Short Answer Questions 1
A shopkeeper marked a pressure cooker at ₹ 1800. The rate of GST on pressure cooker is 12%. The customer has only ₹ 1792 with him and he requests the shopkeeper to reduce the price so that he can buy the cooker in ₹ 1792. What percent discount must the shopkeeper give ?
Answer
M.P. of pressure cooker = ₹ 1800.
Let after discount the price of cooker be ₹ x.
GST on pressure cooker = 12%
According to question,
Discount given by shopkeeper = ₹ 1800 - ₹ 1600 = ₹ 200.
Discount % =
Hence, discount offered = 11.11 %.
A man opened a recurring deposit account in a branch of PNB. The man deposits certain amount of money per month such that after 2 years, the interest accumulated is equal to his monthly deposits. Find the rate of interest per annum that the bank was paying for the recurring deposit account.
Answer
Given,
Time (n) = 2 years or 24 months
Rate = r% (let)
P = ₹ x/month
I = ₹ x
By formula,
I =
Substituting values we get :
Hence, rate of interest = 4%.
Akshay buys 350 shares of ₹ 50 par value of a company. The dividend declared by the company is 14%. If his return percent from the shares is 10%, find the market value of each share.
Answer
Given,
Rate of dividend = 14%
Dividend on ₹ 50 = = ₹ 7.
Given,
Return percent from the shares is 10%.
∴ Interest on ₹ 100 = = ₹ 10.
∴ ₹ 7 will be interest on = ₹ 70.
Hence, market value of each share = ₹ 70.
Solve the following inequation and answer the questions given below.
(a) Write the maximum and minimum values of x for x ∈ R.
(b) What will be the change in maximum and minimum values of x if x ∈ W.
Answer
(a) Given,
Solving L.H.S. of the inequation, we get :
Solving R.H.S. of the inequation, we get :
From equation (1) and (2), we get :
-1 ≤ x ≤ 5 and x ∈ R.
Hence, minimum and maximum value of x is -1 and 5 respectively.
(b) If x ∈ W.
Then, minimum value = 0 and maximum value = 5.
Hence, minimum and maximum value of x is 0 and 5 respectively, when x is a whole number.
Solve for x, if , x ≠ 0
Answer
Given,
Substituting = t in the given equation, we get :
Hence, x =
The marked price of a toy is same as the percentage of GST that is charged. The price of the toy is ₹ 24 including GST. Taking the marked price as x, form an equation and solve it to find x.
Answer
Given,
M.P. of toy = ₹ x
G.S.T. charged = x%
Price including G.S.T. = ₹ 24
Since, M.P. cannot be negative.
∴ M.P. = ₹ 20 and G.S.T. = 20%.
Hence, the marked price of toy = ₹ 20 and G.S.T. = 20%.
The mean proportion between two numbers is 6 and their third proportion is 48. Find two numbers.
Answer
Let the numbers be a and b.
Given,
Mean proportion between the numbers is 6.
Third proportion of the numbers is 48.
Substituting value of b in equation (1), we get :
= 3.
Hence, the numbers are 3 and 12.
Pamela factorized the following polynomial :
2x3 + 3x2 - 3x - 2
She found the result as (x + 2)(x - 1)(x - 2). Using remainder and factor theorem, verify whether her result is correct. If incorrect, give the correct result.
Answer
Dividing the polynomial f(x) = 2x3 + 3x2 - 3x - 2 by (x + 2), we get :
⇒ x + 2 = 0
⇒ x = -2
f(-2) = 2(-2)3 + 3(-2)2 - 3(-2) - 2
= 2(-8) + 3(4) + 6 - 2
= -16 + 12 + 6 - 2
= -18 + 18
= 0.
Dividing the polynomial f(x) = 2x3 + 3x2 - 3x - 2 by (x - 1), we get :
⇒ x - 1 = 0
⇒ x = 1
f(1) = 2(1)3 + 3(1)2 - 3(1) - 2
= 2(1) + 3(1) - 3 - 2
= 2 + 3 - 3 - 2
= 0.
Dividing the polynomial f(x) = 2x3 + 3x2 - 3x - 2 by (x - 2), we get :
⇒ x - 2 = 0
⇒ x = 2
f(2) = 2(2)3 + 3(2)2 - 3(2) - 2
= 2(8) + 3(4) - 6 - 2
= 16 + 12 - 6 - 2
= 20.
Since, f(2) ≠ 0
∴ x - 2 does not divide the polynomial 2x3 + 3x2 - 3x - 2.
Dividing the polynomial f(x) by (x + 2)(x - 1) or by (x2 + x - 2), we get :
∴ 2x3 + 3x2 - 3x - 2 = (x2 + x - 2)(2x + 1)
= (x + 2)(x - 1)(2x + 1).
Hence, 2x3 + 3x2 - 3x - 2 = (x + 2)(x - 1)(2x + 1).
.
Find matrix M, if M = , where l is the identity matrix.
Answer
Given,
Hence, M =
(a) Write the nth term (Tn) of an Arithmetic Progression (A.P.) consisting of all whole numbers which are divisible by 3 and 7.
(b) How many of these are two-digit numbers? Write them.
(c) Find the sum of first 10 terms of this A.P.
Answer
(a) A.P. = 21, 42, 63, .........
The above sequence is an A.P. with first term (a) = 21 and common difference (d) = 21.
By formula,
Tn = a + (n - 1)d
= 21 + (n - 1)21
= 21 + 21n - 21
= 21n.
Hence, the nth term = 21n.
(b) A.P. = 21, 42, 63, 84, 105, ........
Hence, there are four two digit numbers i.e. 21, 42, 63, 84 in the A.P.
(c) By formula,
Sum of A.P. =
Hence, sum of first 10 terms of the A.P. = 1155.
Write the first five terms of the sequence given by , n ∈ N.
(a) Is the sequence an A.P. or G.P.?
(b) If the sum of its first ten terms is , find the value of p.
Answer
Terms of the sequence given by are :
⇒ , .......
⇒
(a) Ratio between terms = .
Hence, the sequence is a G.P. with common ratio = .
(b) By formula,
Sum of G.P. (S) =
Substituting values we get :
Hence, p = 121.
ABC is a triangle as shown in the figure below.
