydroxide which when dissolved in water produces hydroxyl [OH-] ions as the only negatively charged ions. |
| Acids have a sour taste. | Alkalis have a sharp and bitter taste. |
| Acids have pH value less than 7. | Alkalis have pH value greater than 7. |
What should be added to
(a) increase the pH value
(b) decrease the pH value of a neutral solution
Answer
(a) Alkali
(b) Acid
How does tooth enamel get damaged? What should be done to prevent it?
Answer
Substances like chocolates and sweets are degraded by bacteria present in our mouth. When the pH falls to 5.5 tooth decay starts. Tooth enamel is the hardest substance in our body and it gets corroded. The saliva produced by salivary glands is slightly alkaline, it helps to increase the pH, to some extent, but toothpaste which contains basic substance is used to neutralize excess acid in the mouth.
When you use a universal indicator, you see that solutions of different acids produce different colours. Indeed, solutions of the same acid with different concentrations will also give different colours. Why?
Answer
Universal indicators give different colours at different concentrations of hydrogen ions in a solution. The hydrogen ion concentration differs for the same acid with different concentrations. Hence, the universal indicator gives different colours for the same acid with different concentrations.
(a) A solution has a pH of 7. Explain how you would: (i) increase it's pH (ii) decrease it's pH.
(b) If a solution changes the colour of litmus from red to blue, what you can say about it's pH.
(c) What you can say about the pH of a solution, that liberates carbon dioxide from sodium carbonate?
Answer
(a) A solution with pH of 7 is neutral. (i) Increasing it's pH means increasing its basic nature. Hence, we will add alkali to increase it's pH. (ii) Similarly, to decrease it's pH, we will add an acid to the solution.
(b) When a solution changes the colour of litmus from red to blue, it shows it is basic in nature and the pH value will be more than 7.
(c) Acids liberate carbon dioxide on reaction with metallic carbonates and bicarbonates. Hence, the pH of this solution will be less than 7.
Solution P has a pH of 13, solution Q has a pH of 6 and solution R has a pH of 2.
Which solution:
(a) Will liberate ammonia from ammonium sulphate on heating.
(b) is a strong acid?
(c) contains molecules as well as ions?
Answer
(a) Solution P
Reason — When alkalis are warmed with an ammonia salt, ammonia gas is given out.
(b) Solution R
Reason — Number 2 on pH scale represents a strong acid.
(c) Solution Q
Reason — As Q with pH 6 is a weak acid and will not be able to completely dissociate into ions. Hence, will have molecules and ions both.
M is an element in the form of powder. M burns in oxygen and the product obtained is soluble in water. The solution is tested with litmus. Write down only the word which will correctly complete each of the following sentences.
(a) If M is a metal, then the litmus will turn ...............
(b) If M is a non-metal, then the litmus will turn ...............
(c) If M is a reactive metal, then ............... will be evolved when M reacts with dilute sulphuric acid.
(d) If M is a metal, it will form ............... oxide, which will form ............... solution with water.
(e) If M is a non-metal, it will not conduct electricity unless it is in the form of ...............
Answer
(a) If M is a metal, then the litmus will turn blue
(b) If M is a non-metal, then the litmus will turn red
(c) If M is a reactive metal, then hydrogen gas will be evolved when M reacts with dilute sulphuric acid.
(d) If M is a metal, it will form basic oxide, which will form alkaline solution with water.
(e) If M is a non-metal, it will not conduct electricity unless it is in the form of graphite.
Explanation:
(a) Metal, M burns in oxygen to form an oxide. Metallic oxide forms an alkaline solution in water. Hence, turns red litmus blue.
(b) A non-metal on reacting with oxygen produces an acidic oxide. This acidic oxide will turn blue litmus paper blue.
(c) In Simple Displacement reaction, reactive metal and acid react to produce salt and hydrogen gas is evolved.
(d) Metals react with oxygen to form basic oxide which dissolve in water to give alkaline solution.
(e) In Graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms. Thus, one electron of carbon remains free. Due to this free valence electron, graphite is a good conductor of electricity. All other non-metals are poor conductors of electricity.
Define the following and give two examples in each case : (a) a normal salt, (b) an acid salt, (c) a basic salt.
Answer
(a) A normal salt — Normal salts are the salts formed by the complete replacement of the ionisable hydrogen atoms of an acid by a metallic or an ammonium ion.
Examples — Sodium Sulphate [Na2SO4], Sodium Chloride [NaCl]
(b) An acidic salt — Acid salts are formed by the partial replacement of the ionisable hydrogen atoms of a polybasic acid by a metal or an ammonium ion.
Examples — Sodium Hydrogen Sulphate [NaHSO4], Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate [Na2HPO4]
(c) A basic salt — Basic salts are formed by the partial replacement of the hydroxyl group of a di- or a tri-acidic base by an acid radical.
Examples — Basic lead chloride [Pb(OH)Cl], Basic magnesium chloride [Mg(OH)Cl].
Answer the following questions related to salts and their preparations:
(a) What is a 'salt' ?
(b) What kind of salt is prepared by precipitation?
(c) Name a salt prepared by direct combination. Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in preparing the salt you have named.
(d) Name the procedure used to prepare a sodium salt such as sodium sulphate.
Answer
(a) Salt is a compound formed by the partial or total replacement of the ionisable hydrogen atoms of an acid by a metallic ion or an ammonium ion.
(b) An insoluble salt can be prepared by precipitation.
(c) A salt prepared by direct combination is Lead(II) Sulphide.
