Chemical Bonding
How do atoms attain noble gas configuration ?
Answer
Atoms attain noble gas configuration by losing, gaining or sharing of electrons present in their outermost shell.
Define :
(a) a chemical bond,
(b) an electrovalent bond,
(c) a covalent bond.
Answer
(a) Chemical Bond — A chemical bond may be defined as the force of attraction between any two atoms, in a molecule, to maintain stability.
(b) Electrovalent (or ionic) Bond — The chemical bond formed between two atoms by transfer of one or more electrons from the atom of a metallic (electropositive) element to an atom of a non-metallic (electronegative) element is called an electrovalent (or ionic) bond.
(c) Covalent Bond — The chemical bond that is formed between two combining atoms by mutual sharing of one or more pair of electrons is called a covalent bond.
What are the conditions for the formation of an electrovalent bond ?
Answer
The conditions for the formation of an electrovalent bond are:
- Low ionisation potential — If the ionisation potential of a particular atom is low, it will lose electron(s) easily, i.e., a cation is formed easily.
- High electron affinity — If the electron affinity value is high, anion will be formed easily.
- Large electronegativity difference — If the difference in the electronegativities of two elements is higher, then the transfer of electrons will be easier.
An atom X has three electrons more than the noble gas configuration. What type of ion will it form ? Write the formula of its (i) sulphate (ii) nitrate (iii) phosphate (iv) carbonate (v) hydroxide.
Answer
Since there are three electrons more than the noble gas configuration in the atom so the atom will try to lose three electron to gain noble gas configuration. Therefore, it will form a cation X3+.
Formula of its:
(i) Sulphate — X2(SO4)3
(ii) Nitrate — X(NO3)3
(iii) Phosphate — XPO4
(iv) Carbonate — X2(CO3)3
(v) Hydroxide — X(OH)3
Mention the basic tendency of an atom which makes it to combine with other atoms.
Answer
The basic tendency of an atom which makes it to combine with other atoms is the tendency of elements to acquire the nearest noble gas configuration in their outermost orbit and become stable.
The element X has the electronic configuration 2, 8, 18, 8, 1. Without identifying X,
(a) predict the sign and charge on a simple ion of X.
(b) write if X will be an oxidising agent or a reducing agent and why.
Answer
(a) X+ Reason — Since the element X has 1 electron in its valence shell. So, it will lose an electron and gain noble gas configuration. Therefore it forms a cation (X+). The sign is positive and the charge is of 1 proton.
(b) X will be a strong reducing agent as it has the tendency to donate its valence electron.
In the formation of the compound XY2, an atom X gives one electron to each Y atom. What is the nature of bond in XY2 ? Draw the electron dot structure of this compound.
Answer
Since the atom X gives one electron to each Y atom. Therefore, X & Y form an ionic bond in XY2. The electron dot structure of this compound is shown below:

An atom X has 2, 8, 7 electrons in its shell. It combines with Y having 1 electron in its outermost shell.
(a) What type of bond will be formed between X and Y ?
(b) Write the formula of the compound formed .
Answer
(a) Ionic Bond
Reason — Since X has 7 electrons in its outermost shell and Y has only one electron in its outermost shell. So, Y loses its one electron and X gains that electron to form an ionic bond.
(b) The formula of the compound is XY.
Explain with the help of ionic equation and electron dot structural diagram the formation of the following electrovalent compounds.
(a) NaCl
(b) MgCl2
(c) CaO
Answer
(a) Na+ + Cl- ⟶ NaCl
The electron dot structural diagram is:

(b) Mg+2 + 2Cl- ⟶ MgCl2
The electron dot structural diagram is:

(c) Ca+2 + O-2 ⟶ CaO
The electron dot structural diagram is:

Compare :
(a) sodium atom and sodium ion
(b) chlorine atom and chloride ion
with respect to
- atomic structure
- electrical state
- chemical action
- toxicity
Answer
(a) Comparison between sodium atom and sodium ion:
| Property | Sodium Atom | Sodium Ion |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Structure | It has one electron in M shell. | It has 8 electrons in L shell. |
| Electrical State | It is neutral. | It is positively charged. |
| Chemical Action | It is very Active. | It is inactive. |
| Toxicity | It is poisonous. | It is non-poisonous. |
(b) Comparison between chlorine atom and chloride ion:
| Property | Chlorine Atom | Chloride Ion |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Structure | It has 7 electrons in M shell. | It has 8 electrons in M shell. |
| Electrical State | It is neutral. | It is negatively charged. |
| Chemical Action | It is very Active. | It is inactive. |
| Toxicity | It is poisonous. | It is non-poisonous. |
The electronic configuration of Fluoride ion is the same as that of a neon atom. What is the difference between the two ?
Answer
The electronic configuration of Fluoride ion is the same as that of a neon atom i.e., both have 8 electrons in their valence shell but Fluoride attain that configuration by gaining an electron so it is negatively charged but neon atom have its own 8 valence electrons so it is neutral i.e., it have no charge on it.
State which of the following are reduction reaction and which are oxidation
(i) Pb ⟶ Pb2+ + 2e-
(ii) Fe2+ - e- ⟶ Fe3+
(iii) A3+ + e- ⟶ A2+
(iv) Cu ⟶ Cu2+
Answer
(i) Oxidation, since there is a loss of 2 electrons by Lead (Pb).
(ii) Oxidation, since there is a loss of an electron by Iron (Fe).
(iii) Reduction, since there is a gain of an electron by A.
(iv) Oxidation, since there is a loss of 2 electrons by Copper (Cu).
What do you understand by redox reactions ?
Answer
A reaction in which oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously is called an oxidation-reduction reaction or redox reaction. It involves transfer of electrons between two atoms.
Explain oxidation and reduction in terms of loss or gain of electrons.
Answer
The reaction in which electron(s) is gained is called a reduction reaction and the reaction in which there is a loss of electron(s) is called an oxidation reaction.
Explain formation of electrovalent compound is a redox reaction.
Answer
In the formation of electrovalent compounds, the transfer of electrons is involved. The electropositive atom loses electrons and undergoes oxidation while the electronegative atom gains electrons and undergoes reduction. Hence, formation of electrovalent compound is a redox reaction.
Divide the following redox reactions into oxidation and reduction half reactions.
(i) Zn + Pb2+ ⟶ Zn2+ + Pb
(ii) Zn + Cu2+ ⟶ Zn2+ + Cu
(iii) Cl2 + 2Br- ⟶ Br2 + 2Cl-
(iv) Sn2+ + 2Hg2+ ⟶ Sn4+ + Hg22+
(v) 2Cu+ ⟶ Cu + Cu2+
Answer
(i) Oxidation : Zn ⟶ Zn2+
Reduction : Pb2+ ⟶ Pb
(ii) Oxidation : Zn ⟶ Zn2+
Reduction : Cu2+ ⟶ Cu
(iii) Oxidation : 2Br- ⟶ Br2
Reduction : Cl2 ⟶ 2Cl-
(iv) Oxidation : Sn2+ ⟶ Sn4+
Reduction : 2Hg2+ ⟶ Hg22+
(v) Oxidation : Cu+ ⟶ Cu2+
Reduction : Cu+ ⟶ Cu
Potassium (at No. 19) and chlorine (at No.17) react to form a compound. Explain on the basis of electronic concept :
(i) oxidation
(ii) reduction
(iii) oxidising agent
(iv) reducing agent.
Answer
The electronic configuration of:
Potassium (19) = 2, 8, 8, 1
Chlorine (17) = 2, 8, 7
The reaction is :
2K + Cl2 ⟶ K+ + 2Cl-
(i) Oxidation : 2K ⟶ K+
Potassium undergoes oxidation reaction as it loses an electron.
(ii) Reduction : Cl2 ⟶ 2Cl-
Chlorine undergoes reduction reaction as it gains an electron.
(iii) Chlorine acts as an oxidising agent and gets reduced.
(iv) Potassium acts as a reducing agent and gets oxidised.
What are the conditions necessary for the formation of covalent molecules ?
Answer
The necessary conditions for the formation of covalent molecules are:
- Both atoms should have four or more electrons in their outermost shells, i.e., non-metals (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, etc).
- Both the atoms should have high electronegativity.
- Both the atoms should have high electron affinity.
- Both the atoms should have high ionization energy.
- The electronegativity difference between the combining atoms should either be zero or negligible.
Elements A, B and C have atomic numbers 17, 19 and 10 respectively.
(a) State which one is : (i) a non-metal (ii) metal (iii) chemically inert ?
(b) Write down the formula of the compound formed by two of the above elements.
Answer
The electronic configuration of :
A (17) = 2, 8, 7
B (19) = 2, 8, 8, 1
C (10) = 2, 8
(a) (i) A is a non-metal because there are 7 valence electrons in A.
(a) (ii) B is a metal because there is only 1 valence electron in B.
(a) (iii) C is chemically inert element because there are 8 valence electrons in C.
(b) The formula of the compound formed by two of the above elements is BA. The reason being, B loses an electron and A gains that electron to form an ionic bond.
Draw electron dot diagram and structure of :
(a) nitrogen molecule
(b) magnesium chloride
(c) methane
Answer
(a) Electron dot diagram and structure of Nitrogen molecule is shown below:

(b) Electron dot diagram and structure of magnesium chloride is shown below:

(c) Electron dot diagram and structure of methane is shown below:

What is the difference between :
(a) ionic compounds and polar covalent compounds,
(b) ionic compounds and covalent compounds,
(c) a polar covalent compound and a non-polar covalent compound ?
Answer
(a) Difference between ionic compounds and polar covalent compounds:
| Ionic Compounds | Polar Covalent Compounds |
|---|---|
| The chemical compounds formed as a result of the transfer of electrons from one atom of an element to one atom of another element are called ionic compounds. | The compounds formed by mutual sharing of electrons between combining atoms in which the shared pair of electrons are not at equal distance between the two atoms are called polar covalent compounds. |
(b) Difference between ionic compounds and covalent compounds:
| Ionic Compounds | Covalent Compounds |
|---|---|
| The chemical compounds formed as a result of the transfer of electrons from one atom of an element to one atom of another element are called ionic compounds. | The compounds formed by mutual sharing of one or more pair of electrons between combining atoms are called Covalent Compounds |
| They are made up of ions and are hard solids. | They are made up of molecules and are gases or liquids or soft solids. |
| They have high melting and boiling point. | They have low melting and boiling points. |
| They are soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents. | They are insoluble in water but dissolve in organic solvents. |
(c) Difference between a polar covalent compound and a non-polar covalent compound
| Polar Covalent Compound | Non-Polar Covalent Compound |
|---|---|
| The covalent compounds are said to be polar when the shared pair of electrons are not at equal distance between the two atoms. | Covalent compounds are non-polar when the shared pair of electron(s) are equally distributed between the two atoms. |
| They have fractional positive and negative charges on them. | No charge separation takes place. |
| They ionise in water. | They don't ionise in water. |
A solid is crystalline, has a high melting point and is water soluble. Describe the nature of the solid.
Answer
The given properties of the solid indicates that the solid is an ionic compound consisting of oppositely charged ions held tightly together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction of an ionic bond.
What do you understand by dipole (polar) molecule ? Explain it by taking hydrogen chloride as an example.
Answer
A molecule that has both, slight positive and slight negative charge is called a dipole molecule.
For example - In hydrogen chloride, the strong nuclear charge of the chlorine atom (the electro-negativity of chlorine is 3) attracts the shared electron pair towards itself due to which a slight negative charge develops on the chlorine atom. The hydrogen atom (electronegativity 2.1) develops a slight positive charge. Therefore, a polar covalent bond is formed.

Explain the bonding in methane molecule using electron dot structure.
Answer
The valency of hydrogen element is 1 and that of carbon is 4. Hydrogen needs one electron to attain stable duplet structure of nearest noble gas - He [2] and carbon needs four electrons to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ne [2,8]
One carbon atom shares four electron pairs one with each of the four atoms of hydrogen such that hydrogen acquires a duplet configuration and carbon an octet configuration resulting in the formation of four single covalent bonds.
Electron Dot Structure:

Methane molecule is non-polar molecule. Explain.
Answer
The bond formed between dissimilar atoms can be non-polar if their electronegativity difference is little and their structure permits the shared pair of electrons to attract equally the linked atoms and thus the molecule becomes symmetrical.
The shared electron pairs in Methane are at an equal distance from the Carbon and the Hydrogen atoms because the two have nearly equal electronegativities (carbon = 2.5, hydrogen = 2.1).
Give the characteristic properties of :
(a) electrovalent compounds,
(b) covalent compounds.
Answer
(a) The characteristic properties of electrovalent compounds are:
- They are hard solids consisting of ions.
- They are non-volatile with high melting and boiling points.
- They do not conduct electricity in solid state but are good conductors of electricity in the fused or in aqueous state.
- They are good conductors of heat.
- They are soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents.
- They show rapid speed of chemical reactions in aqueous solutions.
(b) The characteristic properties of covalent compounds are:
- Their constituent particles are molecules. They are gases or liquids or soft solids.
- They are volatile with low melting and boiling points.
- They are non-conductors of electricity in solid, molten or aqueous state.
- They are poor conductors of heat.
- They are insoluble in water but dissolve in organic solvents.
- They show slow speed of chemical reactions in aqueous solutions.
State the type of bond formed, when the combining atoms have :
(i) zero E.N. difference
(ii) small E.N. difference
(iii) large E.N. difference
Answer
(i) Non-polar covalent bond.
(ii) Polar covalent bond.
(iii) Ionic or Electrovalent bond.
State the type of bond formed, and draw Lewis structure of
(i) water
(ii) calcium oxide
Answer
(i) In water covalent bond is formed.