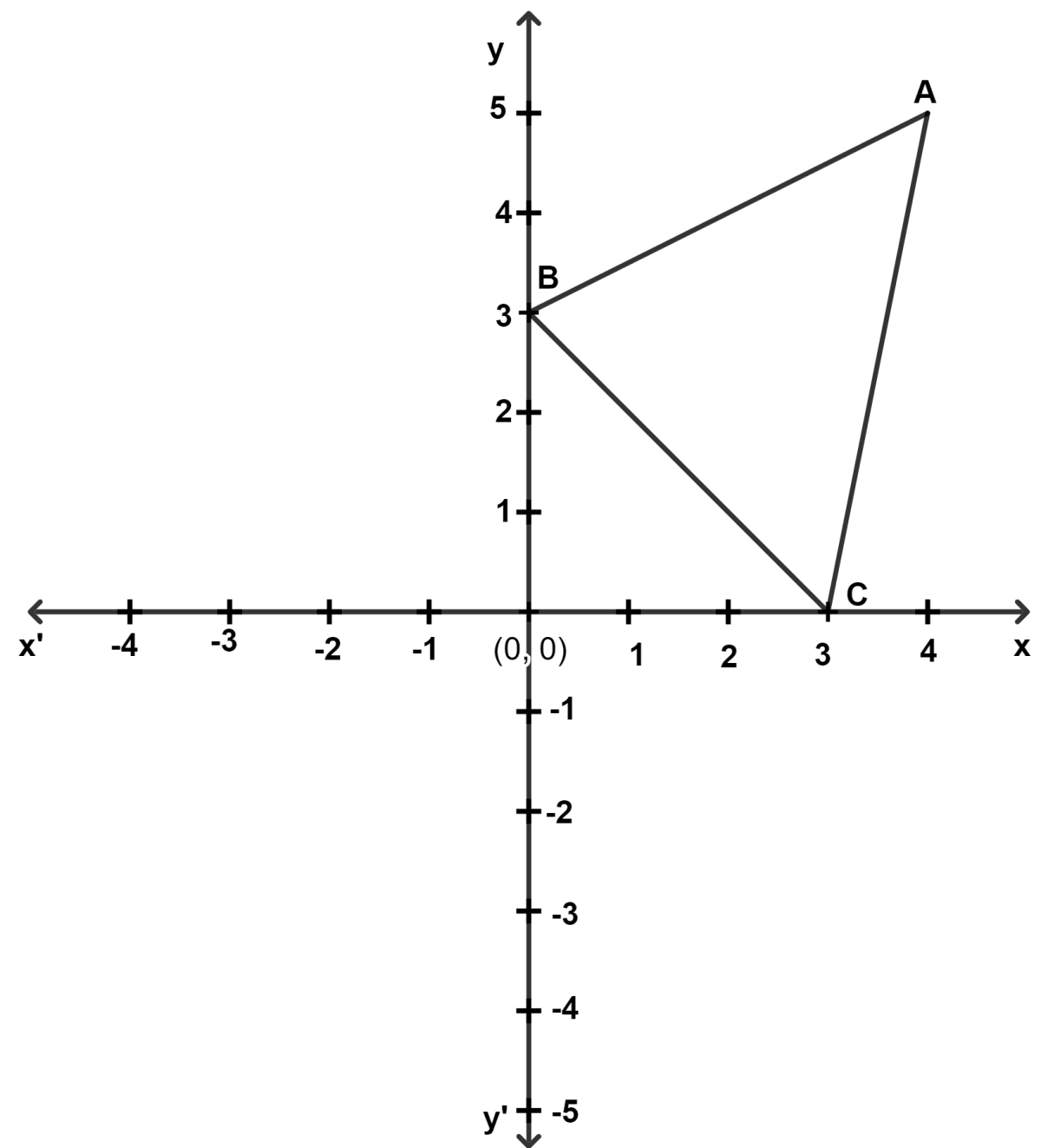
(a) Write down the coordinates of A, B and C on reflecting through the origin.
(b) Write down the coordinates of the point/s which remain invariant on reflecting the triangle ABC on the x-axis and y-axis respectively.
Answer
(a) From figure,
On reflecting in origin A, B and C becomes A', B' and C'.
Coordinates of A' = (-4, -5), B' = (0, -3) and C' = (-3, 0).
Hence, on reflecting A, B and C in origin the coordinates are (-4, -5), (0, -3) and (-3, 0) respectively.
(b) Point C(3, 0) lies on x-axis.
∴ It remains invariant on reflecting in x-axis.
Point B(0, 3) lies on y-axis.
∴ It remains invariant on reflecting in y-axis.
Hence, the invariant point for x-axis is point C and for y-axis is point B.
Determine the ratio in which the line y = 2 + 3x divides the line segment AB joining the points A(-3, 9) and B(4, 2).
Answer
By two point form,
Equation of line :
⇒ y - y1 = (x - x1)
Equation of AB :
Solving equation y = 2 + 3x and x + y = 6 simultaneously,
⇒ x + y = 6 .......(1)
⇒ y = 2 + 3x .......(2)
Substituting value of y from equation (2) in (1), we get :
⇒ x + (2 + 3x) = 6
⇒ 4x + 2 = 6
⇒ 4x = 6 - 2
⇒ 4x = 4
⇒ x =
⇒ x = 1.
Substituting value of x in equation (2), we get :
⇒ y = 2 + 3(1) = 2 + 3 = 5.
Let (1, 5) divide the line AB in the ratio k : 1.
By section formula,
(x, y) =
Substituting values we get :
Hence, the line y = 2 + 3x divides the line segment AB in the ratio 4 : 3.
Square ABCD lies in the third quadrant of a XY plane such that its vertex A is at (-3, -1) and the diagonal DB produced is equally inclined to both the axes. The diagonals AC and BD meets at P(-2, -2). Find the :
(a) Slope of BD
(b) equation of AC
Answer
(a) Given,
BD is equally inclined to both axes.
∴ Slope of BD = tan 45° = 1.
Hence, slope of BD = 1.
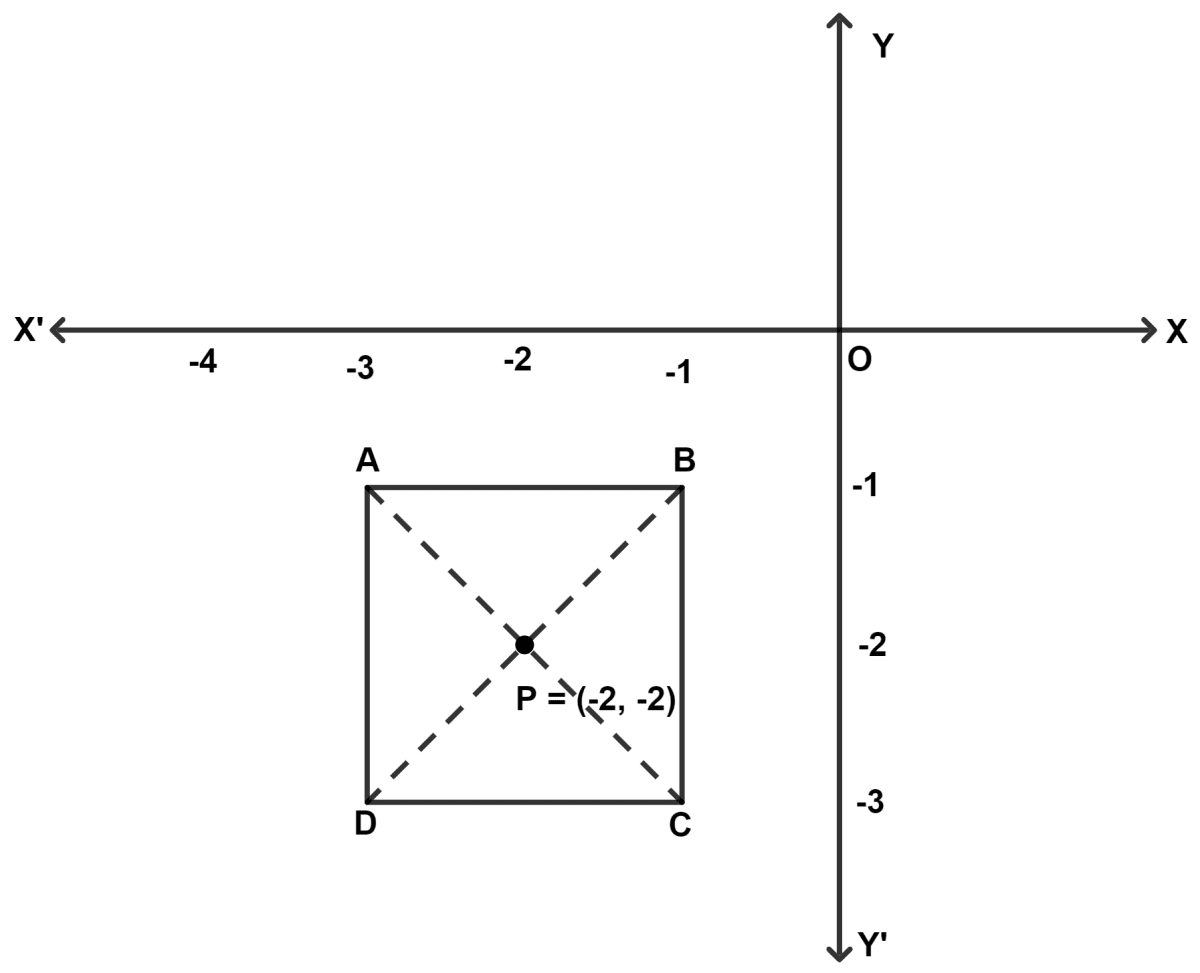
(b) Since, diagonals of a square are perpendicular and product of slope of perpendicular lines equals to -1.