Pb + S PbS
(d) By neutralisation of alkali (caustic soda) with acid (dilute sulphuric acid):
2NaOH + H2SO4 ⟶ Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Explain the following methods with examples:
(a) Direct combination
(b) Displacement
(c) Double decomposition (precipitation)
(d) Neutralization of insoluble base
(e) Neutralization of an alkali (titration)
Answer
(a) In direct combination, a metal and a non-metal are heated together to obtain the corresponding salt.
i.e., Metal + Non-Metal ⟶ Salt
Example:
Pb + S PbS
(b) The displacement method involves action of a dilute acid on active metal producing the corresponding salt with the liberation of Hydrogen gas.
i.e., Active metal + Acid ⟶ Salt + Hydrogen
Example :
Zn + H2SO4 ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2
(c) Double decomposition (precipitation) — A chemical change, in which two compounds in solution react to form two other compounds by the mutual exchange of radicals. A solid precipitate is formed as a result of the reaction.
Example:
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 ⟶ BaSO4↓ + 2NaCl
(d) Neutralization of insoluble base — By the action of dilute acid on an insoluble base.
Example:
CuO + H2SO4 ⟶ CuSO4 + H2O
(e) Neutralization of an alkali (titration) — By the action of dilute acid on an alkali (i.e., soluble base):
Example:
2NaOH + H2SO4 ⟶ Na2SO4 + H2O
How would you prepare :
(a) copper sulphate crystals from a mixture of charcoal and black copper oxide.
(b) zinc sulphate crystals from zinc dust (powdered zinc and zinc oxide),
(c) sodium hydrogen carbonate crystals.
(d) calcium sulphate from calcium carbonate.
Answer
(a) Copper sulphate crystals from a mixture of charcoal and black copper oxide
Method of preparation: Neutralisation of insoluble base
Reaction:
CuO + H2SO4 ⟶ CuSO4 + H2O
CuSO4 + 5H2O ⟶ CuSO4.5H2O (blue vitriol)
Procedure:
- Take dilute sulphuric acid in a beaker and heat it on wire gauze.
- Add black cupric oxide in small quantities at a time, with stirring till no more of it dissolves and the excess compound settles to the bottom.
- Filter it hot and collect the filtrate in a china dish. Evaporate the filtrate by heating to the point of crystallization and then allow it to cool and
- Collect the bright blue crystals of copper (II) sulphate pentahydrate CuSO4.5H2O (blue vitriol) and dry the crystals.
(b) Zinc sulphate crystals from Zinc dust
Method of preparation: Displacement — By the action of dilute acid (dil. H2SO4) on an active metal (Zinc, Iron).
Reaction:
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2↑
ZnSO4 + 7H2O ⟶ ZnSO4.7H2O (white vitriol)
Procedure:
- Take dilute sulphuric acid in a beaker and heat it on a wire gauze. Add some granulated zinc pieces with constant stirring.
- Effervescence take place because of the liberation of hydrogen gas.
Add zinc till the Zinc settles at the base of the beaker.
When effervescence stops, it indicates that all the acid has been used up. - The excess of zinc is filtered off.
- Collect the solution in a china dish and evaporate the solution to get crystals. Filter, wash them with water and dry them between the folds of a filter paper. The white, needle-shaped crystals are of hydrated Zinc sulphate.
(c) Sodium hydrogen carbonate crystals:
Method of preparation: By passing carbon dioxide gas into a cold solution of sodium carbonate.
Reaction:
Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O ⟶ 2NaHCO3
Procedure:
- Dissolve 5 grams of anhydrous sodium carbonate in about 25 cm3 of distilled water in a flask.
- Cool the solution by keeping the flask in a freezing mixture.
- Pass carbon dioxide gas in the solution.
- Crystals of sodium bicarbonate will precipitate out after some time.
- Filter the crystals and dry it in the folds of filter paper.
(d) calcium sulphate from calcium carbonate.
Method of preparation: By Double Decomposition (precipitation)
Reaction:
CaCO3 + 2HNO3 ⟶ Ca(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2↑
Ca(NO3)2 + Na2SO4 ⟶ CaSO4↓ + 2NaNO3
Procedure:
- First insoluble Calcium Carbonate [CaCO3] is converted to soluble Calcium Nitrate [Ca(NO3)2] with the help of dilute nitric acid.
- The resulting solution is then treated with Sodium Sulphate [Na2SO4] and a precipitate of Calcium Sulphate is obtained.
The following is a list of methods for the preparation of salts:
A — direct combination of two elements
B — reaction of a dilute acid with a metal
C — reaction of a dilute acid with an insoluble base
D — titration of a dilute acid with a solution of soluble base.
E — reaction of two solutions of salts to form a precipitate.
Choose from the list A to E, the best method of preparing the following salts by giving a suitable equation in each case:
- Anhydrous ferric chloride
- Lead chloride
- Sodium sulphate
- Copper sulphate
Answer
- Anhydrous ferric chloride — A. (Direct combination of two elements)
2Fe + 3Cl2 ⟶ 2FeCl3 - Lead chloride — E. (Reaction of two solutions of salts to form a precipitate)
Pb(NO3)2 + 2NaCl ⟶ PbCl2 + 2NaNO3 - Sodium sulphate — D. (Titration of dilute acid with a solution of soluble base)
2NaOH + H2SO4 ⟶ Na2SO4 + 2H2O - Copper sulphate — C. (reaction of a dilute acid with an insoluble base)
Cu(OH)2 + H2SO4 ⟶ CuSO4 + 2H2O
Name:
(a) a chloride which is insoluble in cold water but dissolves in hot water,
(b) a chloride which is insoluble
(c) two sulphates which are insoluble
(d) a basic salt,
(e) an acidic salt,
(f) a mixed salt,
(g) a complex salt,
(h) a double salt.