(ii) In calcium oxide ionic bond is formed.

Explain the following :
Electrovalent compounds conduct electricity.
Answer
Electrovalent compounds consists of ions but the strong electrostatic force keeps ions in fixed position in the solid state. The force is weakened in the molten state and disappears in aqueous solution state, hence free ions formed help in the conduction of electricity.
Explain the following :
Electrovalent compounds have a high melting point and boiling point while covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
Answer
Electrovalent compounds have a high melting point and boiling point because there exists a strong force of attraction between the oppositely charged ions, so a large amount of energy is required to break the strong bonding force between ions. While covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points because they have weak forces of attraction between the binding molecules, thus less energy is required to break the force of bonding.
Explain the following :
Electrovalent compounds dissolve in water whereas covalent compounds do not.
Answer
Electrovalent compounds dissolve in water because water is a polar compound, it decreases the electrostatic forces of attraction, resulting in free ions in aqueous solution. Hence they dissolve. Whereas covalent compounds do not dissolve in water because covalent compounds are made up of molecules, they do not ionize in water and hence do not dissolve.
Explain the following :
Electrovalent compounds are usually hard crystals.
Answer
Electrovalent compounds are usually hard crystals because they have strong electrostatic forces of attraction between their ions, which cannot be separated easily.
Explain the following :
Polar covalent compounds conduct electricity.
Answer
Polar covalent compounds have fractional positive and negative charges on them. In aqueous solution state, they undergo ionisation converting the fractional charges to complete charges and ions are produced. These ions helps in the conduction of electricity.
Explain the following :
Water is a polar covalent molecule?
Answer
Water is a polar covalent molecule because the shared pair of electrons between hydrogen and oxygen are not at equal distance. There is a slight difference in electronegativities of Oxygen (3.5) and Hydrogen (2.1) due to which the shared pair of electrons is shifted towards Oxygen creating a slight negative charge on it while a slight positive charge is developed on the two Hydrogen atoms making Water a polar covalent molecule.
Elements X, Y and Z have atomic numbers 6, 9 and 12 respectively. Which one :
(a) forms an anion,
(b) forms a cation,
(c) state type of bond between Y and Z and give its molecular formula.
Answer
The electronic configuration of :
X (6) = 2, 4
Y (9) = 2, 7
Z (12) = 2, 8, 2
(a) Y forms an anion as it needs just one more electron to complete its octet.
(b) Z forms a cation. It will lose its 2 electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration thus forming a cation.
(c) Ionic bond is formed between Y and Z and its molecular formula is ZY2.
Taking MgCl2 as an electrovalent compound, CCl4 as a covalent compound, give four differences between electrovalent and covalent compounds.
Answer
| Electrovalent Compound (MgCl2) | Covalent Compound (CCl4) |
|---|---|
| MgCl2 is formed by transfer of electrons from Magnesium to Chlorine so it consists of ionic bonds. | CCl4 is formed by sharing of electrons between Carbon and Chlorine so it is made up of covalent bonds. |
| MgCl2 consists of ions Mg2+ & Cl-. | CCl4 consists of molecules — 1 Carbon and 4 Chlorine atoms form a molecule of CCl4. |
| MgCl2 has higher melting and boiling point. | CCl4 has lower melting and boiling point. |
| An aqueous solution of MgCl2 functions as an electrolyte and conducts electricity. | CCl4 does not conduct electricity in solid, liquid or molten state. |
| MgCl2 is easily soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents. | CCl4 is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. |
Potassium chloride is an electrovalent compound, while hydrogen chloride is a covalent compound. But, both conducts electricity in their aqueous solutions. Explain.
Answer
Potassium chloride being an electrovalent compound consists of ions. In aqueous solution state, the electrostatic forces between them weaken and the ions become mobile conducting electricity.
On the other hand, hydrogen chloride is a polar covalent compound. The shared electron pair is shifted towards Chlorine thereby developing a slight negative charge on it and a slight positive charge on hydrogen atom. In its aqueous solution state, hydrogen chloride ionises into Hydronium and Chloride ions as shown in the equation below. These ions help in conducting electricity.
HCl + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + Cl-
Draw the electron dot structure of covalent compound methane (non-polar) and HCl (polar) and give two difference between them.
Answer
Electron dot structure of methane:

Electron dot structure of HCl:

| Methane (CH4) | Hydrogen Chloride (HCl) |
|---|---|
| No charge separation takes place. | Charge separation takes place. |
| The molecule is symmetrical and electrically neutral. | There is fractional positive and fractional negative charge on them. |
Name two compounds that are covalent when taken pure but produce ions when dissolved in water.
Answer
Hydrogen Chloride (HCl) & Ammonia (NH3).
For each compound mentioned above give the formulae of ions formed in aqueous solution.
Answer
Hydrogen chloride (HCl)
HCl + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + Cl-
Ammonia (NH3)
NH3 + H2O ⇌ NH4+ + OH-
An element M burns in oxygen to form an ionic bond MO. Write the formula of the compounds formed if this element is made to combine with chlorine and sulphur separately.
Answer
With Chlorine — MCl2
With Sulphur — MS
Explanation:
Given, M reacts with oxygen to form an ionic bond MO. Oxygen needs 2 electrons to complete its octet forming the anion O2-. As the compound formed is MO, it means that M has 2 electrons in its valence shell which it donates to Oxygen to attain a stable electronic configuration forming a cation M2+.
Each Chlorine atom accepts 1 electron to complete its octet so 2 Chlorine atoms combine with 1 atom of M to form MCl2. Each Sulphur atom accepts 2 electrons to complete its Octet so 1 Sulphur atom combines with 1 atom of M to form MS.
Element A has 2 electrons in its M shell. Element B has atomic number 7.
(a) Write equations to show how A and B form ions.
(b) If B is a diatomic gas, write the equation for the direct combination of A and B to form a compound.
(c) If the compound formed between A and B is melted and an electric current is passed through the molten compound, the element A will be obtained at the ............. and B at the ............ of the electrolytic cell.
Answer
A has two electrons in M shell i.e., A has valency 2 (metal), and the electronic configuration of B(7) is 2, 5 i.e., B has valency 3 (non-metal).
(a) A ⟶ A2+ + 2e-
B + 3e- ⟶ B3-
(b) 3A + B2 ⟶ A3B2
(c) Element A will be obtained at the Cathode and B at the Anode of the electrolytic cell.
Reason — As A is a cation, so it is attracted towards cathode as cathode is negatively charged. B is an anion so it is attracted towards anode as anode is positively charged.
Element M forms a chloride with the formula MCl2 which is a solid with high melting point. M would most likely be in the group in which .............. is placed.
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) Al
(d) Si
Answer
Magnesium (Mg).
Reason — Since, element M forms a chloride with the formula MCl2 which is a solid with high melting point. So, M belongs to the group 2 because it has valency 2.
Complete the following
| Sodium | Phosphorus | Carbon | |
| Formula of chloride | |||
| Nature of bonding | |||
| Physical state of chloride |
Answer
| Sodium | Phosphorus | Carbon | |
| Formula of chloride | NaCl | PCl3, PCl5 | CCl4 |
| Nature of bonding | Ionic Bond | Covalent Bond | Covalent Bond |
| Physical state of chloride | Solid | Liquid, Solid | Liquid |
Compound X consists of molecules.
Choose the letter corresponding to the correct answer from the options A, B, C and D given below :
(i) The type of bonding in X will be :
A. ionic
B. electrovalent
C. covalent
D. molecular
(ii) X is likely to have a :
A. low melting point and high boiling point.
B. high melting point and low boiling point.
C. low melting point and low boiling point.
D. high melting point and high boiling point.
(iii) In the liquid state, X will :
A. become ionic,
B. be an electrolyte,
C. conduct electricity,
D. not conduct electricity.
Answer
(i) C → covalent
Reason : Since, X consists of molecules. Therefore, covalent bond is present.
(ii) C → Low melting point and low boiling point.
Reason : Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
(iii) D → not conduct electricity.
Reason : Covalent compounds are non-conductor of electricity in solid, molten or aqueous state.
The property which is characteristic of an electrovalent compound is that :
- it is easily vaporized
- it has a high melting point
- it is a weak electrolyte
- it often exists as a liquid
Answer
it has a high melting point
Reason — Electrovalent compounds have a high melting point because there exists a strong force of attraction between the oppositely charged ions, so a large amount of energy is required to break the strong bonding force between ions.
When a metal atom becomes an ion :
- it loses electrons and is oxidized
- it gains electrons and is reduced
- it gains electrons and is oxidized
- it loses electrons and is reduced
Answer
it loses electrons and is oxidized
Reason — Metals readily give the valence electron during reactions and are hence oxidised.
Which of the following compounds has all three bonds — ionic, covalent and coordinate bonds ?
- Ammonia
- Ammonium chloride
- Sodium hydroxide
- Calcium chloride
Answer
Ammonium chloride
Reason — When ammonium chloride NH4Cl is formed cation NH4+ (having 3 covalent and one coordinate bond) and anion Cl- are attracted towards each other, due to electrical charge existing between them and ionic bond is formed. Thus, ammonium chloride is a good example of compound having all three types of bonds i.e., covalent, coordinate and ionic bond.