∴ Slope of BD × Slope of AC = -1
⇒ 1 × Slope of AC = -1
⇒ Slope of AC = -1.
Since, diagonals meet at point (-2, -2).
By point-slope form,
⇒ y - y1 = m(x - x1)
⇒ y - (-2) = -1[x - (-2)]
⇒ y + 2 = -1[x + 2]
⇒ y + 2 = -x - 2
⇒ x + y + 2 + 2 = 0
⇒ x + y + 4 = 0.
Hence, equation of AC is x + y + 4 = 0.
ABCD is a rectangle where side BC is twice side AB. If △ACQ ~ △BAP, find area of △BAP : area of △ACQ.
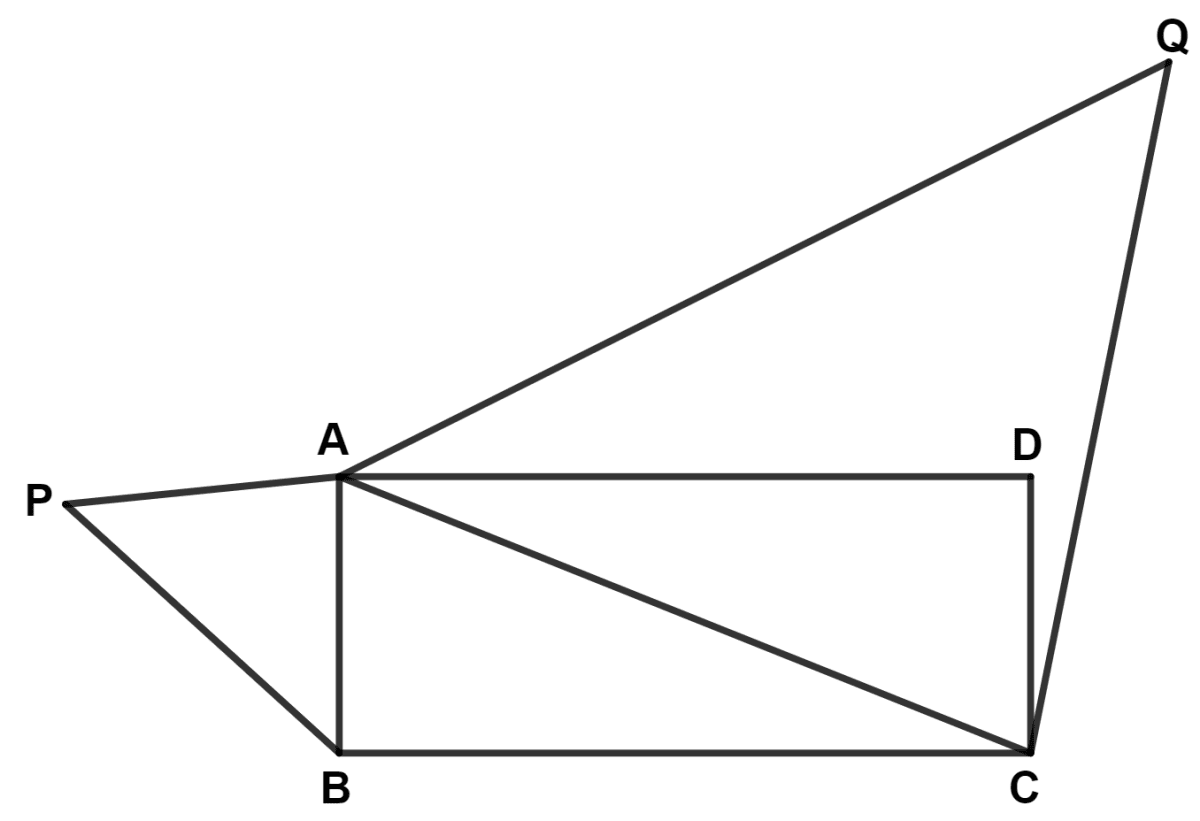
Answer
Given,
ABCD is a rectangle where side BC is twice side AB.
⇒ BC = 2AB
In right angled triangle ABC,
By pythagoras theorem,
⇒ AC2 = AB2 + BC2
⇒ AC2 = AB2 + (2AB)2
⇒ AC2 = AB2 + 4AB2
⇒ AC2 = 5AB2
⇒ AC = AB.
We know that,
The ratio of the area of two similar triangles is equal to the square of the ratio of any pair of the corresponding sides of the similar triangles.
Area of △BAP : Area of △ACQ = 1 : 5.
Hence, Area of △BAP : Area of △ACQ = 1 : 5.
Given a triangle ABC, and D is a point on BC such that BD = 4 cm and DC = x cm. If ∠BAD = ∠C and AB = 8 cm, then,
(a) prove that triangle ABD is similar to triangle CBA.
(b) find the value of 'x'.