Answer
(a) a chloride which is insoluble in cold water but dissolves in hot water - Lead Chloride [PbCl2]
(b) a chloride which is insoluble - Silver chloride [AgCl]
(c) two sulphates which are insoluble - Barium sulphate [BaSO4] and Lead Sulphate [PbSO4]
(d) a basic salt - Basic lead chloride [Pb(OH)Cl]
(e) an acidic salt - Sodium hydrogen sulphate [NaHSO4]
(f) a mixed salt - Sodium potassium carbonate [NaKCO3]
(g) a complex salt - Sodium zincate [Na2ZnO2]
(h) a double salt - Dolomite [CaCO3.MgCO3]
Fill in the blanks with suitable words :
An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water forms hydronium ions as the only ............... ions. A base is a compound which is soluble in water contains ............... ions. A base reacts with an acid to form a ............... and water only. This type of reaction is known as ................
Answer
An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water forms hydronium ions as the only positively charged ions. A base is a compound which is soluble in water and contains O2- ions. A base reacts with an acid to form a salt and water only. This type of reaction is known as neutralisation.
What would you observe when:
(a) blue litmus is introduced into a solution of hydrogen chloride gas.
(b) red litmus paper is introduced into a solution of ammonia in water,
(c) red litmus paper is introduced in caustic soda solution?
Answer
(a) Blue litmus will turn into red showing acidic nature of solution.
(b) Red litmus will turn into blue showing alkaline nature of ammonia.
(c) Red litmus will turn into blue showing basic nature of solution.
Explain why :
(a) it is necessary to find out the ratio of reactants required in the preparation of sodium sulphate,
(b) fused calcium chloride is used in the preparation of FeCl3
(c) Anhydrous FeCl3 cannot be prepared by heating hydrated Iron (III) chloride.
Answer
(a) Since sodium hydroxide and sulphuric acid both are soluble, an excess of either of them cannot be removed by filtration. Therefore, it is necessary to find out on a small scale, the ratio of the solutions of the two reactants required for complete neutralisation before preparation.
(b) Iron (III) Chloride (FeCl3) is highly deliquescent. So, to keep it dry fused calcium chloride is used which is a drying agent.
(c) Anhydrous FeCl3 cannot be prepared by heating the hydrated Iron (III) chloride (FeCl3.6H2O) because on heating, FeCl3.6H2O produces Fe2O3, H2O, HCl.
2[FeCl3.6H2O] Fe2O3 + 9H2O + 6HCl
Match the salts given in column A to their methods of preparation in column B. Write a balanced equation for each preparation.
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| Zinc sulphate | Precipitation |
| Ferrous sulphide | Oxidation |
| Barium sulphate | Displacement |
| Ferric sulphate | Neutralisation |
| Sodium sulphate | Synthesis. |
Answer
Zinc Sulphate — Displacement
Zn + H2SO4 ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2
Ferrous sulphide — Synthesis
Fe + S ⟶ FeS
Barium sulphate — Precipitation
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 ⟶ BaSO4 ↓ + 2NaCl
Ferric Sulphate — Displacement
Fe + H2SO4 ⟶ FeSO4 + H2
Sodium sulphate — Neutralisation
2NaOH + H2SO4 ⟶ Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Give the pH value of pure water. Does it change if common salt is added to it.
Answer
pH of pure water is 7. No, it does not change when common salt is added.
Common salt is sodium chloride (NaCl). It is a salt derived from a strong acid (HCl) and strong base (NaOH) hence it gives a neutral solution with water.
Classify the following solutions as acids, bases or salts.
Ammonium hydroxide, barium chloride, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide, H2SO4 and HNO3
Answer
Acids — H2SO4 and HNO3
Bases — Ammonium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide.
Salts — Barium chloride and sodium chloride.
Complete the following table and write one equation for each to justify the statement:
| Reactants | Products | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Soluble base + Acid (dil) | Salt + water | Neutralisation Titration |
| Metal + Non-metal | Salt (soluble/insoluble) | ............... |
| Insoluble base + ............... | Salt (soluble) + water | ............... |
| Active metal + Acid (dil) | ............... + ............... | ............... |
| Soluble salt solution (A) + Soluble salt solution (B) | Precipitated salt + soluble salt | ............... |
| Carbonate/bicarbonate + Acid (dil) | Salt + ............... + ............... | Decomposition of carbonate |
| Chlorides/nitrates + Acid (conc.) | ............... + ............... | Decomposition of chlorides and nitrates. |
Answer
Completed table along with the equations is given below:
| Sl. No. | Reactants | Products | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soluble base + Acid (dil) | Salt + water | Neutralisation Titration |
| Eqn: HNO3 + NaOH ⟶ NaNO3 + H2O | |||
| 2. | Metal + Non-metal | Salt (soluble/insoluble) | Direct combination |
| Eqn: 2Fe + 3Cl2 ⟶ 2FeCl3 | |||
| 3. | Insoluble base + acid | Salt (soluble) + water | Neutralisation |
| Eqn: 2HCl + MgO ⟶ MgCl2 + H2O | |||
| 4. | Active metal + Acid (dil) | salt + hydrogen | Simple Displacement |
| Eqn: Fe + 2HCl ⟶ FeCl2 + H2 ↑ | |||
| 5. | Soluble salt solution (A) + Soluble salt solution (B) | Precipitated salt + soluble salt | Precipitation |
| Eqn: Na2SO4 + BaCl2 ⟶ BaSO4 ↓ + 2NaCl | |||
| 6. | Carbonate/bicarbonate + Acid (dil) | Salt + water + carbon dioxide | Decomposition of carbonate |
| Eqn: MgCO3 + H2SO4 ⟶ MgSO4 + H2O + CO2 ↑ | |||
| 7. | Chloride/nitrate + Acid (conc.) | salt + acid (HCl/HNO3) | Decomposition of chloride and nitrates. |
| Eqn: AgNO3 + HCl ⟶ AgCl ↓ + HNO3 | |||
Write the balanced equations for the preparation of the following salts in the laboratory.