Which of the following is not a typical property of an ionic compound ?
- High melting point
- Conduction of electricity in molten and aqueous states
- Insolubility in water
- Existence as oppositely charged ions even in the solid state.
Answer
Insolubility in water
Reason — Ionic compounds are soluble in water. They are insoluble in organic solvents. Water [polar solvent] has a high dielectric constant i.e., capacity to weaken the force of attraction, thus resulting in free ions. Organic solvents [non-polar] have low dielectric constants and do not cause dissolution.
Metals lose electrons during ionization. This change is called :
- Oxidation
- Reduction
- Redox reaction
- Displacement
Answer
Oxidation
Reason — Oxidation is the process when an atom or ion loses electrons in order to attain a stable state.
Compound 'X' consists of only molecules. 'X' will have :
- A crystalline hard structure
- Low melting and low boiling point
- An ionic bond
- A strong force of attraction between its molecules
Answer
Low melting and low boiling point
Reason — There are weak Vander Waals forces of attraction between molecules. Thus, less amount of energy is required to break these forces of attraction.
The molecule which contains a triple covalent bond is :
- ammonia
- methane
- water
- nitrogen
Answer
nitrogen
Reason — The valency of nitrogen element is 3. Nitrogen needs three electrons to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ne [2,8]. Each of the two N atoms contributes three electron so as to have three shared pair of electrons between them. Both atoms attain stable – octet structure, resulting in the – formation of a – triple covalent bond [N≡N] between them.
Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct word from the brackets :
(a) When the nuclei of two different reacting atoms are of ............... mass, then a bond so formed is called covalent bond (equal, unequal, polar, non-polar).
(b) In case of non-polar covalent bond, the covalent bond is formed in the ............... of atoms and shared electrons are distributed (corner, middle, equally, unequally).
(c) Ionic or electrovalent compounds do not conduct electricity in their ............... state (fused/solid).
(d) The ions in ............... compounds are held very strongly due to strong ............... forces (electrovalent, covalent, electromagnetic, electrostatic).
(e) In covalent compounds, the bond is formed due to ............... [sharing/transfer] of electrons.
(f) Electrovalent compounds have a ............... [low/high] boiling point.
Answer
(a) Unequal, Polar
(b) Middle, Equally
(c) Solid
(d) Electrovalent, Electrostatic
(e) Sharing
(f) High
Give one word or phrase for the following :
(a) Formation of ions from molecules.
(b) A bond formed by a shared pair of electrons with both electrons coming from the same atom.
(c) A bond formed by a shared pair of electrons, each bonding atom contributing one electron to the pair.
Answer
(a) Ionisation
(b) Coordinate bond
(c) Covalent Bond
In the formation of magnesium chloride (by direct combination between magnesium and chlorine), name the substance that is oxidized and the substance that is reduced.
Answer
Magnesium is oxidized and Chlorine is reduced.
In the formation of magnesium chloride the reaction is :
Mg + Cl2 ⟶ Mg+2 + 2Cl-
Oxidation : Mg ⟶ Mg+2
Reduction : Cl2 ⟶ 2Cl-
Give an example in each of the following :
(a) Co-ordinate bond compound,
(b) Solid covalent compound,
(c) Gaseous polar compound,
(d) Gaseous non polar compound,
(e) Liquid non polar compound,
(f) Compound with electrovalent and covalent bond,
(g) Compound with all three types of bonds.
Answer
(a) Ammonium ion (NH4+) & Hydronium ion (H3O+),
(b) Phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) & Silicon dioxide or Silica (SiO2),
(c) Hydrogen sulphide (H2S) & Ammonia (NH3),
(d) Hydrogen (H2) & Oxygen (O2),
(e) Toluene & Gasoline.
(f) Calcium Carbonate (CaCO2)
(g) Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl)
Electrons are getting added to an element Y :
(i) Is Y getting oxidized or reduced ?
(ii) Which electrode will Y migrate to during the process of electrolysis ?
Answer
(i) Y is getting reduced as reduction is gain of electrons.
(ii) Y migrates towards anode. Y is negatively charged as electrons are added to it. So, it migrates towards the positive terminal that is anode.
What do you understand by lone pair of electrons.
Answer
A pair of electrons which is not shared with any other atom is known as the lone pair of electrons.
State the type of bonding in the following molecules.
(a) water,
(b) calcium oxide,
(c) hydroxyl ion,
(d) methane,
(e) ammonium ion,
(f) ammonium chloride
Answer
(a) Polar Covalent Bond,
(b) Ionic Bond,
(c) Polar Covalent Bond,
(d) Non Polar Covalent Bond,
(e) Coordinate & Covalent Bond,
(f) Ionic, Covalent and Co-ordinate Bond.
Give reasons — Hydrogen chloride can be termed as a polar covalent compound.
Answer
In hydrogen chloride, the strong nuclear charge of the chlorine atom attracts the shared electron pair towards itself, i.e., negative charge shifts towards the chlorine atom thereby developing a slight negative charge on it. The hydrogen atom develops a slight positive charge. Therefore, a polar covalent bond is formed as shown below :