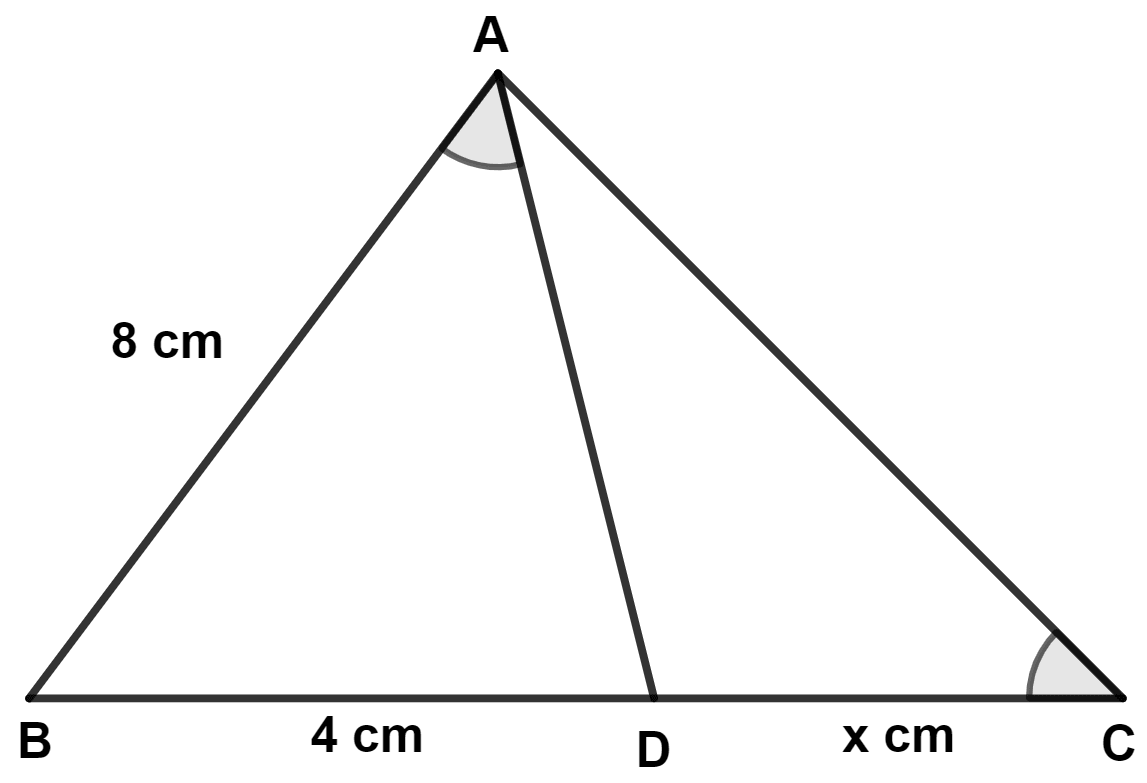
Answer
(a) In △ ABD and △ CBA,
⇒ ∠ABD = ∠CBA (Common angle)
⇒ ∠BAD = ∠ACB (Given)
∴ △ ABD ~ △ CBA (By A.A. axiom)
Hence, proved that △ ABD ~ △ CBA.
(b) We know that,
Corresponding sides of similar triangle are proportional.
Hence, x = 12 cm.
In the extract of Survey of India map G43S7, prepared on a scale of 2 cm to 1 km, a child finds the length of the cart track between two settlements is 7.6 cm. Find :
(a) the actual length of the cart track on the ground.
(b) actual area of a grid square, if each has an area of 4 cm2.
Answer
Scale factor (k) = 2 cm to 1 km or 2 cm to 100000 cm =
(a) Length of cart track on map = k × Length of cart track on ground
× Length of cart track on ground
Length of cart track on ground = 7.6 × 50000 = 380000 cm = = 3.8 km
Hence, length of actual cart track on ground = 3.8 km
(b) Area of model grid square = k2 × Area of actual grid square
⇒ 4 = × Area of actual grid square
⇒ 4 = × Area of actual grid square
⇒ Area of actual grid square =
⇒ Area of actual grid square = 100 × 108 = 102 × 108 = 1010 cm2
= km2 = 1 km2.
Hence, actual area of a grid square = 1 km2.
Construct a triangle ABC such that AB = 7 cm, BC = 6 cm and CA = 5 cm.
(a) Draw the locus of the points such that
(i) it is equidistant from BC and BA.
(ii) it is equidistant from points A and B.
(b) Mark P where the loci (i) and (ii) meet, measure and write length of PA.
Answer
We know that,
Locus of the points equidistant from two sides is the angle bisector between two sides.
Locus of the points equidistant from two points is the perpendicular bisector of the line joining two points.
Steps of construction :
Draw a line segment AB = 7 cm.
With A and B as center and radii 5 cm and 6 cm respectively draw arcs intersecting at C.
Join AC and BC.
Draw BD, angle bisector of B.
Draw XY perpendicular bisector of AB.
Mark point P, the intersection point of XY and BD.
Measure AP.
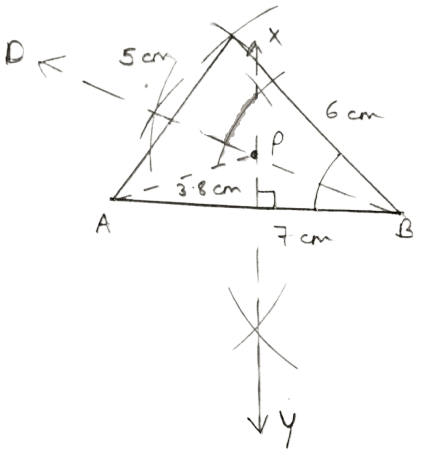
Hence, AP = 3.8 cm.
In the given figure O is the centre of the circle. ABCD is a quadrilateral where sides AB, BC, CD and DA touch the circle at E, F, G and H respectively. If AB = 15 cm, BC = 18 cm and AD = 24 cm, find the length of CD.
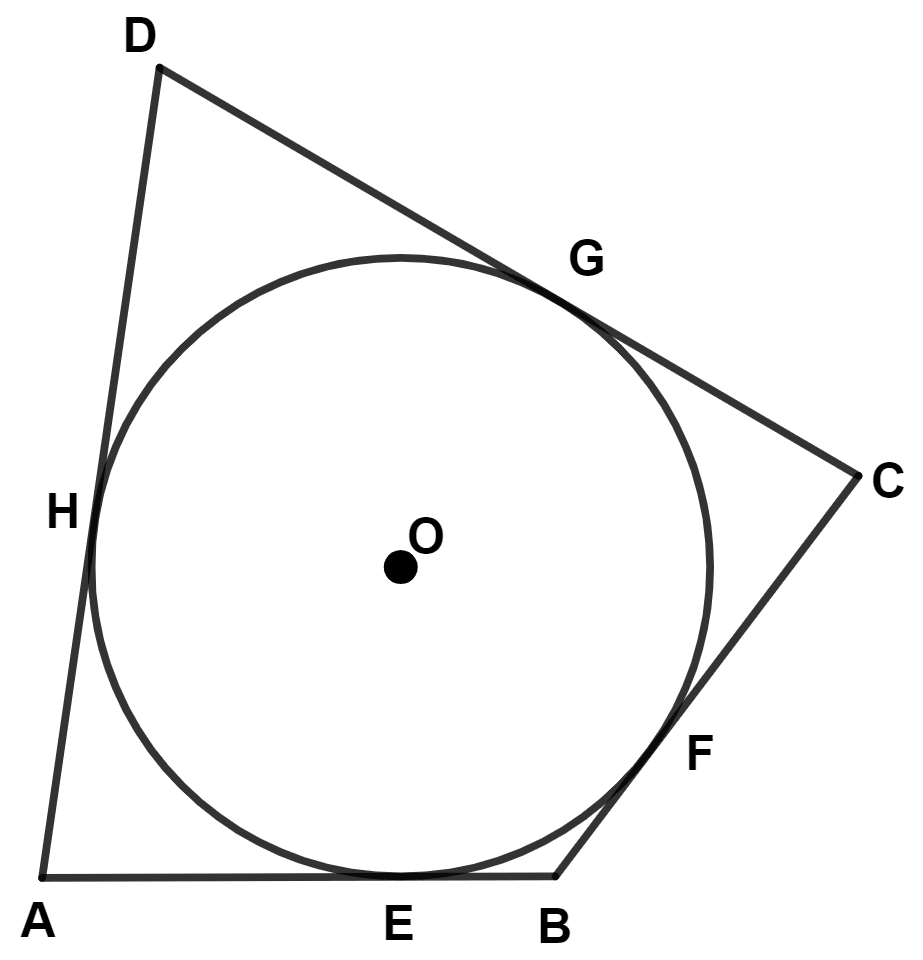
Answer
We know that,
The length of tangents drawn from an external point to the circle are equal.