(a) A soluble sulphate by the action of an acid on an insoluble base,
(b) An insoluble salt by the action of an acid on another salt,
(c) An insoluble base by the action of a soluble base on a soluble salt,
(d) A soluble sulphate by the action of an acid on a metal.
Answer
(a) CuO + H2SO4 ⟶ CuSO4 + H2O
(b) AgNO3 + HCl ⟶ AgCl ↓ + HNO3
(c) FeCl3 + 3NaOH [base] ⟶ 3NaCl + Fe(OH)3 ↓
(d) Zn + H2SO4 ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2↑
You are provided with the following chemicals:
NaOH, Na2CO3, H2O, Zn(OH)2, CO2, HCl, Fe, H2SO4, Cl2, Zn.
Using the suitable chemicals from the given list only, state briefly how you would prepare :
(a) iron (III) chloride
(b) sodium sulphate
(c) sodium zincate
(d) iron (II) sulphate
(e) sodium chloride
Answer
(a) Iron (III) Chloride: By synthesis i.e., direct combination of elements.
2Fe + 3Cl2 ⟶ 2FeCl2
(b) Sodium sulphate: By neutralisation of an alkali (caustic soda) with acid (dilute sulphuric acid)
2NaOH + H2SO4 ⟶ Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(c) Sodium zincate: By the action of metals with alkalis
Zn + 2NaOH ⟶ Na2ZnO2 + H2
(d) Iron (II) sulphate: Method of Simple Displacement by the action of dilute acid (H2SO4) on an active metal (iron).
Fe + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ FeSO4 + H2
(e) Sodium chloride: By the neutralisation reaction of strong acid (HCl) with strong base (NaOH) also known as titration NaOH + HCl ⟶ NaCl + H2O
For each of the salt : A, B, C and D, suggest a suitable method of it's preparation.
(a) A is a sodium salt,
(b) B is an insoluble salt,
(c) C is a soluble salt of copper
(d) D is a soluble salt of zinc.
Answer
(a) By neutralisation:
NaOH + HCl ⟶ NaCl + H2O
(b) By precipitation:
AgNO3 + HCl ⟶ AgCl + HNO3
(c) By Neutralisation :
Cu(OH)2 + H2SO4⟶ CuSO4 + 2H2O
(d) Simple displacement:
Zn + H2SO4 ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2↑
Choosing only substances from the list given in the box below, write equations for the reactions which you would use in the laboratory to obtain:
(a) Sodium sulphate
(b) Copper sulphate
(c) Iron (II) sulphate
(d) Zinc carbonate
| Dilute sulphuric acid | Copper | Copper carbonate |
| Iron | Sodium carbonate | |
| Sodium | ||
| Zinc |
Answer
a. Na2CO3 + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2↑
b. CuCO3 + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ CuSO4 + H2O + CO2↑
c. Fe + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ FeSO4 + H2↑
d. Zn + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2↑
ZnSO4 + Na2CO3 ⟶ ZnCO3 + Na2SO4
From the formula listed below, choose one, in each case, corresponding to the salt having the given description :
AgCl, CuCO3, CuSO4.5H2O, KNO3, NaCl, NaHSO4, Pb(NO3)2, ZnCO3, ZnSO4.7H2O
(a) an acid salt.
(b) an insoluble chloride.
(c) on treating with concentrated sulphuric acid, this salt changes from blue to white.
(d) on heating, this salt changes from green to black.
(e) this salt gives nitrogen dioxide on heating.
Answer
(a) NaHSO4
(b) AgCl
(c) CuSO4.5H2O
(d) CuCO3
(e) Pb(NO3)2
(a) Ca(H2PO4)2 is an example of compound called ............... (acid salt / basic salt / normal salt).
(b) Write the balanced equation for the reaction of :
A named acid and a named alkali.
Answer
(a) Ca(H2PO4)2 is an example of compound called acid salt
(b) NaOH + HCl ⟶ NaCl + H2O
State the terms defined by the following sentences:
(a) A soluble base
(b) The insoluble solid formed when two solution are mixed together.
(c) An acidic solution in which there is only partial ionization of the solute molecules.
Answer
(a) Alkali
(b) Precipitate
(c) Weak acid
Which of the following methods A, B, C, D or E is generally used for preparing the chlorides listed below from (i) to (v). Answer by writing down the chloride and the letter pertaining to the corresponding method. Each letter is to be used only once.
| A | Action of an acid on a metal |
| B | Action of an acid on an oxide or carbonate |
| C | Direct combination |
| D | Neutralization of an alkali by an acid |
| E | Precipitation (double decomposition) |
| (i) | Copper (II) chloride |
| (ii) | Iron (II) chloride |
| (iii) | Iron (III) chloride |
| (iv) | Lead (II) chloride |
| (v) | Sodium chloride |
Answer
The methods for preparation of the given chlorides are listed below:
| Sl. No. | Chloride | Method |
|---|---|---|
| (i) | Copper (II) chloride | B |
| (ii) | Iron (II) chloride | A |
| (iii) | Iron (III) chloride | C |
| (iv) | Lead (II) chloride | E |
| (v) | Sodium chloride | D |
From the list given below, which one is:
[SO2, SiO2, Al2O3, CO, MgO, Na2O]
(a) A covalent oxide of a metalloid
(b) An oxide which when dissolved in water form acid.
(c) A basic oxide
(d) An amphoteric oxide
Answer
(a) SiO2
(b) SO2
(c) Na2O
(d) Al2O3
What do you understand by the water of crystallisation?
Give four substances which contain water of crystallisation and write their common names.
Answer
It is the amount of water molecules which enter into loose chemical combination with the salts and can be driven out by heating the crystals above 100°C.
| Chemical name | Formula | Common name |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium carbonate decahydrate | Na2CO3.10H2O | Washing soda crystals |
| Magnesium sulphate heptahydrate | MgSO4.7H2O | Epsom salt |
| Sodium sulphate decahydrate | Na2SO4.10H2O | Glauber's salt |
| Copper (II) sulphate pentahydrate | CuSO4.5H2O | Blue vitriol |
(a) Define efflorescence. Give examples.