Give reasons — Covalent compounds can exist as gases, liquids or soft solids.
Answer
Covalent compounds exist as gases, liquids or soft solids as they have weak force of attraction between their molecules.
Give reasons — Carbon tetrachloride does not dissolve in water.
Answer
Carbon tetrachloride is a non-polar compound and water is a polar compound. Same kind of compounds dissolve in each other that's why carbon tetrachloride does not dissolve in water.
There are three elements E, F, G with atomic numbers 19, 8 and 17 respectively. Give the molecular formula of the compound formed between E and G and state the type of chemical bond in this compound.
Answer
EG is the chemical formula.
The electronic configuration of E is (2,8,8,1) and G is (2,8,7). We observe that E tends to donate one electron and G tends to gain one electron to attain a stable state. Hence, the the two oppositely charged ions attract each other to form an ionic compound EG.
Ionic bond will be formed.
Define a coordinate bond and give the conditions for its formation.
Answer
The bond formed between two atoms by sharing a pair of electrons, provided entirely by one of the combining atoms but shared by both is called a coordinate bond.
Conditions for the formation of coordinate bond are:
(i) One of the two atoms must have at least one lone pair of electrons, e.g., ammonia (NH3), water (H2O).
(ii) Another atom should be short of at least a pair of electrons, e.g., Hydrogen ion (H+).
Draw an electron dot diagram for the formation of each of the following :
(i) Hydronium ion,
(ii) Ammonium ion,
(iii) Hydroxyl ion.
State the type of bonding present in them.
Answer
(i) Hydronium ion
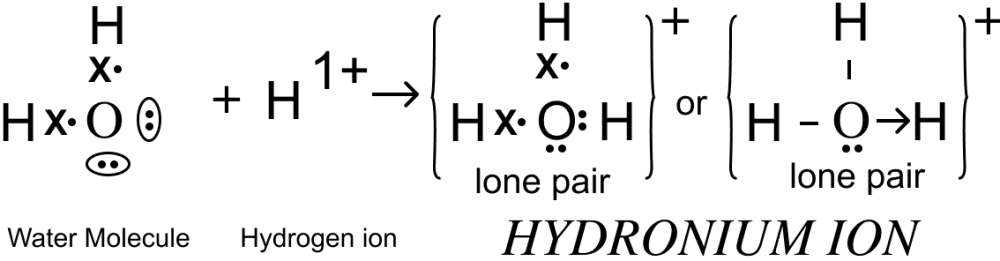
Co-ordinate & Covalent Bond.
(ii) Ammonium ion

Co-ordinate & Covalent Bond.
(iii) Hydroxyl ion

Polar Covalent Bond.
How many atoms of each kind are present in the following molecules : calcium oxide, chlorine, water, carbon tetrachloride ?
Answer
Calcium oxide (CaO) is formed by one calcium and one oxygen atom.
Chlorine (Cl2) molecule is formed by two chlorine atoms.
Water (H2O) is formed by two hydrogen and one oxygen atom.
Carbon Tetrachloride(CCl4) is formed by one carbon and four chlorine atoms.
How many electrons are required or released by each atom mentioned in (a) to attain the nearest noble gas configuration ?
Answer
In Calcium oxide (CaO), Calcium needs to lose 2 electrons and Oxygen gains that 2 electrons to attain the nearest noble gas configuration.
In Chlorine (Cl2) molecule, each Chlorine atom needs an electron to complete its octet. So, two Chlorine atoms share a pair of electrons to attain the nearest noble gas configuration.
In Water (H2O), each Hydrogen atom needs one electron and one Oxygen atom needs two electrons to complete their duplet and octet respectively. So, each Hydrogen shares a pair of electrons with Oxygen to attain the nearest noble gas configuration.
In Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4), each Carbon atom needs 4 electrons and each Chlorine atom needs one electron to complete their octet. So, each Chlorine shares a pair of electrons with Carbon to attain the nearest noble gas configuration.
Acids dissolve in water and produce positively charged ions. Draw the structure of these positive ions.
Answer
When acids dissolve in water they produce hydronium ion. Structure of hydronium ion is shown below:

Elements Q and S react together to form an ionic compound. Under normal conditions, which physical state will the compound QS exist in ?
Answer
QS exist in hard solid state.
Reason — As QS is an ionic compound, it consists of ions bond tightly together by strong electrostatic forces between them. Due to this it is a hard solid.
Elements Q and S react together to form an ionic compound. Can Q and S, both be metals ? Justify your answer.
Answer
No, Q and S both can't be metals because Q and S react together to form an ionic compound. It is only possible when one of them is metal and the other one is non-metal.
Draw the structural formula of carbon tetrachloride and state the type of bond present in it.
Answer
Structural formula of carbon tetrachloride is given below:
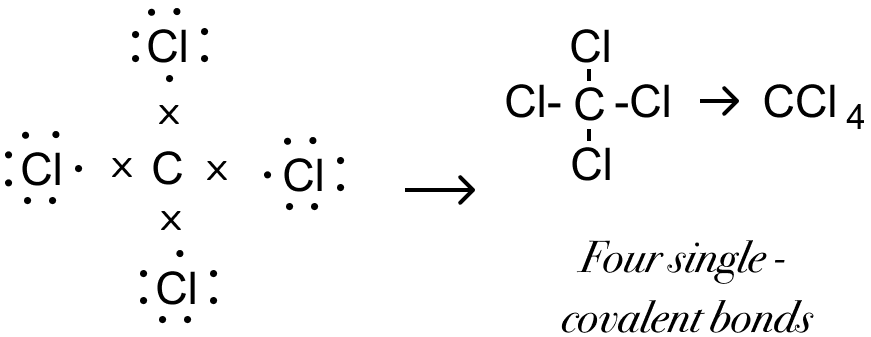
Covalent bond is present in carbon tetrachloride.
Compare carbon tetrachloride and sodium chloride with regard to solubility in water and electrical conductivity.
Answer
| Carbon tetrachloride | Sodium chloride | |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility in water | Insoluble in water | Soluble in water |
| Electrical conductivity | Non Conductor | Good conductors in aqueous state or molten state |
Draw an electron dot diagram of hydronium ion. State the type of bonding present in it.
Answer
Electron dot diagram showing the structure of Hydronium ion is given below:

Co-ordinate bond is present in hydronium ion.
By drawing an electron dot diagram, show the lone pair effect leading to the formation of — ammonium ion from ammonia gas and hydrogen ion.
Answer
Electron dot diagram showing the lone pair effect for formation of NH41+ ion from NH3 gas and H1+ is given below:

The following table shows the electronic configuration of the elements W, X, Y, Z :
| Element | W | X | Y | Z |
| Electronic Configurations | 2, 8, 1 | 2, 8, 7 | 2, 5 | 1 |
Answer the following questions based on the table above:
(i) What type of bond is formed between:
- W and X
- Y and Z
(ii) What is the formula of the compound formed between :
- X and Z
- W and X
Answer
(i) Type of bond formed
(a) W (2,8,1) and X (2,8,7) — Electrovalent bond is formed as W donates 1 electron and X takes up that electron and both attain a stable octet.
(b) Y (2, 5) and Z (1) — Covalent bond as electron sharing takes place between the two elements. The valency of Z element is 1 and that of Y is 3. Z needs one electrons to attain stable duplet structure of nearest noble gas - He [2] and Y needs three electrons to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ne [2,8]
One Y atom shares three electron pairs one with each of the three atoms of Z such that Z acquires a duplet configuration and Y attain a stable octet configuration resulting in the formation of three single covalent bonds.
(ii) Formula of the compound formed
(a) X (2,8,7) and Z (1) — XZ as X needs one 1 electron to complete it's octet and Z needs needs one electron to complete it's duplet hence, they both share one electron pair and forms ZX compound.
(b) W (2,8,1) and X (2,8,7) — WX as W has the tendency to donate one electron and gain stability whereas X has the tendency to gain one electron to be stable. Hence, W donates one electron and X takes it and form WX compound.