⇒ AE = AH = x (let)
⇒ BE = BF = y (let)
⇒ CF = CG = z (let)
⇒ DG = DH = k (let)
Given,
⇒ AB = 15
⇒ AE + EB = 15
⇒ x + y = 15 .......(1)
⇒ BC = 18
⇒ BF + CF = 18
⇒ y + z = 18 ........(2)
⇒ AD = 24
⇒ AH + DH = 24
⇒ x + k = 24 ..........(3)
Adding equations (2) and (3), we get :
⇒ y + z + x + k = 18 + 24
⇒ x + y + z + k = 42
⇒ 15 + z + k = 42 [From equation (1)]
⇒ z + k = 42 - 15
⇒ z + k = 27.
⇒ CD = CG + DG = k + z = 27 cm.
Hence, length of CD = 27 cm.
In the given diagram, ABCDEF is a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle with centre O. PQ is a tangent to the circle at D. Find the value of :
(a) ∠FAG
(b) ∠BCD
(c) ∠PDE
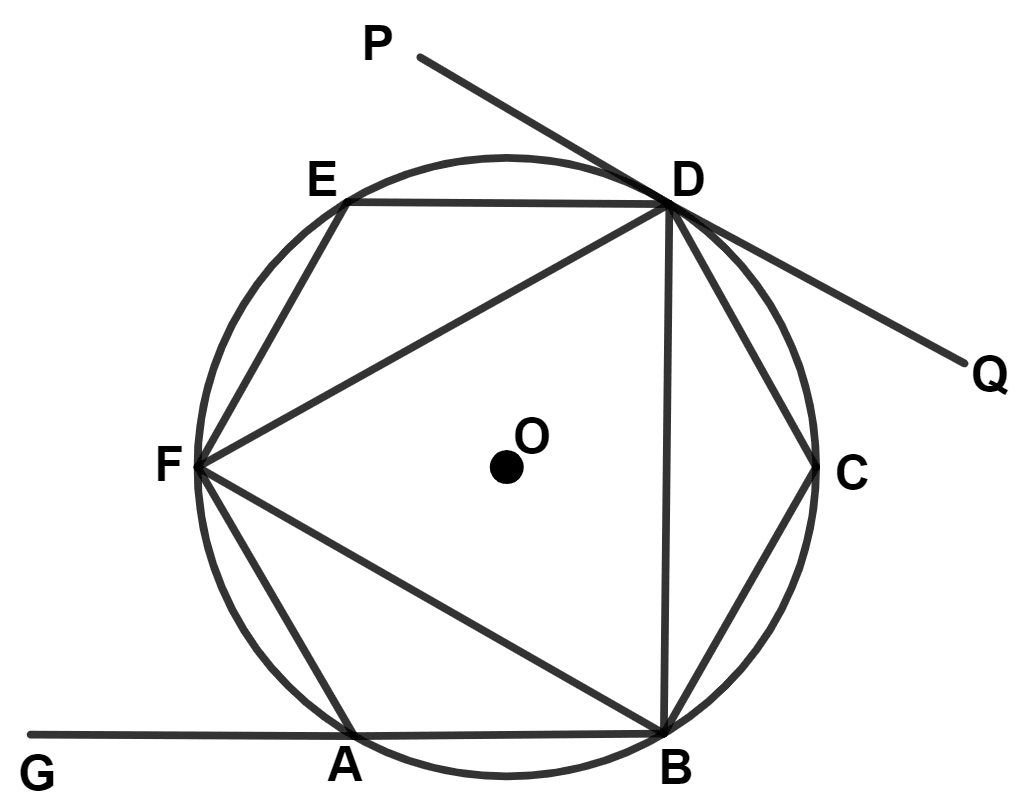
Answer
(a) By formula,
Each interior angle of a n sided polygon =
∴ ∠FAB = 120°
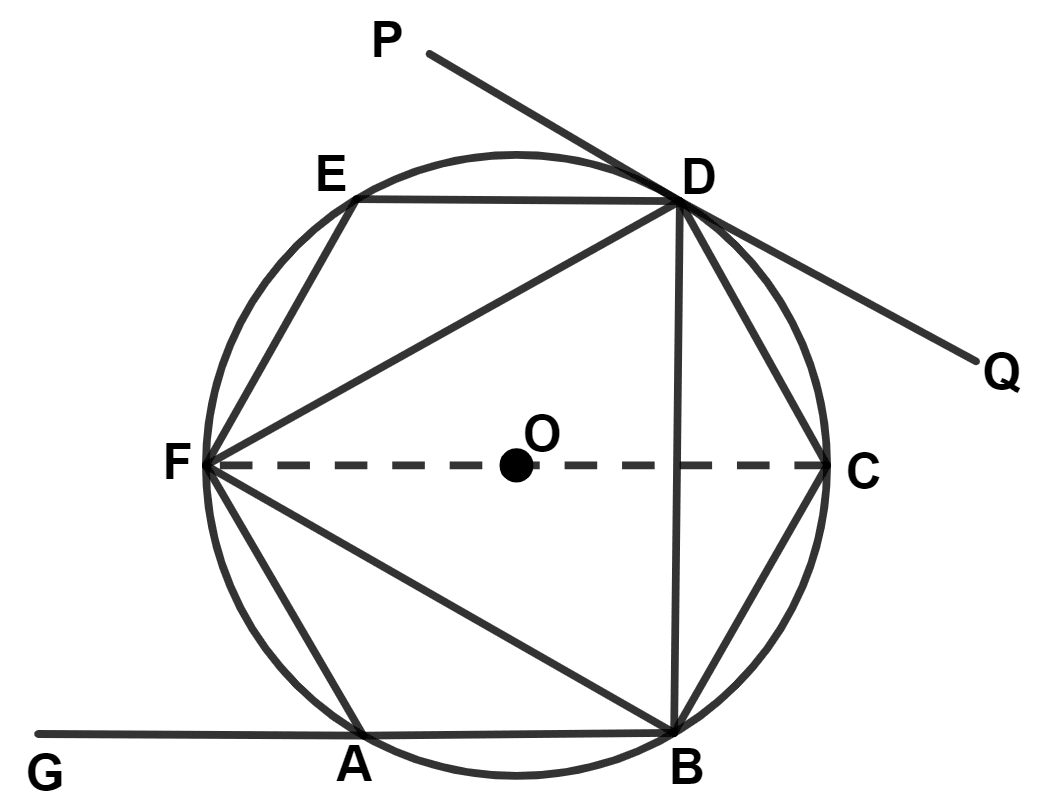
From figure,
∠FAG and ∠FAB form a linear pair.
∴ ∠FAB + ∠FAG = 180°
⇒ 120° + ∠FAG = 180°
⇒ ∠FAG = 180° - 120° = 60°.
Hence, ∠FAG = 60°.
(ii) Each interior angle of regular hexagon = 120°.
Hence, ∠BCD = 120°.
(iii) Join FC.