(b) Define deliquescence. Give examples.
Answer
(a) Efflorescence is the property of some salts to loose wholly or partly their water of crystallisation when their crytals are exposed to dry air even for a short time.
Examples: MgSO4.7H2O (Epsom salt) , Na2SO4.10H2O (Glauber's salt).
(b) Certain water-soluble substances, when exposed to the atmosphere at ordinary temperature, absorb moisture from the atmospheric air to become moist and ultimately dissolve in the absorbed water, forming a saturated solution. The phenomenon is called deliquescence and the salts are called deliquescent.
Examples: Caustic soda (NaoH), Caustic potash (KOH)
Answer the questions below:
(a) What name is given to the water in the compound copper sulphate-5-water?
(b) If copper sulphate-5-water is heated, anhydrous copper sulphate is formed. What is it's colour?
(c) By what means, other than heating, could you dehydrate copper sulphate-5-water and obtain anhydrous copper sulphate?
(d) Name a deliquescent salt.
(e) Why does hydrated copper sulphate turn white on heating?
Answer
(a) Water of crystallization
(b) White
(c) By adding concentrated sulphuric acid which acts as a dehydrating agent.
(d) Iron [III] chloride FeCl3
(e) The blue coloured hydrous copper sulphate changes to white anhydrous copper sulphate as the water of crystallization is removed on heating.
CuSO4.5H2O ⟶ CuSO4 + 5H2O
State your observation when the following are exposed to the atmosphere:
(a) Washing soda crystals
(b) Iron (III) chloride salts.
Answer
(a) When washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O) is exposed to air, it loses 9 molecules of water to form a monohydrate.
Na2CO3.10H2O Na2CO3.H2O + 9H2O
(b) When Iron (III) chloride (FeCl3) is exposed to the atmosphere at ordinary temperature, it absorbs moisture from the atmospheric air to become moist and ultimately dissolve in the absorbed water, forming a saturated solution.
Give reasons for the following:
(a) Sodium hydrogen sulphate is not an acid, but it dissolves in water to give hydrogen ions according to the equation
NaHSO4 ⇌ H+ + Na+ + SO42-
(b) Anhydrous calcium chloride is used in a desiccator.
Answer
(a) Sodium hydrogen sulphate [NaHSO4] is not an acid but due to the partial replacement of the replaceable hydrogen ion in a dibasic acid [H2SO4] releases a [H+] ion. Thus, we get the above equation.
Therefore, on dissolving in water, it gives hydrogen ions.
(b) Desiccating agents are used to absorb moisture. Anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2) has the capacity to absorb moisture as it is hygroscopic hence used as a desiccating agent.
Explain clearly how conc. H2SO4 is used as a dehydrating as well as a drying agent.
Answer
Conc. sulphuric acid is hygroscopic in nature and can remove moisture from other substances; therefore, it is used as a drying agent.
Conc. sulphuric acid can remove water molecules from blue vitriol (CuSO4.5H2O), so it is a dehydrating agent as well.
Distinguish between drying and dehydrating agent.
Answer
| Drying Agent | Dehydrating Agent |
|---|---|
| Drying Agents remove moisture from other substances. | Dehydrating Agents remove chemically combined elements of water in the ratio of 2:1 (hydrogen:oxygen) from a compound. |
| Drying Agents are used to dry gases like chlorine, sulphur dioxide and hydrogen chloride. They are also used in dessicators to keep substances dry. | Dehydrating Agents prepare substances such as carbon monoxide and sugar charcoal. |
| They represent a physical change. | They represent a chemical change. |
| Example: Phosphorous pentoxide (P2O5), Calcium Oxide (CaO) | Example: Conc. Sulphuric Acid H2SO4 |
State whether a sample of each of the following would increase or decrease in mass if exposed to air.
(a) Solid NaOH
(b) Solid CaCl2
(c) Solid Na2CO3.10H2O
(d) Conc. Sulphuric acid
(e) Iron (III) Chloride
Answer
(a) Increase
(b) Increase
(c) Decrease
(d) Increase
(e) Increase
Explanation — Efflorescent substances lose their weight while hygroscopic and deliquescent substances gain weight when exposed to atmosphere. Solid NaOH, Solid CaCl2 and Iron (III) Chloride (FeCl3) are deliquescent substances while Conc. Sulphuric acid is hygroscopic hence they gain weight when exposed to air. Solid Na2CO3.10H2O is an efflorescent substance hence it loses weight.
(a) Why does common salt get wet during the rainy season?
(b) How can this impurity be removed?
(c) Name a substance which changes the blue colour of copper sulphate crystals to white.
(d) Name two crystalline substances which do not contain water of crystallisation.
Answer
(a) Common salt gets wet during the rainy season, as it is deliquescent and absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. Though pure sodium chloride is not deliquescent, the commercial version of the salt contains impurities like, magnesium chloride and calcium chloride which are deliquescent substances.
(b) The impurity can be removed by passing a current of dry hydrogen chloride gas through a saturated solution of the affected salt. Pure sodium chloride is produced as a precipitate which can be recovered by filtering and washing first with a little water and finally with alcohol.
(c) Conc. sulphuric acid
(d) Common salt and sugar
Name the salt which on hydrolysis forms
(a) Acidic
(b) Basic and
(c) Neutral solution.
Give a balanced equation for each reaction.
Answer
(a) Iron chloride(FeCl3)
FeCl3 + 3H2O ⟶ 3HCl + Fe(OH)3
(b) Ammonium acetate (CH3COONH4)
CH3COONH4 + H2O ⟶ CH3COOH + NH4OH
(c) Sodium chloride
NaCl + H2O ⟶ NaOH + HCl
State the change noticed when blue litmus and red litmus are introduced in the following solutions:
(a) Na2CO3 solution
(b) NaCl solution
(c) NH4NO3
(d) MgCl2 Solution
Answer
(a) Na2CO3 solution — Red litmus changes to blue as Na2CO3 gives alkaline solution.
(b) NaCl solution — No change in the colour of the litmus paper as NaCl solution is neutral.
(c) NH4NO3 — Acidic so blue litmus changes to red.
(d) MgCl2 — Blue litmus changes to red showing acidic nature.
The acid which contains four hydrogen atoms is :
- Formic acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Nitric acid
- Acetic acid
Answer
Acetic acid
Reason — The formulas of the given acids are:
| Acid | Formula |
|---|---|
| Formic acid | HCOOH |
| Sulphuric acid | H2SO4 |
| Nitric acid | HNO3 |
| Acetic acid | CH3COOH |
Hence, out of the given acids, Acetic acid contains four hydrogen atoms.
A black coloured solid which on reaction with dilute sulphuric acid forms a blue coloured solution is :
- Carbon
- Manganese [IV] oxide
- Lead [II] oxide
- Copper [II] oxide
Answer
Copper [II] oxide
Reason — Copper [II] oxide is black in colour and the following reaction takes place when it is treated with dilute sulphuric acid —
CuO + H2SO4 ⟶ CuSO4 + H2O
CuSO4 is a blue coloured soln.
A weak organic acid is :
- Formic acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Nitric acid
- Hydrochloric acid
Answer
Formic acid
Reason — Formic acid (HCOOH) is a weak organic acid whereas Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Nitric acid (HNO3) and Hydrochloric acid (HCl) are strong mineral (or inorganic) acids.
A complex salt is :
- Zinc sulphate
- Sodium hydrogen sulphate
- Iron [ammonium sulphate]
- Tetraammine copper [II] sulphate
Answer
Tetraammine copper [II] sulphate
Reason — Tetraammine copper [II] sulphate ([Cu(NH3)4]SO4) is a complex salt as on dissociation, it gives one simple ion and one complex ion:
[Cu(NH3)4]SO4 ⟶ [Cu(NH3)4]2+ + SO42-
Which one of the following will not produce acid with water ?
- CO
- CO2
- NO2
- SO3
Answer
CO
Reason — Carbon monoxide reacts with water to form carbon dioxide and releases hydrogen gas. Hence, acid is not formed.
CO + H2O ⟶ CO2 + H2
The basicity of acetic acid is:
- 3
- 1
- 4
- 2
Answer
1
Reason — Acetic acid has four hydrogen atoms in it but it ionises in aqueous solution to produce one hydrogen ion per molecule of the acid. Hence, basicity of acetic acid is 1.
Select the word/s given below which are required to correctly complete the blanks — [ammonia, ammonium carbonate, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, hydronium, hydroxide, precipitate, salt water] :
(i) A solution M turns blue litmus red, so it must contain (i) ............... ions ; another solution O turns red litmus blue and hence, must contain, (ii) ............... ions.
(ii) When solution M and O are mixed together, the products will be (iii) ............... and (iv) ............... .
(iii) If a piece of magnesium was put into a solution M, (v) ............... gas would be evolved.
Answer
(i) A solultion M turns blue litmus red, so it must contain (i) hydronium ions ; another solution O turns red litmus blue and hence, must contain, (ii) hydroxide ions.
(ii) When solution M and O are mixed together, the products will be (iii) salt and (iv) water.
(iii) If a piece of magnesium was put into a solution M, (v) hydrogen gas would be evolved.
Match the following:
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| (i) Acid salt | (A) Ferrous ammonium sulphate |
| (ii) Double salt | (B) Contains only ions |
| (iii) Ammonium hydroxide solution | (C) Sodium hydrogen sulphate |
| (iv) Dilute hydrochloric acid | (D) Contains only molecules |
| (v) Carbon tetrachloride | (E) Contains ions and molecules |
Answer
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| (i) Acid salt | (C) Sodium hydrogen sulphate |
| (ii) Double salt | (A) Ferrous ammonium sulphate |
| (iii) Ammonium hydroxide solution | (E) Contains ions and molecules |
| (iv) Dilute hydrochloric acid | (B) Contains only ions |
| (v) Carbon tetrachloride | (D) Contains only molecules |
Match the salts given in column I with their method of preparation given in column II.
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| (i) Pb(NO3)2 from PbO | (A) Simple displacement |
| (ii) MgCl2 from Mg | (B) Titration |
| (iii) FeCl3 from Fe | (C) Neutralization |
| (iv) NaNO3 from NaOH | (D) Precipitation |
| (v) ZnCO3 from ZnSO4 | (E) Combination |
Answer
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| (i) Pb(NO3)2 from PbO | (C) Neutralization |
| (ii) MgCl2 from Mg | (A) Simple displacement |
| (iii) FeCl3 from Fe | (E) Combination |
| (iv) NaNO3 from NaOH | (B) Titration |
| (v) ZnCO3 from ZnSO4 | (D) Precipitation |
From — Na2O, SO2, SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, CO — Select an oxide which dissolves in water forming an acid.
Answer
SO2
The following reaction takes place.
SO2 + H2O ⟶ H2SO3
From the list given below, which one is :
- a deliquescent compound
- a compound soluble in hot water but insoluble in cold water
- a compound which in the aqueous solution state, is neutral in nature.
A. Nitroso iron [II] sulphate
B. Iron [III] chloride
C. Chromium sulphate
D. Lead chloride
E. Sodium chloride
Answer
- B: Iron [III] chloride
- D: Lead [II] chloride
- E: Sodium chloride
From the list of salts — AgCl, MgCl2, NaHSO4, PbCO3, ZnCO3, KNO3, Ca(NO3)2
Choose the salt that most appropriately fits the description given below :
(i) a deliquescent salt
(ii) an insoluble chloride.