We know that,
Angle in a semicircle is a right angle.
∴ ∠FBC = 90°
In triangle BCD,
⇒ BC = CD (Sides of regular hexagon)
⇒ ∠CBD = ∠CDB = x (Angles opposite to equal sides are equal)
By angle sum property of triangle,
⇒ ∠BCD + ∠CDB + ∠CBD = 180°
⇒ 120° + x + x = 180°
⇒ 2x = 180° - 120°
⇒ 2x = 60°
⇒ x = = 30°.
From figure,
⇒ ∠FBD = ∠FBC - ∠CBD = 90° - x = 90° - 30° = 60°.
We know that,
The angle between a tangent and a chord through the point of contact is equal to an angle in the alternate segment.
⇒ ∠PDE = ∠FBD = 60°.
Hence, ∠PDE = 60°.
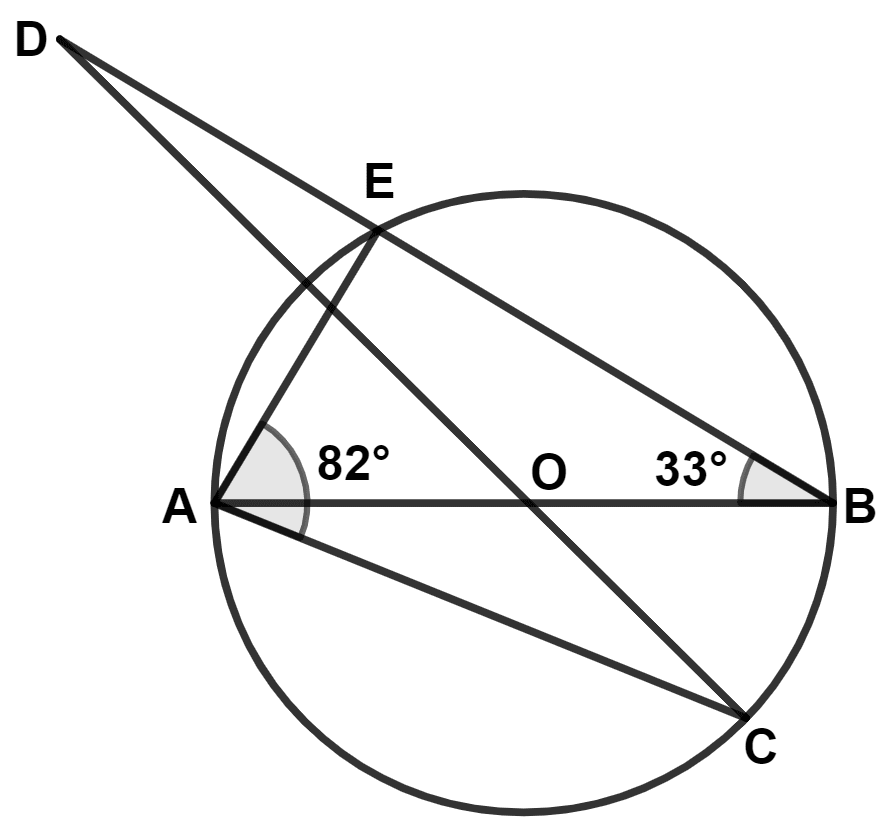
AB and CD intersect at the center O of the circle given in the above diagram. If ∠EBA = 33° and ∠EAC = 82°, find
(a) ∠BAE
(b) ∠BOC
(c) ∠ODB
Answer
(a) In △ BAE,
⇒ ∠AEB = 90° (Angle in a semicircle is a right angle)
By angle sum property of triangle,
⇒ ∠AEB + ∠EBA + ∠BAE = 180°
⇒ 90° + 33° + ∠BAE = 180°
⇒ ∠BAE + 123° = 180°
⇒ ∠BAE = 180° - 123° = 57°.
Hence, ∠BAE = 57°.
(b) From figure,
⇒ ∠EAC = ∠EAB + ∠BAC
⇒ 82° = 57° + ∠BAC
⇒ ∠BAC = 82° - 57° = 25°.
We know that,
The angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
⇒ ∠BOC = 2∠BAC = 2 × 25° = 50°.
Hence, ∠BOC = 50°.
(c) From figure,
∠BOC and ∠BOD form a linear pair.
∴ ∠BOC + ∠BOD = 180°
⇒ 50° + ∠BOD = 180°
⇒ ∠BOD = 180° - 50° = 130°.
In △ BOD,
⇒ ∠BOD + ∠ODB + ∠DBO = 180°
⇒ 130° + ∠ODB + 33° = 180°
⇒ ∠ODB + 163° = 180°
⇒ ∠ODB = 180° - 163° = 17°.
Hence, ∠ODB = 17°.
A famous sweet shop “Madanlal Sweets” sells tinned rasgullas. The tin container is cylindrical in shape with diameter 14 cm, height 16 cm, and it can hold 20 spherical rasgullas of diameter 6 cm and sweetened liquid such that the can is filled and then sealed. Find out how much sweetened liquid the can contains. Take π = 3.14.
Answer
Given,
Diameter of container = 14 cm
Radius (R) = = 7 cm
Height of container (H) = 16 cm
Diameter of rasgulla = 6 cm
Radius of rasgulla (r) = = 3 cm
Volume of container = Volume of rasgullas + Volume of liquid
⇒ πR2H = πr3 + Volume of liquid
⇒ Volume of liquid = πR2H - πr3
⇒ Volume of liquid = π(R2H - )
⇒ Volume of liquid = 3.14 × (72 × 16 - )
⇒ Volume of liquid = 3.14 × (784 - 720)
⇒ Volume of liquid = 3.14 × 64
⇒ Volume of liquid = 200.96 cm3.
Hence, volume of sweetened liquid in the container = 200.96 cm3.
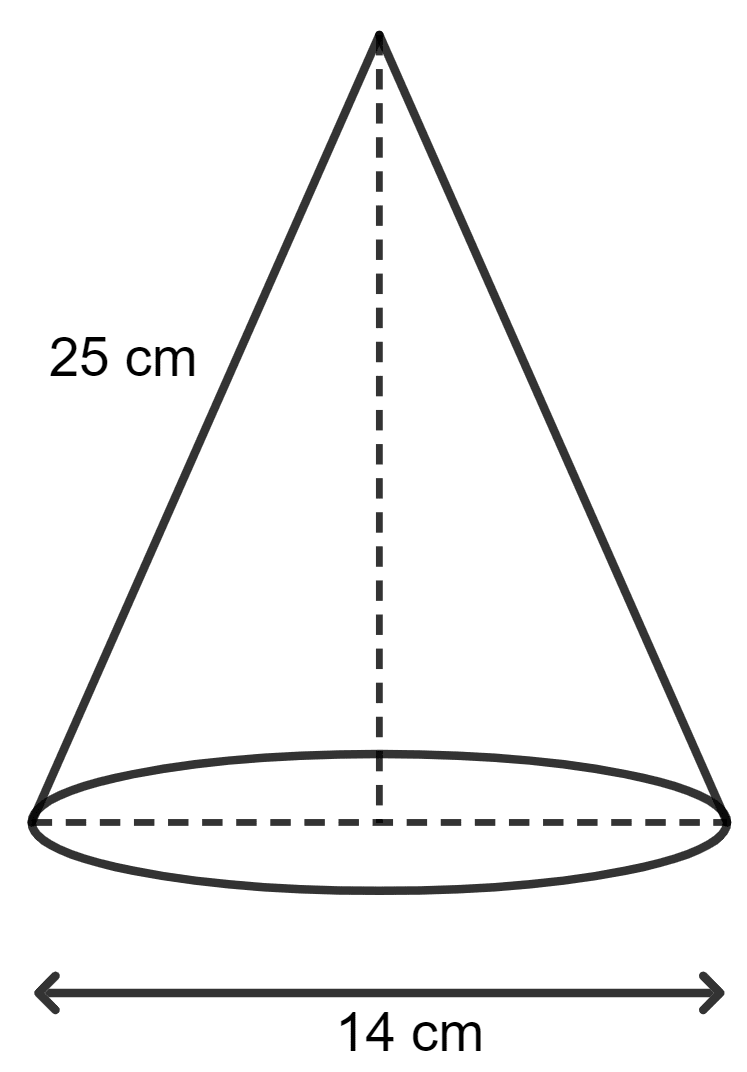
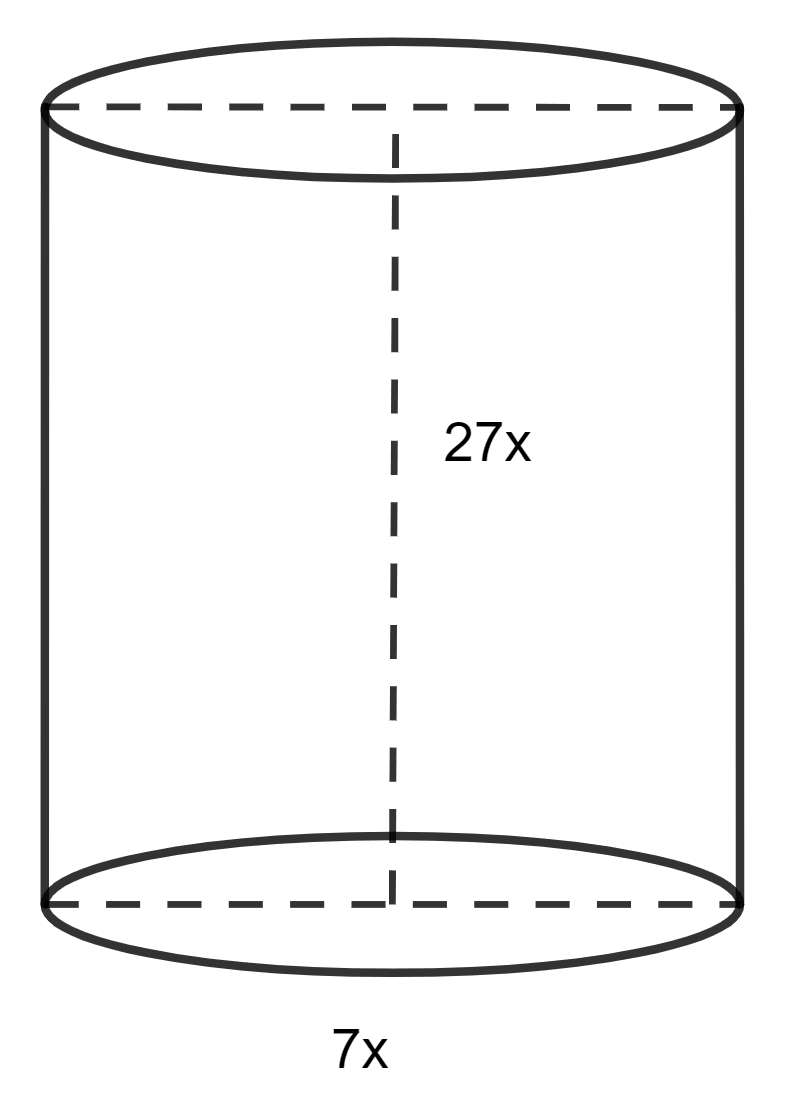
The ratio of the radius and the height of a solid metallic right circular cylinder is 7 : 27. This is melted and made into a cone of diameter 14 cm and slant height 25 cm. Find the height of the :
(a) cone
(b) cylinder
Answer
Given,
Diameter of cone = 14 cm
Radius of cone (r) = = 7 cm
Slant height (l) = 25 cm
Ratio of the radius and the height of a solid metallic right circular cylinder is 7 : 27.
Radius of cylinder (R) = 7x
Height of cylinder (H) = 27x
(a) Let height of cone be h cm.
By formula,
⇒ l2 = r2 + h2
⇒ 252 = 72 + h2
⇒ 625 = 49 + h2
⇒ h2 = 625 - 49
⇒ h2 = 576
⇒ h = = 24 cm.
Hence, height of cone = 24 cm.
(b) Given,
A solid metallic right circular cylinder is melted and made into a cone.
∴ Volume of cylinder = Volume of cone
⇒ πR2H =
⇒ R2H =
⇒ (7x)2 × 27x =
⇒ 1323x3 =
⇒ 1323x3 = 392
⇒ x3 =
⇒ x3 =
⇒ x3 =
⇒ x =
Height of cylinder (H) = 27x = = 18 cm.
Hence, height of cylinder = 18 cm.
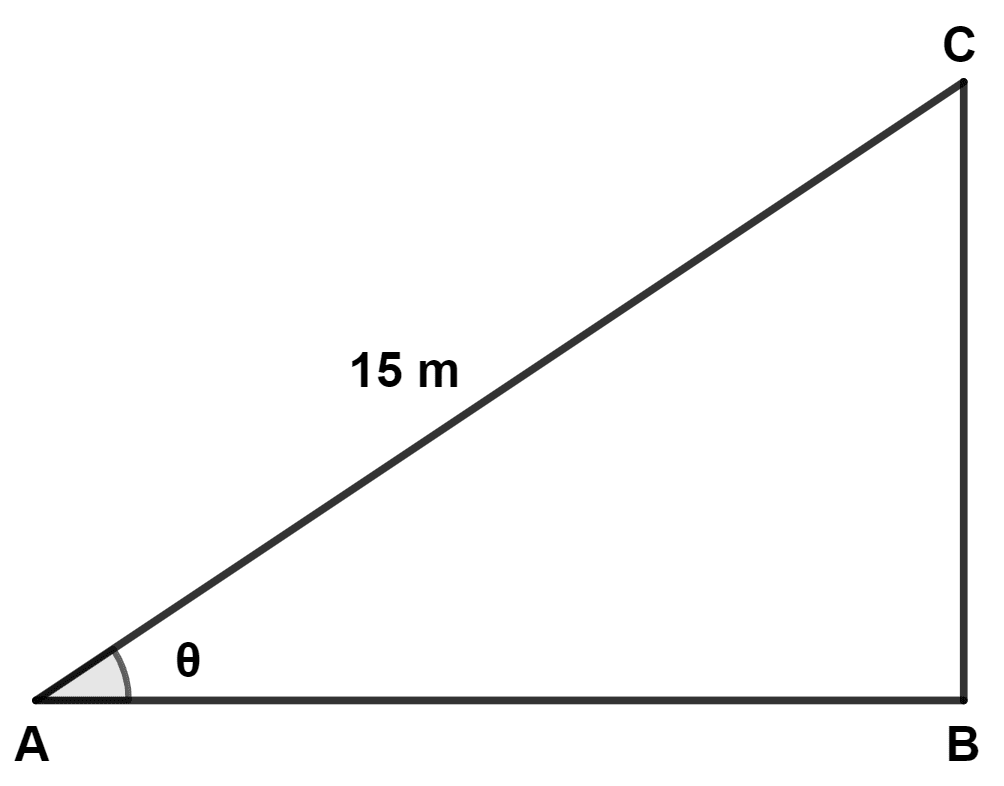
An inclined plane AC is prepared with its base AB which is √3 times its vertical height BC. The length of the inclined plane is 15 m. Find:
(a) value of θ.