Answer
(i) MgCl2
(ii) AgCl
Give a suitable word or phrase for :
- A salt formed by incomplete neutralisation of an acid by a base.
- The definite number of water molecules bound to some salts.
- The process in which a substance absorbs moisture from the atmospheric air to become moist, and ultimately dissolves in the absorbed water.
- A salt containing a metal ion surrounded by other ions or molecules.
- A base which is soluble in water.
Answer
- Acid salt
- Water of crystallisation
- Deliquescence
- Complex salts
- Alkali
Name the method used for the preparation of the following salts from the list given below –
(i) Sodium nitrate
(ii) Iron (III) chloride
(iii) Lead chloride
(iv) Zinc sulphate
(v) Sodium hydrogen sulphate.
List:
A : Simple displacement
B : Neutralization
C : Decomposition by acid
D : Double decomposition
E : Direct synthesis
Answer
(i) Sodium nitrate — B : Neutralization
(ii) Iron (III) chloride — E : Direct synthesis
(iii) Lead chloride — D : Double decomposition
(iv) Zinc sulphate — A : Simple displacement
(v) Sodium hydrogen sulphate — C : Decomposition by acid
Define the following terms — Neutralization
Answer
Neutralization — It is the process due to which [H+] ions of an acid react completely or combine with [OH-] ions of a base to give salt and water only.
Acid + Base ⟶ Salt + Water
HCl + NaOH ⟶ NaCl + H2O
H+Cl- + Na+OH- ⟶ Na+Cl- + H2O
[H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) ⇌ H2O (l)]
State your observation when zinc granule is added to copper sulphate solution.
Answer
Zinc displaces copper to form zinc sulphate and thus copper gets deposited and the blue coloured solution becomes colourless.
Zn + CuSO4 ⟶ Cu + ZnSO4
Salt S is prepared by reacting dilute sulphuric acid with copper oxide. Identify S.
Answer
Salt S is Copper sulphate CuSO4
CuO + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ CuSO4 + H2O
From the substances given in the list below, write the equations for the reactions by which you could obtain the compounds given ahead :
| Dilute sulphuric acid | sodium carbonate |
| Zinc | sodium sulphite |
| Lead | calcium carbonate |
- hydrogen,
- sulphur dioxide,
- carbon dioxide,
- zinc carbonate (two steps required).
Answer
Equations for the reactions are :
Zn + H2SO4 ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2↑
Na2SO3 + 2HCl ⟶ 2NaCl + H2O + SO2↑
Na2CO3 + H2SO4 Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2↑
Zn + H2SO4 ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2↑
ZnSO4 + Na2CO3 ⟶ Na2SO4 + ZnCO3
Choosing the substances from the list given:
dil. Sulphuric acid, Copper, Iron, Sodium, Copper (II) carbonate, Sodium carbonate, Sodium chloride, Zinc nitrate
Write balanced equations for the reactions which would be used in the laboratory to obtain the following salts:
- Sodium sulphate
- Zinc carbonate
- Copper (II) sulphate
- Iron (II) sulphate.
Answer
Sodium sulphate
Na2CO3 + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2Zinc carbonate
Zn(NO3)2 + Na2CO3⟶ 2NaNO3 + ZnCO3Copper (II) sulphate
CuCO3 + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ CuSO4 + H2O + CO2Iron (II) sulphate
Fe + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ FeSO4 + H2
You are given three solutions A, B and C. A is a strong acid, B is a weak acid and C is a strong alkali.
(a) Which solution contains solute molecules in addition to water molecules ?
(b) Which solution gives gelatinous white precipitate with zinc sulphate which disappears in excess solution ?
Answer
(a) Solution B — weak acid
Reason — Weak Acid is an acid which dissociates only partially in aqueous solution thereby producing a low concentration of hydrogen [H+] ions [or H3O+ ions]. For example — CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COO- + H+ [contains molecules and ions]
(b) Solution C — strong alkali
Reason — Alkalis react with certain salt solutions to precipitate insoluble hydroxide. Hence,
ZnSO4 + 2NaOH ⟶ Na2SO4 + Zn(OH)2 [gelatinous white precipitate]
Write balanced chemical equations for the following:
(a) Reaction of silver nitrate solution and sodium chloride solution.
(b) Lead nitrate solution is added to sodium chloride solution.
(c) State what happens to the crystals of washing soda when they are exposed to air. Name the phenomenon exhibited.
Answer
(a) AgNO3 + NaCl ⟶ NaNO3 + AgCl ↓
(b) Pb(NO3)2 + 2NaCl ⟶ PbCl2 ↓ + 2NaNO3
(c) When crystals of washing soda are exposed to air, it loses its water of crystallisation and the phenomenon is known as Efflorescence.
Give a balanced equation for the preparation of the following salts:
(a) Copper [II] sulphate from copper [II] oxide.
(b) Iron [III] chloride from the metal iron.
(c) Lead sulphate from lead carbonate.
(d) Potassium sulphate from KOH solution.
(e) Lead [II] chloride from lead carbonate [give two equations].
Answer
(a) CuO + H2SO4 ⟶ CuSO4 + H2O
(b) 2Fe + 3Cl2 ⟶ 2FeCl3
(c) PbCO3 + 2HNO3 ⟶ Pb(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2
Pb(NO3)2 + Na2SO4 ⟶ 2NaNO3 + PbSO4
(d) 2KOH + H2SO4 [dil.] ⟶ K2SO4 + 2H2O
(e) PbCO3 + 2HNO3 ⟶ Pb(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2 ↑
Pb(NO3)2 + 2NaCl ⟶ 2NaNO3 + PbCl2
Write the balanced equations for the preparation of the following compounds (as the major product) starting from iron and using only one other substance :
(a) Iron (II) chloride
(b) Iron (III) chloride
(c) Iron (II) sulphate
(d) Iron (II) sulphide
Answer
(a) Fe + 2HCl (dil) ⟶ FeCl2 + H2↑
(b) 2Fe (heated) + 3Cl2 (dry) ⟶ 2FeCl3
(c) Fe + H2SO4 (dil) ⟶ FeSO4 + H2↑
(d) Fe + S FeS
Draw the structure of the stable positive ion formed when an acid dissolves in water.