(b) length of its base AB, in nearest metre.
Answer
(a) According to question,
⇒ AB =
⇒ AB =
⇒ BC =
From figure,
⇒ tan θ =
⇒ tan θ =
⇒ tan θ =
⇒ tan θ = tan 30°
⇒ θ = 30°.
Hence, θ = 30°.
(b) In right angle triangle ABC,
By pythagoras theorem,
⇒ AC2 = BC2 + AB2
⇒ 152 = + AB2
⇒ 225 = + AB2
⇒ 225 =
⇒ 225 =
⇒ AB2 =
⇒ AB2 =
⇒ AB2 = 168.75
⇒ AB =
⇒ AB = 12.99 m
Rounding off,
AB = 13 m.
Hence, AB = 13 m.
Prove that :
tan2 θ + cos2 θ - 1 = tan2 θ. sin2 θ
Answer
Solving L.H.S. of the above equation, we get :
⇒ tan2 θ + cos2 θ - 1
⇒ - (1 - cos2 θ)
⇒ - sin2 θ
⇒ sin2 θ
⇒
⇒ . sin2 θ
⇒ tan2 θ. sin2 θ.
Since. L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Hence, proved that tan2 θ + cos2 θ - 1 = tan2 θ. sin2 θ
The class mark and frequency of a data is given in the graph. From the graph, Find:
(a) the table showing the class interval and frequency.
(b) the mean
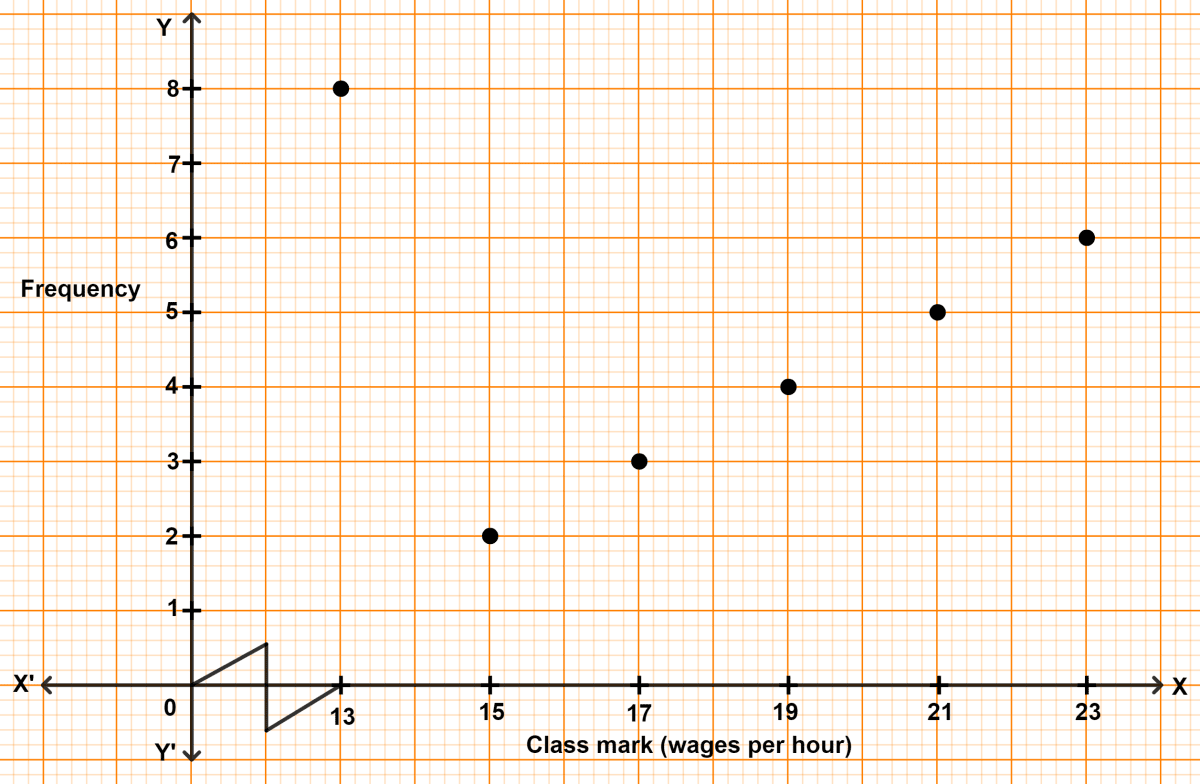
Answer
(a) Class marks : 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23.
Difference between two consecutive class marks = 15 - 13 = 2.
Lower limit of class = Class mark - 1
Upper limit of class = Class mark + 1
| Class | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 12 - 14 | 8 |
| 14 - 16 | 2 |
| 16 - 18 | 3 |
| 18 - 20 | 4 |
| 20 - 22 | 5 |
| 22 - 24 | 6 |
(b)
| Class | Class mark (x) | Frequency (f) | fx |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 - 14 | 13 | 8 | 104 |
| 14 - 16 | 15 | 2 | 30 |
| 16 - 18 | 17 | 3 | 51 |
| 18 - 20 | 19 | 4 | 76 |
| 20 - 22 | 21 | 5 | 105 |
| 22 - 24 | 23 | 6 | 138 |
| Total | Σf = 28 | Σfx = 504 |
Mean = = 18.
Hence, mean = 18.
The mean of 5, 7, 8, 4 and m is n and the mean of 5, 7, 8, 4, m and n is m. Find the values of m and n.
Answer
Given,
The mean of 5, 7, 8, 4 and m is n.
The mean of 5, 7, 8, 4, m and n is m.
Substituting value of m from equation (1) in above equation, we get :
⇒ 5n - 24 + n + 24 = 6m
⇒ 6n = 6m
⇒ n = m .........(2)
Substituting value of n from equation (2) in (1), we get :
⇒ m = 5m - 24
⇒ 5m - m = 24
⇒ 4m = 24
⇒ m = = 6
⇒ n = 6.
Hence, m = 6 and n = 6.
The probability of selecting a blue marble and a red marble from a bag containing red, blue and green marbles is and respectively. If the bag contains 14 green marbles, then find :
(a) number of red marbles.
(b) total number of marbles in the bag.
Answer
As the bag contains red, blue and green marbles.
∴ Probability of selecting a red marble + Probability of selecting a blue marble + Probability of selecting a green marble = 1
⇒ + Probability of selecting a green marble = 1
⇒ + Probability of selecting a green marble = 1
⇒ Probability of selecting a green marble =
⇒ Probability of selecting a green marble =
⇒ Probability of selecting a green marble = .
(a) Given,
⇒ Probability of selecting a red marble = .
Hence, no. of red marbles = 6.
(b) Hence, total no. of marbles in the bag = 30.