Answer
Hydronium ion is the stable positive ion formed when an acid dissolves in water. Its structure is shown below:
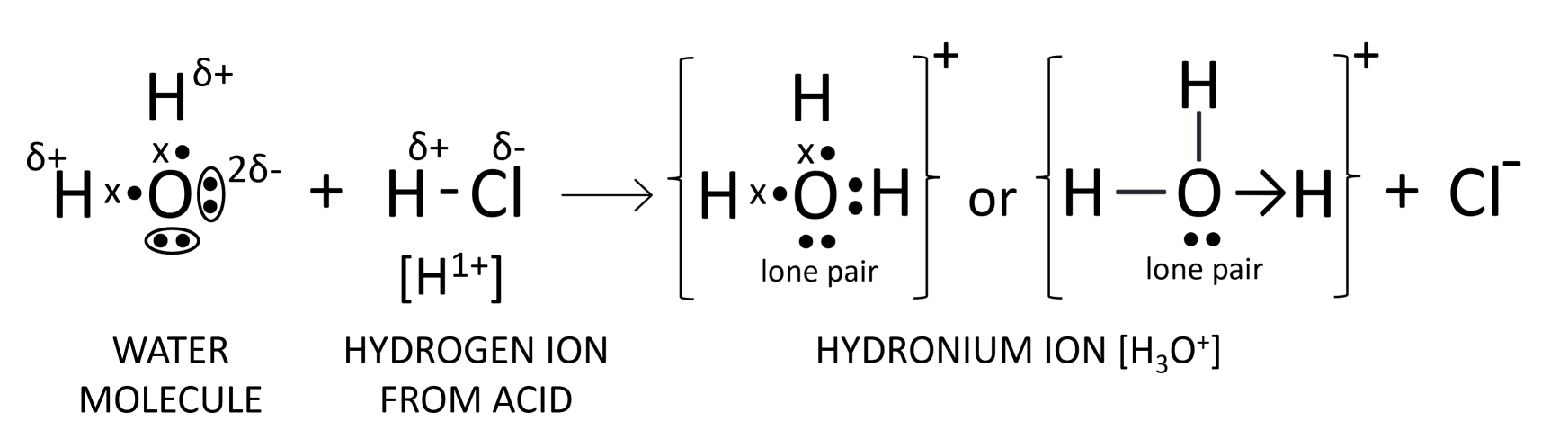
Write balanced reactions for the following conversions (A,B,C,D)
Answer
A = HCl
B = Na2CO3
C = HNO3
D = NaOH
A: Fe + 2HCl ⟶ FeCl2 + H2 ↑
B: FeCl2 + Na2CO3 ⟶ FeCO3 + 2NaCl
C: FeCO3 + 2HNO3 ⟶ Fe(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2
D: Fe(NO3)2 + 2NaOH ⟶ Fe(OH)2 + 2NaNO3
Give an equation for the conversions A to E —

Answer
(i) ZnSO4 + Na2CO3 ⟶ Na2SO4 + ZnCO3 ↓
(ii) ZnCO3 + 2HNO3 ⟶ Zn(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2 ↑
(iii) Zn(NO3)2 + 2NaOH ⟶ Zn(OH)2 + 2NaNO3
(iv) Zn(OH)2 ZnO + H2O
(v) ZnO + H2SO4 ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2O
The preparation of lead sulphate from lead carbonate is a two step process. (lead sulphate cannot be prepared by adding dilute sulphuric acid to lead carbonate.)
(a) What is the first step that is required to prepare lead sulphate from lead carbonate?
(b) Write the equation for the reaction that will take place when this first step is carried out.
(c) Why is the direct addition of dilute sulphuric acid to lead carbonate an impractical method of preparing lead sulphate?
Answer
(a) The first step is to convert insoluble lead carbonate into soluble lead nitrate by treating lead carbonate with dilute nitric acid.
(b) PbCO3 (s) + 2HNO3(dil) ⟶ Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2
(c) Adding dilute sulphuric acid (H2SO4) to lead carbonate (PbCO3) in order to prepare lead sulphate (PbSO4) is an impractical method because an insoluble crust of lead sulphate is formed on lead carbonate which prevents further reaction.
The diagram given below is to prepare Iron [III] chloride in the laboratory.
![The diagram given below is to prepare Iron [III] chloride in the laboratory. Why iron[III] chloride closed container. What is substance B. What is the purpose of B. Acids, Bases and Salts, Concise Chemistry Solutions ICSE Class 10](https://cdn1.knowledgeboat.com/img/cc10/iron-3-chloride-lab-prep-concise-chemistry-solutions-icse-class-10-426x158.png)
(i) What is substance B.
(ii) What is the purpose of B.
(iii) Why is iron[III] chloride to be stored in a closed container.
(iv) Write the equation for the reaction between iron and chlorine.
Answer
(i) Substance B is fused calcium chloride.
(ii) Iron (III) chloride is highly deliquescent so it is kept dry with the help of B [fused calcium chloride (drying agent)]
(iii) Iron[III] chloride is to be stored in a closed container because iron (III) chloride is highly deliquescent and it absorbs moisture from the surrounding air to form a saturated solution.
(iv) 2Fe (heated) + 3Cl2 (dry) ⟶ 2FeCl3